Chart of Accounts for a Merchandising Enterprise: A Complete Information
Associated Articles: Chart of Accounts for a Merchandising Enterprise: A Complete Information
Introduction
On this auspicious event, we’re delighted to delve into the intriguing subject associated to Chart of Accounts for a Merchandising Enterprise: A Complete Information. Let’s weave fascinating info and supply contemporary views to the readers.
Desk of Content material
Chart of Accounts for a Merchandising Enterprise: A Complete Information

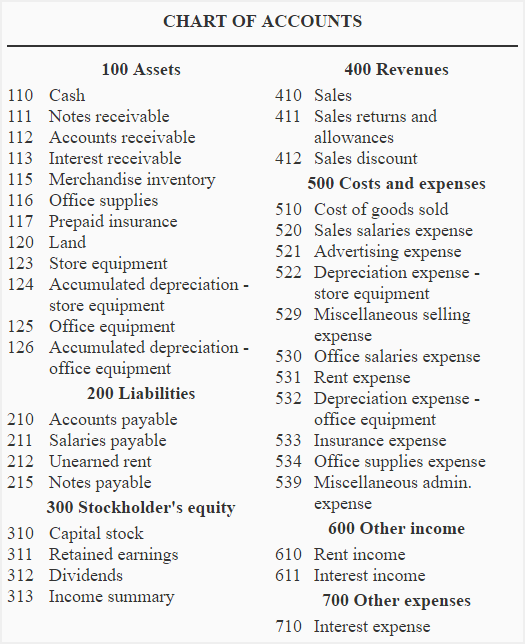
A well-structured chart of accounts (COA) is the spine of any profitable enterprise, significantly within the dynamic world of merchandising. It serves as an in depth classification system for all monetary transactions, offering a transparent and arranged view of an organization’s monetary well being. For merchandising companies, the COA must accommodate the distinctive complexities of stock administration, gross sales, purchases, and value of products bought (COGS). This text gives a complete information to creating a sturdy chart of accounts tailor-made to the particular wants of a merchandising enterprise.
Understanding the Fundamentals:
Earlier than diving into the specifics of a merchandising COA, it is essential to know some basic accounting ideas. A COA makes use of a system of accounts categorized by their perform. These are usually organized utilizing a numbering system for simple identification and retrieval. The principle classes embody:
- Property: Assets owned by the enterprise (e.g., money, accounts receivable, stock, gear).
- Liabilities: Obligations owed to others (e.g., accounts payable, loans payable).
- Fairness: The proprietor’s stake within the enterprise (e.g., retained earnings, capital contributions).
- Income: Earnings generated from the sale of products or companies.
- Bills: Prices incurred in operating the enterprise.
Particular Accounts for Merchandising Companies:
The COA for a merchandising enterprise expands upon these basic classes to incorporate accounts particularly related to the shopping for, promoting, and managing of stock. This is an in depth breakdown:
I. Property:
-
Present Property: Property anticipated to be transformed into money inside one yr.
- Money: Consists of checking accounts, financial savings accounts, petty money.
- Accounts Receivable: Cash owed to the enterprise by prospects.
-
Stock: Items held on the market within the odd course of enterprise. That is additional categorized:
- Uncooked Supplies: (If relevant) The essential supplies used to create completed items.
- Work in Course of: (If relevant) Items partially accomplished.
- Completed Items: Accomplished items prepared on the market.
- Pay as you go Bills: Bills paid upfront (e.g., insurance coverage, hire).
- Provides: Workplace provides, packaging supplies, and so on.
-
Non-Present Property: Property anticipated to last more than one yr.
- Property, Plant, and Tools (PP&E): Land, buildings, equipment, gear. This typically requires depreciation accounts.
- Intangible Property: Patents, emblems, copyrights.
- Lengthy-Time period Investments: Investments not anticipated to be liquidated inside one yr.
II. Liabilities:
-
Present Liabilities: Obligations due inside one yr.
- Accounts Payable: Cash owed to suppliers for purchases.
- Salaries Payable: Wages owed to workers.
- Utilities Payable: Excellent payments for electrical energy, water, gasoline.
- Brief-Time period Loans Payable: Loans due inside one yr.
-
Non-Present Liabilities: Obligations due in multiple yr.
- Lengthy-Time period Loans Payable: Loans due in multiple yr.
- Mortgage Payable: Mortgage secured by actual property.
III. Fairness:
- Proprietor’s Fairness (Sole Proprietorship): The proprietor’s capital contribution and retained earnings.
- Shareholder’s Fairness (Company): Widespread inventory, retained earnings.
- Retained Earnings: Accrued income reinvested within the enterprise.
IV. Income:
- Gross sales Income: Earnings from the sale of products. This is likely to be additional categorized by product line or gross sales channel (e.g., on-line gross sales, retail gross sales).
- Gross sales Returns and Allowances: Reductions in income as a result of returned items or worth changes.
- Gross sales Reductions: Reductions in income as a result of early cost reductions.
V. Bills:
- Value of Items Bought (COGS): The direct prices related to producing or buying the products bought. This consists of the price of stock bought through the interval. This account is essential for merchandising companies.
-
Promoting Bills: Prices associated to advertising and promoting items.
- Promoting Expense: Prices of promoting and promotion.
- Gross sales Salaries Expense: Salaries paid to gross sales employees.
- Gross sales Commissions Expense: Commissions paid to gross sales employees.
- Delivery Expense: Prices of delivering items to prospects.
-
Common and Administrative Bills: Prices associated to operating the enterprise.
- Lease Expense: Value of renting workplace area or warehouse.
- Utilities Expense: Value of electrical energy, water, gasoline.
- Salaries Expense: Salaries paid to administrative employees.
- Insurance coverage Expense: Value of insurance coverage protection.
- Depreciation Expense: Allocation of the price of PP&E over its helpful life.
- Workplace Provides Expense: Value of workplace provides.
- Authorized and Skilled Charges: Prices of authorized {and professional} companies.
- Curiosity Expense: Value of borrowing cash.
Chart of Accounts Construction and Numbering System:
A well-organized COA makes use of a constant numbering system to facilitate simple identification and reporting. A standard method is a hierarchical system utilizing a mix of numbers and letters. For instance:
- 1000 – Property
- 1100 – Present Property
- 1110 – Money
- 1120 – Accounts Receivable
- 1130 – Stock
- 1131 – Uncooked Supplies
- 1132 – Work in Course of
- 1133 – Completed Items
- 1200 – Non-Present Property
- 1100 – Present Property
- 2000 – Liabilities
- 2100 – Present Liabilities
- 2200 – Non-Present Liabilities
- 3000 – Fairness
- 4000 – Income
- 5000 – Bills
- 5100 – Value of Items Bought
- 5200 – Promoting Bills
- 5300 – Common and Administrative Bills
Selecting an Accounting Software program:
Implementing a sturdy COA requires the usage of accounting software program. Software program packages like QuickBooks, Xero, and Sage supply options to handle stock, observe COGS, and generate monetary studies. Choosing the proper software program relies on the scale and complexity of the enterprise.
Common Evaluation and Updates:
The COA isn’t a static doc. Because the enterprise grows and evolves, the COA must be reviewed and up to date to replicate modifications within the enterprise operations. New accounts could should be added, and present accounts could should be modified. Common critiques make sure the COA stays related and correct.
Conclusion:
A well-designed chart of accounts is crucial for a merchandising enterprise to successfully handle its funds and make knowledgeable enterprise choices. By fastidiously categorizing all transactions, the COA gives precious insights into profitability, stock ranges, and general monetary well being. Utilizing a structured numbering system and choosing applicable accounting software program will streamline the accounting course of and supply a transparent, correct, and complete image of the enterprise’s monetary efficiency. Common assessment and updates are essential to make sure the COA stays a precious device all through the enterprise’s lifecycle.

:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/chart-accounts-4117638b1b6246d7847ca4f2030d4ee8.jpg)





Closure
Thus, we hope this text has supplied precious insights into Chart of Accounts for a Merchandising Enterprise: A Complete Information. We hope you discover this text informative and helpful. See you in our subsequent article!