Chart Instance Knowledge: A Deep Dive into Efficient Visualization
Associated Articles: Chart Instance Knowledge: A Deep Dive into Efficient Visualization
Introduction
On this auspicious event, we’re delighted to delve into the intriguing subject associated to Chart Instance Knowledge: A Deep Dive into Efficient Visualization. Let’s weave attention-grabbing info and provide recent views to the readers.
Desk of Content material
Chart Instance Knowledge: A Deep Dive into Efficient Visualization
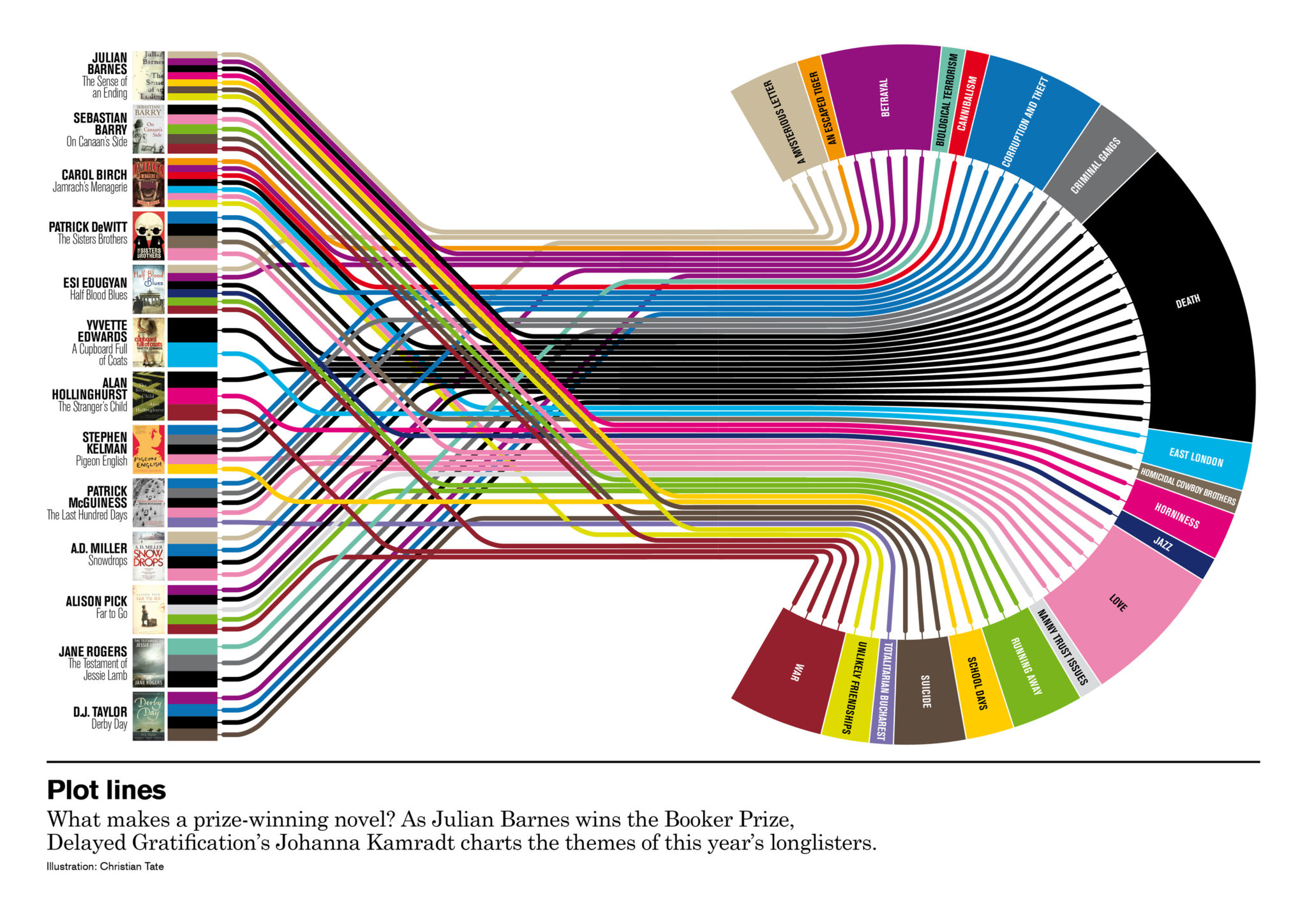
Knowledge visualization is paramount in right this moment’s data-driven world. Charts remodel uncooked numbers into simply digestible insights, permitting us to establish tendencies, patterns, and anomalies at a look. Nonetheless, the effectiveness of a chart hinges not simply on the chart kind chosen, however crucially on the standard and presentation of the underlying information. This text explores numerous examples of chart information, highlighting finest practices, potential pitfalls, and methods for creating compelling and informative visualizations.
I. Understanding the Basis: Knowledge Varieties and Buildings
Earlier than delving into particular chart examples, it is essential to grasp the basic information varieties and buildings utilized in charting. Knowledge can broadly be categorized as:
-
Categorical Knowledge: Represents teams or classes, similar to colours (pink, blue, inexperienced), areas (North, South, East, West), or product varieties (A, B, C). Categorical information is usually represented utilizing nominal (unordered) or ordinal (ordered) scales.
-
Numerical Knowledge: Represents portions or measurements, similar to temperature, gross sales figures, or age. Numerical information will be additional divided into:
- Discrete Knowledge: Takes on solely particular, separate values (e.g., variety of college students, variety of automobiles).
- Steady Knowledge: Can tackle any worth inside a given vary (e.g., top, weight, temperature).
The construction of the info is equally necessary. Knowledge is usually offered in tabular format, with rows representing particular person information factors and columns representing completely different variables. This tabular construction is quickly imported into most charting software program and libraries. For instance, take into account a dataset monitoring month-to-month web site visits:
| Month | Visits |
|---|---|
| January | 1500 |
| February | 1800 |
| March | 2200 |
| April | 2500 |
| Could | 2000 |
| June | 2800 |
| July | 3000 |
| August | 2700 |
| September | 2400 |
| October | 2600 |
| November | 3200 |
| December | 3500 |
This easy desk types the premise for numerous chart varieties, as we’ll discover beneath.
II. Chart Examples and Knowledge Concerns
Let’s study a number of widespread chart varieties and the info required for his or her efficient use:
A. Line Chart: Ideally suited for exhibiting tendencies over time or throughout steady variables. The instance above of month-to-month web site visits is completely fitted to a line chart. The x-axis represents time (Month), and the y-axis represents the numerical worth (Visits). Key issues:
- Knowledge Granularity: The frequency of information factors influences the smoothness of the road. Each day information would produce a extra detailed line than month-to-month information.
- Knowledge Scaling: Acceptable scaling of the y-axis is essential to keep away from deceptive impressions. A logarithmic scale is likely to be vital for information with a variety.
- A number of Strains: Line charts can successfully evaluate tendencies throughout a number of classes (e.g., web site visits from completely different sources).
B. Bar Chart: Glorious for evaluating discrete values throughout completely different classes. For instance, we might use a bar chart to match the gross sales of various product classes in a given quarter. The x-axis represents the product class (categorical), and the y-axis represents the gross sales figures (numerical). Concerns:
- Class Ordering: Think about the logical order of classes on the x-axis (e.g., alphabetically, by gross sales quantity).
- Bar Width: Keep constant bar width for correct comparability.
- Stacked Bar Charts: Helpful for exhibiting the composition of a complete worth throughout a number of sub-categories.
C. Pie Chart: Successfully reveals the proportion of various classes inside an entire. For instance, a pie chart might signify the market share of various cell phone manufacturers. Every slice represents a class, and its measurement corresponds to its proportion of the overall. Concerns:
- Restricted Classes: Pie charts turn out to be cluttered with too many classes. Restrict to 5-7 classes for optimum readability.
- Knowledge Labeling: Clearly label every slice with its class and proportion.
D. Scatter Plot: Shows the connection between two numerical variables. For instance, we might use a scatter plot to point out the connection between promoting expenditure and gross sales income. Every level represents an information level, with its x-coordinate representing promoting expenditure and its y-coordinate representing gross sales income. Concerns:
- Correlation: Observe the sample of factors to establish potential correlations (constructive, adverse, or no correlation).
- Outliers: Determine any information factors that considerably deviate from the general sample.
- Development Strains: Including a development line can spotlight the general relationship between the variables.
E. Histogram: Exhibits the distribution of a single numerical variable. For instance, we might use a histogram to point out the distribution of buyer ages. The x-axis represents the age ranges (bins), and the y-axis represents the frequency (variety of clients) in every vary. Concerns:
- Bin Width: The selection of bin width impacts the looks of the histogram. Experiment with completely different bin widths to seek out essentially the most informative illustration.
- Knowledge Skewness: Observe the form of the histogram to establish any skewness (symmetry or asymmetry) within the information distribution.
III. Superior Chart Examples and Knowledge Manipulation
Past these primary chart varieties, extra superior strategies contain information manipulation and the usage of extra refined visualizations:
-
Heatmaps: Characterize information as a color-coded matrix, helpful for visualizing correlation matrices or geographical information. Requires a matrix of numerical information.
-
Field Plots: Present the distribution of a numerical variable throughout completely different classes, highlighting median, quartiles, and outliers. Requires numerical information grouped by classes.
-
Geographic Maps: Visualize information geographically, utilizing completely different shade schemes or sizes of markers to signify information values. Requires geographical coordinates and information values related to places.
-
Community Graphs: Visualize relationships between entities, typically utilized in social community evaluation. Requires information representing connections between nodes.
IV. Knowledge Cleansing and Preprocessing
The standard of your chart relies upon closely on the standard of your information. Earlier than creating any chart, guarantee your information is clear and preprocessed:
-
Knowledge Cleansing: Deal with lacking values, outliers, and inconsistencies in your information. Strategies embrace imputation (filling lacking values), outlier removing, and information transformation.
-
Knowledge Transformation: Apply transformations (e.g., logarithmic, sq. root) to enhance information normality or handle skewed distributions.
-
Knowledge Aggregation: Group or summarize information to cut back its complexity and make it extra manageable for visualization.
V. Selecting the Proper Chart:
Choosing the suitable chart kind is essential for efficient communication. Think about the next components:
-
Knowledge Sort: The kind of information (categorical, numerical) dictates the appropriate chart varieties.
-
Message: What story are you making an attempt to inform along with your information? Select a chart that finest highlights the important thing insights.
-
Viewers: Think about the technical experience of your viewers when selecting the complexity of your chart.
Conclusion:
Efficient information visualization depends on each the selection of chart kind and the meticulous preparation of the underlying information. By understanding completely different information varieties, buildings, and chart capabilities, and by using acceptable information cleansing and preprocessing strategies, we are able to create compelling visualizations that successfully talk insights and facilitate data-driven decision-making. The examples offered on this article function a place to begin for exploring the huge prospects of information visualization, encouraging additional exploration and experimentation with completely different chart varieties and information manipulation strategies to attain optimum readability and impression. Keep in mind that the objective isn’t just to show information, however to disclose the story hidden inside.






Closure
Thus, we hope this text has offered precious insights into Chart Instance Knowledge: A Deep Dive into Efficient Visualization. We hope you discover this text informative and useful. See you in our subsequent article!