bar graph vs pareto chart
Associated Articles: bar graph vs pareto chart
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate via the intriguing matter associated to bar graph vs pareto chart. Let’s weave fascinating info and supply contemporary views to the readers.
Desk of Content material
Bar Graphs vs. Pareto Charts: Selecting the Proper Software for Your Information
Information visualization is essential for efficient communication and insightful evaluation. Whereas quite a few chart sorts exist, bar graphs and Pareto charts are ceaselessly used to signify categorical information. Nonetheless, their purposes and the data they convey differ considerably. Selecting the suitable chart relies upon closely on the character of the information and the insights you intention to extract. This text delves into the intricacies of bar graphs and Pareto charts, highlighting their strengths and weaknesses to information you in choosing the optimum visualization approach.
Understanding Bar Graphs: A Basis of Information Visualization
Bar graphs, often known as bar charts, are one of many easiest and most generally understood strategies for displaying categorical information. They signify information utilizing rectangular bars, with the size of every bar proportional to the worth it represents. The classes are usually displayed alongside the horizontal axis (x-axis), whereas the values are represented on the vertical axis (y-axis). Bar graphs may be both horizontal or vertical, with the selection typically influenced by aesthetic preferences or the size of class labels.
Strengths of Bar Graphs:
- Simplicity and Ease of Understanding: Bar graphs are inherently intuitive and simple to interpret, even for people with restricted statistical data. The visible comparability of bar lengths instantly communicates relative magnitudes.
- Clear Illustration of Categorical Information: They successfully showcase the distribution of information throughout completely different classes, permitting for a fast grasp of the relative frequencies or values related to every class.
- Versatile Software: Bar graphs are relevant to a broad vary of information sorts, together with frequencies, counts, percentages, averages, and sums.
- Simple to Create: Quite a few software program packages and instruments readily facilitate the creation of bar graphs, making them accessible to a large viewers.
- Efficient for Evaluating Classes: Direct visible comparability between completely different classes is easy, enabling fast identification of the best and lowest values.
Limitations of Bar Graphs:
- Restricted Perception into Cumulative Results: Bar graphs primarily deal with particular person class values and don’t inherently reveal cumulative results or the contribution of every class to the general complete.
- Ineffective for Giant Variety of Classes: When coping with quite a few classes, bar graphs can develop into cluttered and troublesome to interpret, hindering efficient communication.
- No Indication of Underlying Relationships: Bar graphs typically don’t reveal relationships between classes or underlying traits within the information.
Pareto Charts: Unveiling the Important Few
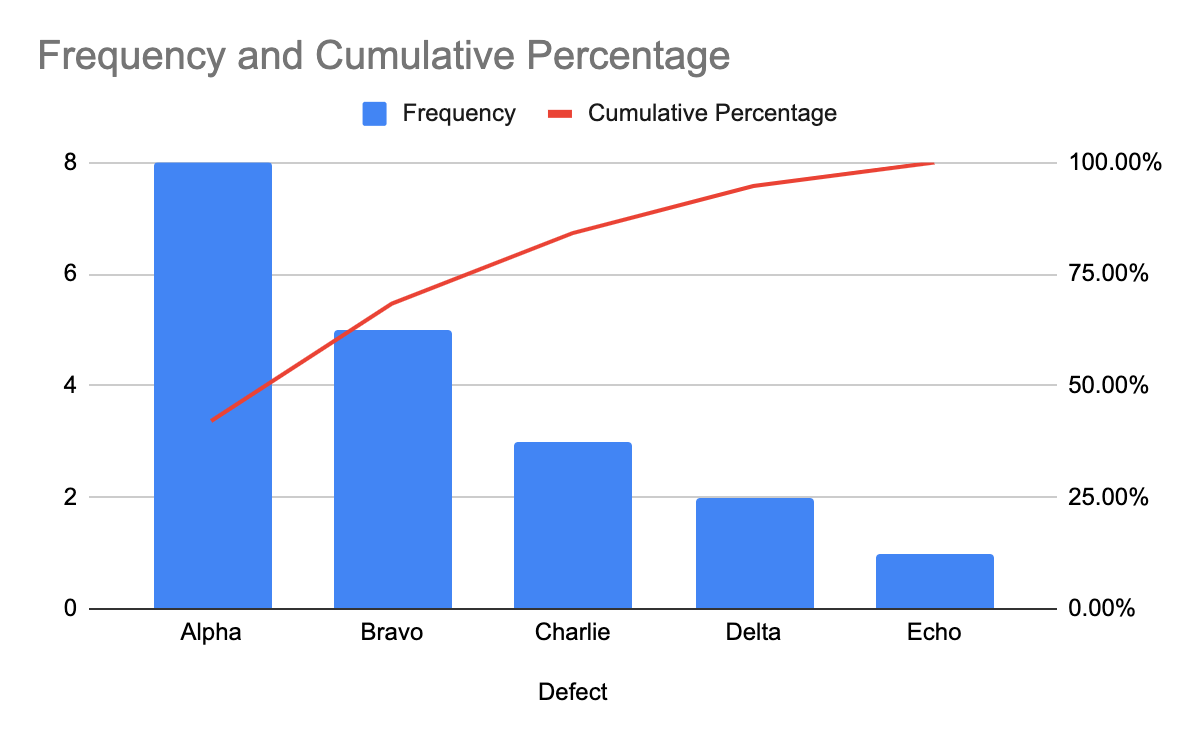
Pareto charts, named after Vilfredo Pareto, are a specialised sort of bar graph that mixes the visible illustration of categorical information with the cumulative frequency distribution. They’re notably helpful for figuring out the "very important few" elements that contribute considerably to an issue or phenomenon, typically following the Pareto precept (often known as the 80/20 rule). In a Pareto chart, the bars are organized in descending order of frequency, and a line graph is superimposed to point out the cumulative proportion of the overall.
Strengths of Pareto Charts:
- Highlighting Key Contributors: Pareto charts successfully pinpoint essentially the most vital contributors to a complete impact, permitting for targeted consideration on essentially the most impactful elements.
- Prioritization and Useful resource Allocation: By figuring out the very important few, Pareto charts assist in prioritizing efforts and allocating assets successfully to handle essentially the most important points.
- Improved Downside Fixing: They supply a structured strategy to downside fixing by focusing consideration on the foundation causes slightly than treating signs.
- Visible Illustration of Cumulative Results: The cumulative frequency line clearly demonstrates the proportion of the overall contributed by the main classes, offering a holistic view of the information.
- Efficient for High quality Enchancment Initiatives: Pareto charts are ceaselessly employed in Six Sigma and different high quality enchancment methodologies to determine and tackle main sources of defects or issues.
Limitations of Pareto Charts:
- Much less Intuitive than Easy Bar Graphs: The mixture of bars and a cumulative frequency line could be much less intuitive for these unfamiliar with Pareto charts.
- Requires Information Ordering: The effectiveness of a Pareto chart hinges on the information being ordered, which can require pre-processing or sorting.
- Might Oversimplify Complicated Relationships: Whereas highlighting key contributors, Pareto charts would possibly oversimplify complicated relationships between various factors.
- Not Appropriate for All Information Units: Pareto charts are only when coping with categorical information exhibiting a major skew, the place a couple of classes account for a considerable portion of the overall.
Selecting Between Bar Graphs and Pareto Charts: A Choice Framework
The selection between a bar graph and a Pareto chart will depend on the particular objectives of your evaluation and the character of your information. Take into account the next elements:
- Analysis Query: What insights are you attempting to realize out of your information? Are you curious about merely evaluating classes, or do you need to determine essentially the most vital contributors to a complete?
- Information Distribution: Does your information exhibit a skewed distribution, the place a couple of classes dominate? In that case, a Pareto chart could be extra acceptable.
- Viewers: Take into account the familiarity of your viewers with completely different chart sorts. An easier bar graph could be preferable for a much less statistically savvy viewers.
- Variety of Classes: For numerous classes, a Pareto chart would possibly develop into cluttered, whereas a bar graph may additionally develop into troublesome to interpret. Take into account various visualization methods in such instances, equivalent to treemaps or heatmaps.
- Want for Cumulative Data: If understanding the cumulative contribution of classes is essential, a Pareto chart is the superior selection.
Examples Illustrating the Variations:
State of affairs 1: Evaluating Gross sales of Totally different Product Traces
If you wish to merely evaluate the gross sales figures of various product strains in an organization, a bar graph would suffice. The size of every bar would signify the gross sales income for every product line, permitting for simple visible comparability.
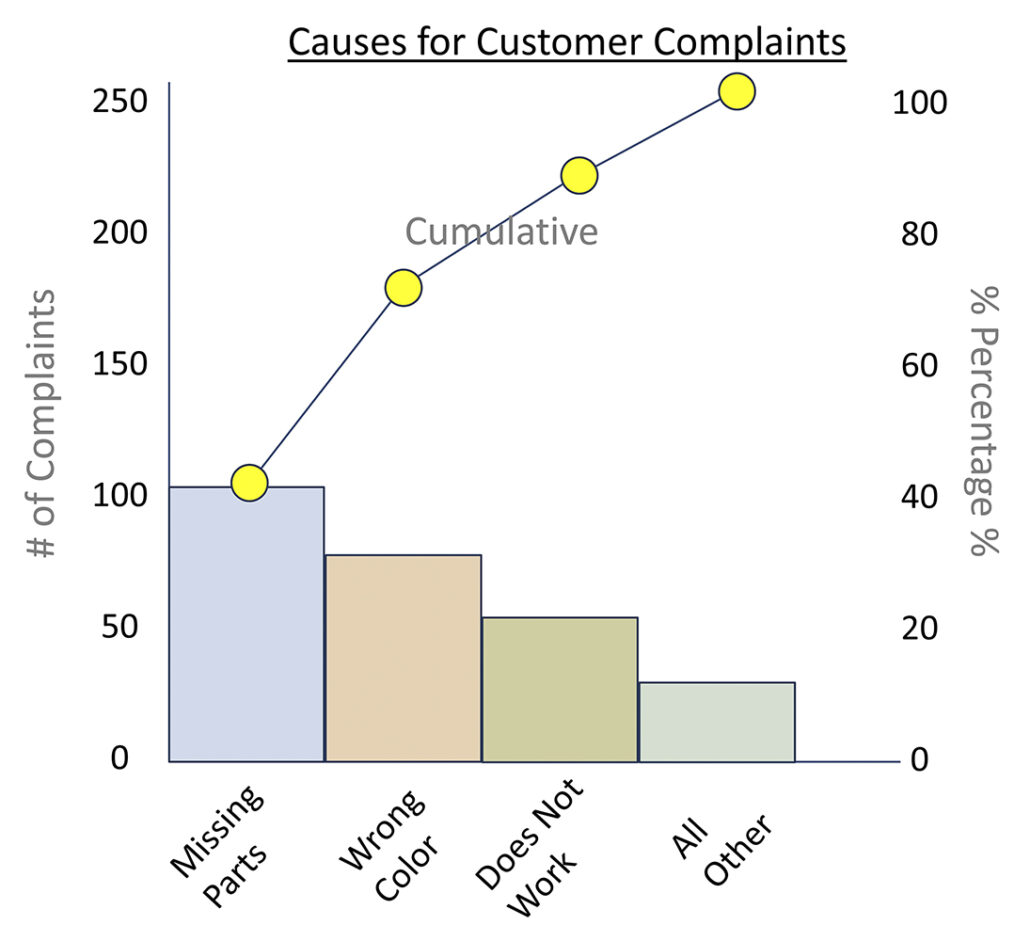
State of affairs 2: Figuring out the Main Causes of Buyer Complaints
Should you’re analyzing buyer complaints to determine the first causes, a Pareto chart can be simpler. The bars would signify the completely different grievance classes, organized in descending order of frequency. The cumulative frequency line would spotlight the few main causes accounting for almost all of complaints, enabling targeted enchancment efforts.
State of affairs 3: Analyzing Survey Responses on Most popular Options
When you have survey responses on most well-liked options of a product, a bar graph can be enough to point out the distribution of preferences throughout completely different options. Nonetheless, if you wish to determine the highest three most most well-liked options contributing to the vast majority of responses, a Pareto chart might be useful.
Conclusion:
Each bar graphs and Pareto charts are precious instruments for information visualization, however their purposes differ considerably. Bar graphs excel in offering a easy and clear illustration of categorical information, facilitating simple comparability of particular person classes. Pareto charts, however, are particularly designed to determine and spotlight essentially the most vital contributors to a complete, enabling efficient prioritization and useful resource allocation. By rigorously contemplating the character of your information and your analytical objectives, you’ll be able to select essentially the most acceptable visualization approach to successfully talk your findings and derive significant insights. Keep in mind that the last word aim is evident and efficient communication, and the selection of chart ought to at all times be guided by this precept.



Closure
Thus, we hope this text has offered precious insights into bar graph vs pareto chart. We thanks for taking the time to learn this text. See you in our subsequent article!