bar chart vs pareto chart
Associated Articles: bar chart vs pareto chart
Introduction
On this auspicious event, we’re delighted to delve into the intriguing subject associated to bar chart vs pareto chart. Let’s weave attention-grabbing data and supply contemporary views to the readers.
Desk of Content material
Bar Charts vs. Pareto Charts: Selecting the Proper Device for Knowledge Visualization
Knowledge visualization is essential for successfully speaking insights derived from information. Whereas quite a few chart sorts exist, bar charts and Pareto charts are incessantly used to symbolize categorical information. Nevertheless, they serve distinct functions and are finest fitted to totally different analytical targets. This text delves into the nuances of bar charts and Pareto charts, evaluating their strengths and weaknesses to information you in deciding on the suitable chart on your information evaluation wants.
Understanding Bar Charts:
A bar chart, also referred to as a bar graph, is without doubt one of the easiest and most generally understood strategies for visualizing categorical information. It shows information utilizing rectangular bars, with the size of every bar representing the worth of a particular class. Bars could be oriented both horizontally or vertically, relying on desire and the complexity of the info.
Key Options of Bar Charts:
- Simplicity: Bar charts are simple to grasp and interpret, even for people with restricted statistical information.
- Comparability: They excel at evaluating the values of various classes. The visible variations in bar lengths instantly spotlight which classes have greater or decrease values.
- Categorical Knowledge: They’re particularly designed for categorical information, the place the info factors are grouped into distinct classes.
- Flexibility: Bar charts can be utilized to symbolize each frequency counts and different numerical measures related to every class.
- Variations: A number of variations exist, together with clustered bar charts (evaluating a number of variables inside every class) and stacked bar charts (displaying the contribution of sub-categories to a essential class).
Strengths of Bar Charts:
- Clear and Concise: They supply a simple illustration of knowledge, making it simple to establish the most important and smallest values.
- Straightforward to Create: Quite a few software program packages and instruments readily generate bar charts.
- Versatile: They are often tailored to show a variety of knowledge, together with percentages, averages, and sums.
- Efficient for Comparisons: They facilitate fast comparisons between totally different classes.
Weaknesses of Bar Charts:
- Restricted Insights: Bar charts primarily present the magnitude of every class; they do not inherently reveal relationships or traits between classes.
- Overwhelming with Many Classes: When coping with numerous classes, bar charts can turn into cluttered and tough to interpret.
- No inherent rating: Whereas the visible illustration permits for straightforward comparability, the chart itself does not inherently rank the classes.
Understanding Pareto Charts:
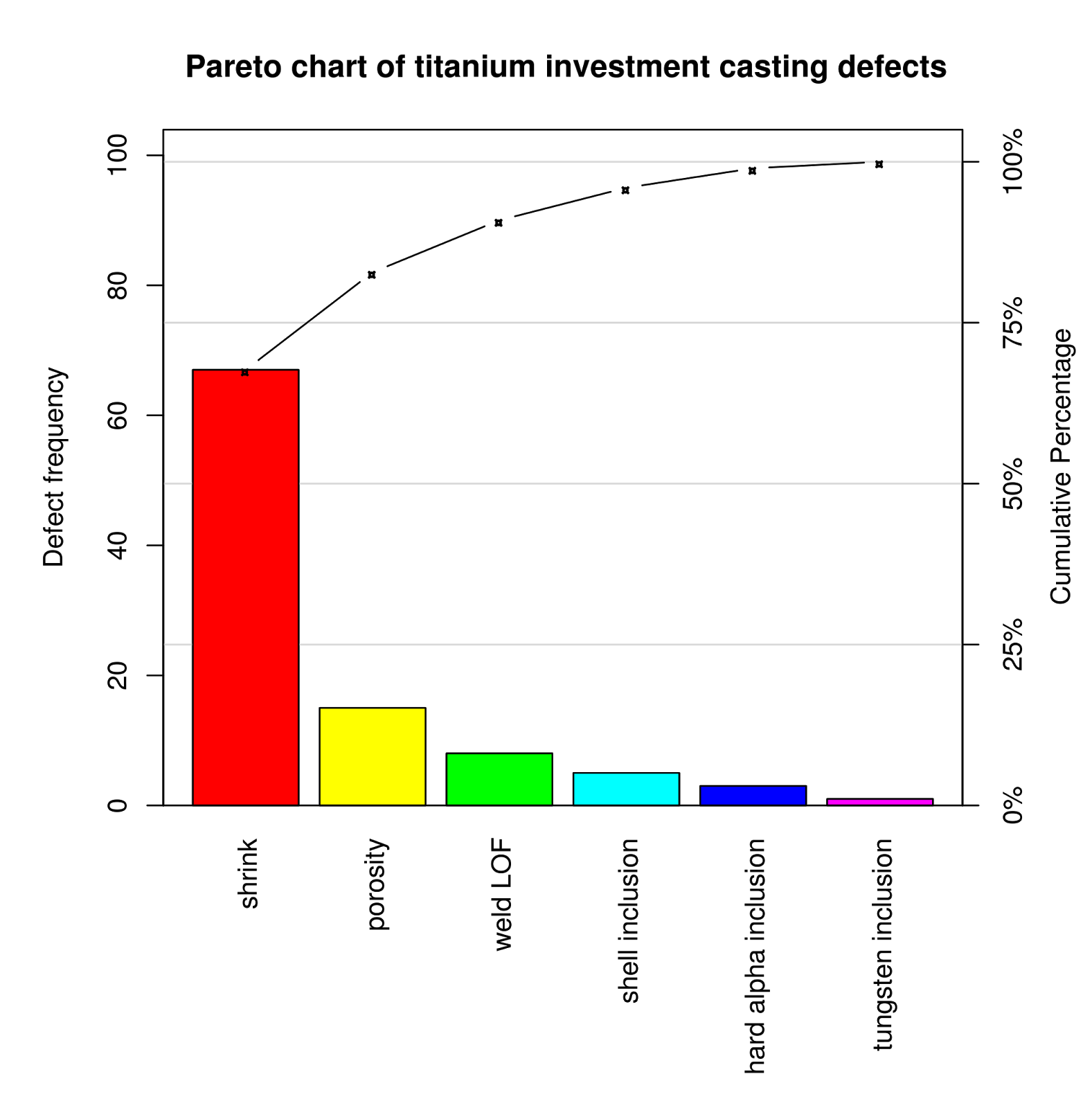
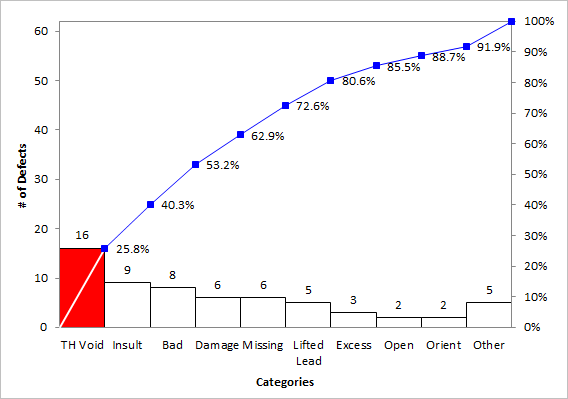
A Pareto chart is a particular kind of bar chart that mixes the options of a bar chart with a line graph. It is named after Vilfredo Pareto, who noticed the "Pareto precept" (also referred to as the 80/20 rule), which means that a good portion of results (typically round 80%) come from a comparatively small share of causes (typically round 20%).
Key Options of Pareto Charts:
- Bar Chart Element: Just like a bar chart, it makes use of bars to symbolize the frequency or magnitude of various classes. These classes are normally ranked in descending order, from essentially the most frequent to the least frequent.
- Line Graph Element: A cumulative frequency line graph is overlaid on the bar chart. This line exhibits the operating whole of the frequencies as you progress from left to proper throughout the classes.
- Concentrate on the "Very important Few": The Pareto chart highlights the "important few" classes that contribute essentially the most to the general impact, permitting for centered consideration on essentially the most impactful components.
- Prioritization: It helps prioritize efforts by figuring out the important thing areas the place enhancements will yield the best impression.
Strengths of Pareto Charts:
- Prioritization: It clearly identifies essentially the most important contributors to an issue or consequence.
- Concentrate on Key Points: It helps to pay attention assets and efforts on addressing essentially the most impactful components.
- Visible Illustration of the Pareto Precept: It visually demonstrates the disproportionate impression of a small variety of classes.
- Improved Resolution-Making: It helps data-driven decision-making by highlighting areas for enchancment.
Weaknesses of Pareto Charts:
- Much less Intuitive than Bar Charts: The mixed bar and line graph could be barely extra advanced to grasp than a easy bar chart.
- Restricted Applicability: It is simplest when coping with conditions the place the Pareto precept is prone to apply.
- Knowledge Dependency: The effectiveness of a Pareto chart depends closely on the accuracy and completeness of the underlying information. Inaccurate information will result in deceptive conclusions.
- Oversimplification: Focusing solely on the "important few" can generally overlook necessary components that, whereas individually much less important, would possibly collectively contribute considerably.
Selecting Between Bar Charts and Pareto Charts:
The selection between a bar chart and a Pareto chart relies upon closely in your analytical targets.
Use a bar chart when:
- You might want to merely evaluate the values of various classes.
- You need a clear and easy-to-understand visualization of categorical information.
- You needn’t spotlight the relative significance of classes.
- You have got numerous classes and wish a transparent visible illustration.
Use a Pareto chart when:
- You need to establish essentially the most important contributors to an issue or consequence.
- You need to prioritize efforts primarily based on the impression of various components.
- You watched that the Pareto precept applies to your information.
- You might want to visually display the disproportionate impression of a small variety of classes.
- You need to concentrate on bettering essentially the most impactful areas for optimum effectivity.
Examples:
-
Bar Chart Instance: Evaluating the gross sales figures of various product traces in an organization over a 12 months. This merely exhibits which product line carried out finest, however does not inherently recommend any prioritization for enchancment efforts.
-
Pareto Chart Instance: Analyzing the causes of defects in a producing course of. This might establish the few most frequent defect sorts, permitting the corporate to focus enchancment efforts on these areas for the best impression on total high quality.
Conclusion:
Each bar charts and Pareto charts are invaluable instruments for visualizing categorical information. Nevertheless, they serve distinct functions. Bar charts are finest suited for easy comparisons of classes, whereas Pareto charts are perfect for figuring out and prioritizing essentially the most important contributors to a selected consequence. Understanding the strengths and weaknesses of every chart kind permits for knowledgeable decision-making, making certain that the simplest visualization methodology is chosen on your information evaluation wants. The secret is to decide on the chart that finest aligns together with your analytical targets and successfully communicates your insights to your meant viewers. Contemplate the context of your information and the message you need to convey when making your choice. Utilizing the improper chart can result in misinterpretations and ineffective communication of invaluable information insights.


Closure
Thus, we hope this text has supplied invaluable insights into bar chart vs pareto chart. We respect your consideration to our article. See you in our subsequent article!