bar chart histogram distinction
Associated Articles: bar chart histogram distinction
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate via the intriguing matter associated to bar chart histogram distinction. Let’s weave attention-grabbing info and supply recent views to the readers.
Desk of Content material
Bar Charts vs. Histograms: A Deep Dive into Knowledge Visualization
![What is the difference between a bar graph and a histogram? [SOLVED]](https://d138zd1ktt9iqe.cloudfront.net/media/seo_landing_files/screenshot-2021-03-01-at-9-17-06-am-1614570481.png)
Bar charts and histograms are each highly effective instruments for visualizing knowledge, notably categorical and numerical knowledge, respectively. Whereas they share a superficial resemblance – each use rectangular bars to characterize knowledge – their underlying functions and interpretations differ considerably. An intensive understanding of those variations is essential for efficient knowledge evaluation and communication. This text will delve into the nuances of bar charts and histograms, highlighting their distinct traits, acceptable makes use of, and potential pitfalls.
Bar Charts: Categorical Knowledge at a Look
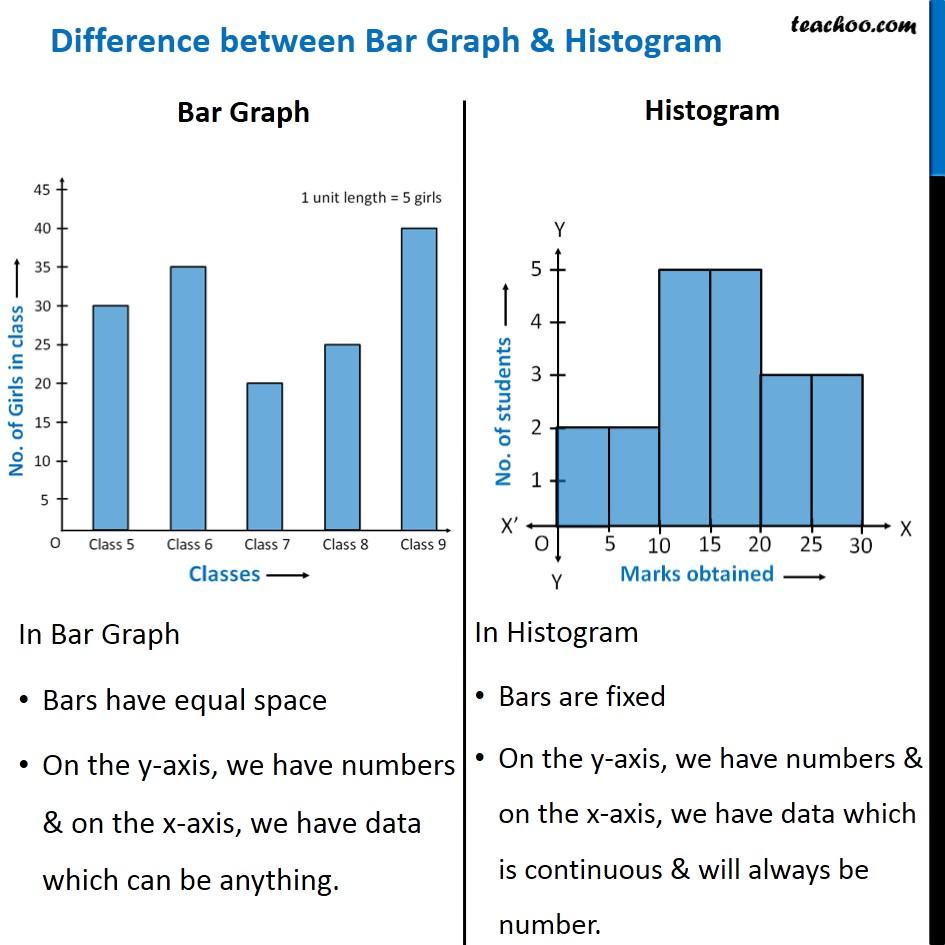
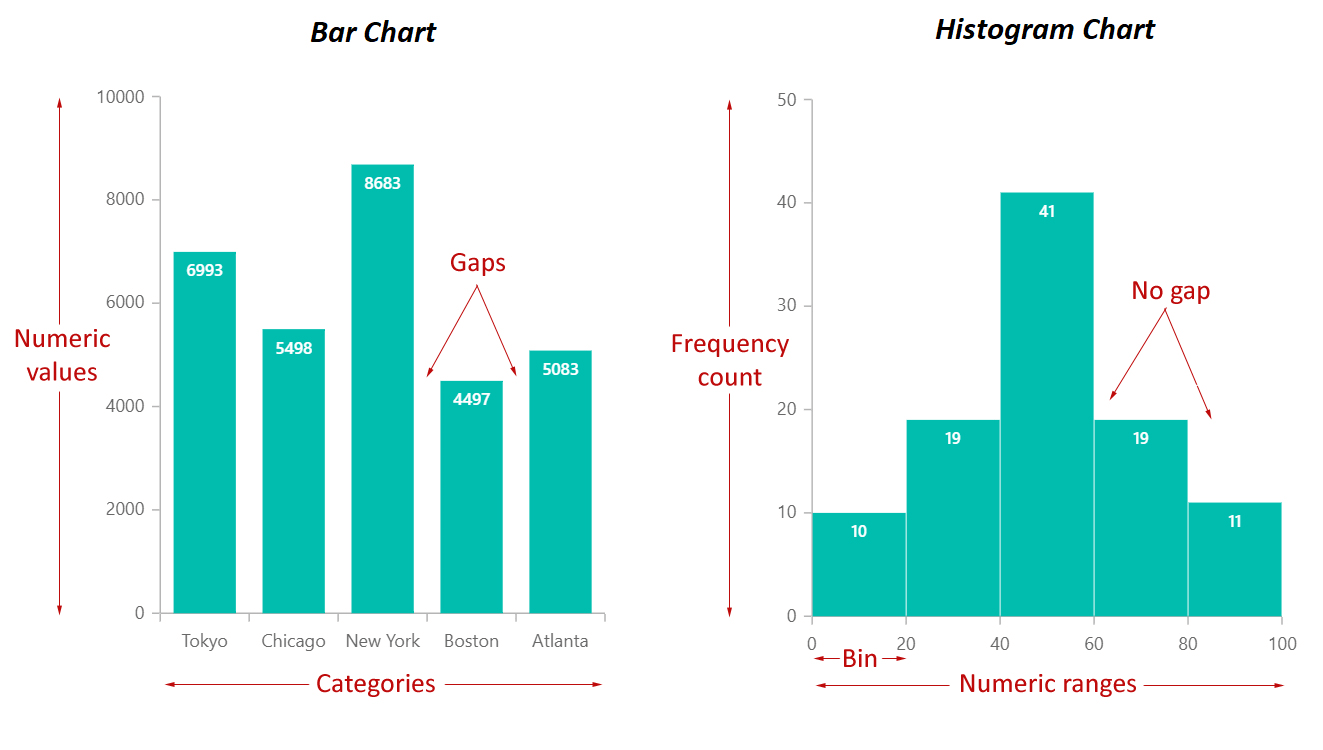
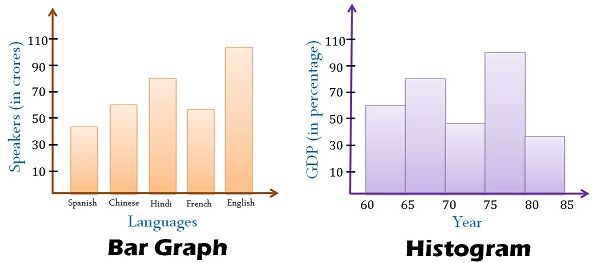
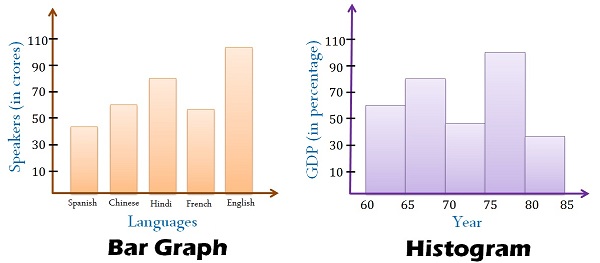
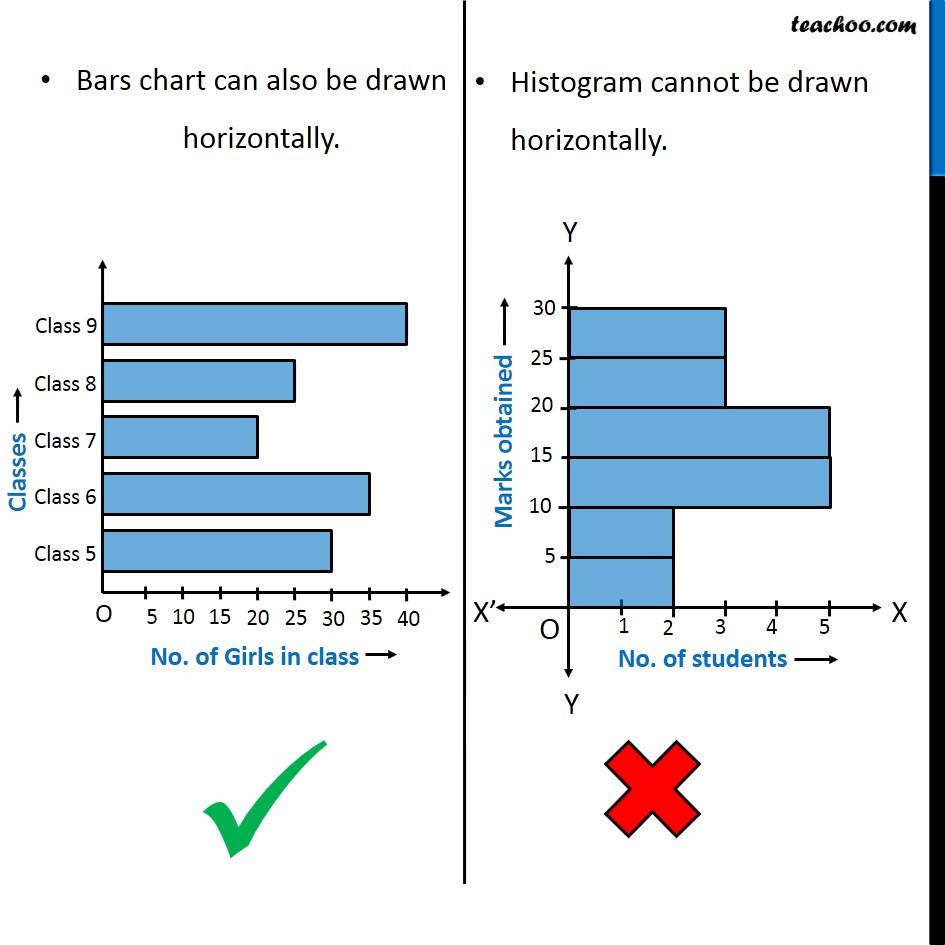
Bar charts are primarily designed to show and evaluate categorical knowledge. They characterize completely different classes on the horizontal (x) axis and the corresponding frequencies, counts, or values on the vertical (y) axis. Every bar represents a single class, and its top (or size, if the chart is oriented horizontally) is proportional to the worth related to that class. The bars are sometimes separated by gaps, emphasizing the discrete nature of the specific knowledge.
Key traits of bar charts:
- Categorical knowledge: The x-axis represents distinct, separate classes, akin to colours, manufacturers, areas, or months. These classes usually are not inherently ordered numerically.
- Discrete bars: The bars are separated, highlighting the independence of every class.
- Comparability: The first objective is to match the values throughout completely different classes.
- Frequency or values: The y-axis represents the frequency (rely) of every class or a selected worth related to every class (e.g., gross sales figures, common temperature).
- Variations: Bar charts will be additional categorized into clustered bar charts (evaluating a number of variables inside every class) and stacked bar charts (exhibiting the contribution of various sub-categories to a complete).
Instance: A bar chart may successfully show the gross sales figures of various automotive fashions in a selected month. Every automotive mannequin could be a class on the x-axis, and the peak of every bar would characterize its gross sales quantity.
Histograms: Unveiling the Distribution of Numerical Knowledge
Histograms, not like bar charts, are designed to characterize the distribution of numerical knowledge. They show the frequency distribution of a steady variable by dividing the info into intervals (bins) and exhibiting the variety of knowledge factors falling into every bin. The horizontal axis represents the vary of the continual variable, divided into these bins, whereas the vertical axis exhibits the frequency or relative frequency (proportion) of information factors inside every bin. Crucially, the bars in a histogram are adjoining, with no gaps between them, reflecting the continual nature of the underlying knowledge.
Key traits of histograms:
- Numerical knowledge: The x-axis represents a steady numerical variable, akin to top, weight, temperature, or earnings.
- Bins or intervals: The info is grouped into bins (intervals) of equal width. The variety of bins considerably impacts the histogram’s look and interpretation.
- Steady knowledge illustration: The bars are adjoining, emphasizing the continual nature of the variable. There are not any gaps between bars.
- Distribution visualization: The first objective is to visualise the distribution of the info – figuring out patterns like skewness, symmetry, and modality (variety of peaks).
- Density estimation: Histograms can present a visible estimate of the chance density operate of the underlying knowledge.
Instance: A histogram may successfully show the distribution of pupil scores on an examination. The x-axis could be divided into rating ranges (bins), and the peak of every bar would characterize the variety of college students who scored inside that vary.
Key Variations Summarized:
| Function | Bar Chart | Histogram |
|---|---|---|
| Knowledge Kind | Categorical | Numerical (steady) |
| X-axis | Classes | Vary of numerical values (bins) |
| Y-axis | Frequency or worth per class | Frequency or relative frequency per bin |
| Bar Separation | Bars are separated | Bars are adjoining |
| Function | Examine classes; present frequencies | Visualize knowledge distribution; establish patterns |
| Order of X-axis | Order is bigoted (until ordinal knowledge) | Order is fastened (numerical) |
Selecting the Proper Chart:
The selection between a bar chart and a histogram hinges on the kind of knowledge being visualized. If the info is categorical, a bar chart is the suitable selection. If the info is numerical and steady, a histogram is the higher possibility. Misusing one for the opposite can result in misinterpretations. As an illustration, presenting steady knowledge as a bar chart with separate bars would obscure the continual nature of the info and stop the visualization of its distribution. Conversely, utilizing a histogram for categorical knowledge could be inappropriate and deceptive.
Past the Fundamentals: Superior Concerns
1. Bin Width in Histograms: The selection of bin width in a histogram is essential. Too few bins can obscure necessary particulars, whereas too many bins could make the histogram seem too jagged and tough to interpret. Varied strategies exist for choosing optimum bin widths, together with Sturges’ rule, Scott’s rule, and Freedman-Diaconis rule. Experimentation and consideration of the info’s traits are important.
2. Kernel Density Estimation (KDE): KDE is a non-parametric option to estimate the chance density operate of a random variable. It offers a smoother illustration of the info distribution in comparison with a histogram, lowering the affect of bin choice. KDE plots are sometimes used as options to histograms, notably when coping with smaller datasets.
3. Overlapping Knowledge: Whereas histograms primarily take care of single variables, methods exist to visualise the distribution of a number of variables concurrently, akin to utilizing overlaid histograms or density plots.
4. Knowledge Transformations: Remodeling the info (e.g., utilizing logarithmic or sq. root transformations) can generally enhance the visible readability of a histogram by addressing skewness or different distributional points.
5. Context and Interpretation: Each bar charts and histograms ought to at all times be accompanied by clear labels, titles, and contextual info to facilitate correct interpretation. The selection of chart kind, bin width (for histograms), and different visualization decisions needs to be fastidiously thought of to successfully talk the info’s story.
Conclusion:
Bar charts and histograms are elementary instruments in knowledge visualization, every serving a definite objective. Understanding their variations and acceptable purposes is essential for efficient knowledge evaluation and communication. By fastidiously choosing the correct chart kind and listening to particulars akin to bin width (for histograms), knowledge transformations, and context, we will leverage these highly effective instruments to extract significant insights from our knowledge and talk them successfully to a wider viewers. Keep in mind, the aim isn’t just to create a chart however to create a chart that precisely and clearly conveys the data contained inside the knowledge.



Closure
Thus, we hope this text has supplied precious insights into bar chart histogram distinction. We thanks for taking the time to learn this text. See you in our subsequent article!