Chart Patterns: Decoding Market Sentiment and Defining Danger with Targets and Cease Losses
Associated Articles: Chart Patterns: Decoding Market Sentiment and Defining Danger with Targets and Cease Losses
Introduction
On this auspicious event, we’re delighted to delve into the intriguing subject associated to Chart Patterns: Decoding Market Sentiment and Defining Danger with Targets and Cease Losses. Let’s weave fascinating info and provide contemporary views to the readers.
Desk of Content material
Chart Patterns: Decoding Market Sentiment and Defining Danger with Targets and Cease Losses
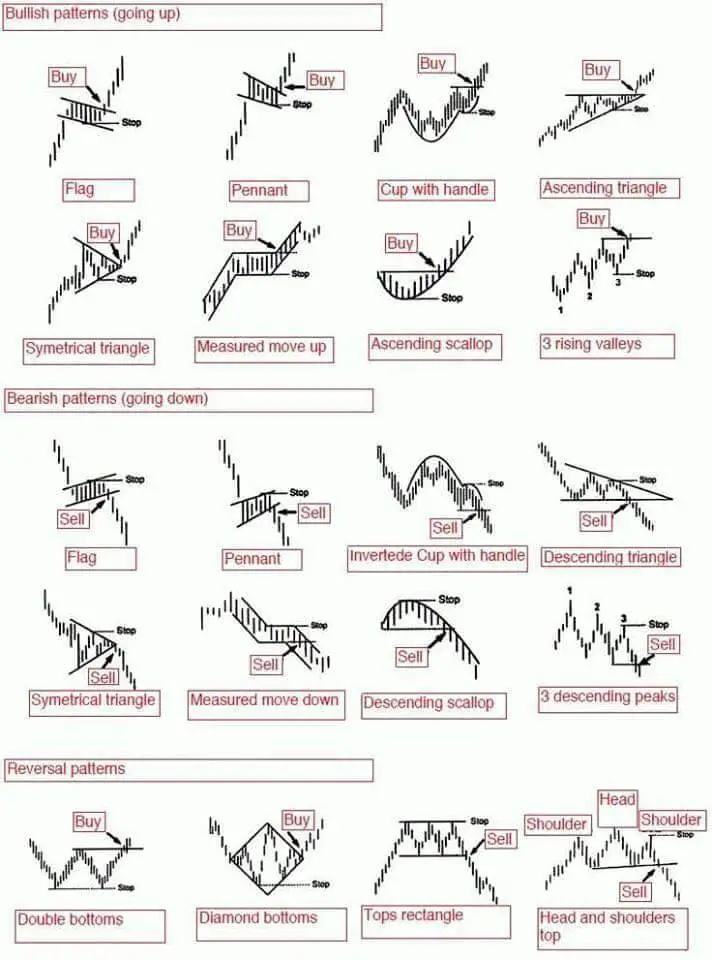
Chart patterns, recurring formations on value charts, present invaluable insights into market sentiment and potential future value actions. Whereas not foolproof predictors, they provide a probabilistic edge, enhancing buying and selling selections when mixed with different technical indicators and elementary evaluation. Understanding these patterns, coupled with the strategic placement of goal and stop-loss orders, is essential for efficient danger administration and maximizing profitability.
This text delves into the world of chart patterns, exploring their significance, frequent varieties, and the essential function of goal and stop-loss ranges in maximizing potential good points whereas minimizing losses.
Understanding Chart Patterns: A Visible Language of the Market
Chart patterns emerge from the interaction of provide and demand. They mirror the collective actions of consumers and sellers, revealing shifts in market sentiment and momentum. These formations, usually characterised by particular shapes and value actions, can sign potential breakouts, reversals, or continuations of present tendencies. Recognizing these patterns permits merchants to anticipate future value motion and place themselves accordingly.
Categorizing Chart Patterns:
Chart patterns are broadly categorized into two predominant teams: continuation and reversal patterns.
1. Continuation Patterns: These patterns counsel that the prevailing pattern will possible proceed after a brief pause or consolidation. Examples embrace:
-
Triangles: These patterns are characterised by converging trendlines, indicating a interval of indecision between consumers and sellers. There are symmetrical, ascending, and descending triangles, every with barely completely different implications. Symmetrical triangles often counsel a continuation of the previous pattern, whereas ascending triangles counsel bullish continuation and descending triangles bearish continuation.
-
Flags and Pennants: These patterns resemble flags or pennants connected to a flagpole (the previous pattern). They characterize short-term consolidations inside a bigger pattern. Flags are usually characterised by parallel trendlines, whereas pennants show converging trendlines. Each often sign a continuation of the previous pattern after the consolidation interval.
-
Rectangles: Rectangles are characterised by horizontal help and resistance ranges. They point out a interval of sideways buying and selling, suggesting a brief pause earlier than the pattern resumes in its unique path.
2. Reversal Patterns: These patterns sign a possible change within the prevailing pattern. Examples embrace:
-
Head and Shoulders: This can be a traditional reversal sample characterised by three peaks, with the center peak (the "head") being considerably larger than the opposite two ("shoulders"). A neckline connects the troughs between the peaks. A break beneath the neckline usually indicators a bearish reversal. The inverse sample, the inverse head and shoulders, indicators a bullish reversal.
-
Double Tops and Double Bottoms: These patterns include two comparable peaks (double prime) or troughs (double backside) adopted by a break beneath (double prime) or above (double backside) the neckline. They counsel a possible reversal of the prevailing pattern.
-
Triple Tops and Triple Bottoms: Just like double tops and bottoms, however with three peaks or troughs, providing stronger affirmation of a possible reversal.
-
Rounding Tops and Bottoms: These patterns are characterised by a gradual curve, indicating a sluggish and regular change in market sentiment. Rounding tops counsel a bearish reversal, whereas rounding bottoms counsel a bullish reversal.
Defining Targets and Cease Losses: Danger Administration Necessities
Whereas chart patterns provide insights into potential value actions, they don’t seem to be exact predictions. Due to this fact, implementing efficient danger administration methods, together with setting goal and stop-loss ranges, is essential.
Cease Losses: These orders routinely promote your place when the value reaches a predetermined stage, limiting potential losses. The position of stop-loss orders is essential. They need to be positioned beneath help ranges for lengthy positions and above resistance ranges for brief positions, ideally exterior the sample’s consolidation space to keep away from untimely triggering. The space of the stop-loss order from the entry value displays your danger tolerance.
Goal Ranges: These characterize the anticipated revenue stage for a commerce. Goal ranges will be decided utilizing varied strategies:
-
Sample-based targets: For a lot of patterns, the goal will be projected primarily based on the sample’s dimensions. For instance, in triangles, the goal will be the peak of the triangle projected from the breakout level. In head and shoulders, the goal will be the space between the top and the neckline projected downwards from the neckline breakout.
-
Fibonacci retracements and extensions: These instruments, primarily based on the Fibonacci sequence, establish potential help and resistance ranges, which can be utilized as goal ranges.
-
Assist and resistance ranges: Vital help and resistance ranges, recognized by technical evaluation, can function potential goal ranges.
-
A number of targets: As a substitute of a single goal, some merchants use a number of targets, taking partial income at every stage, lowering danger and securing some good points even when the value does not attain the final word goal.
Instance: Head and Shoulders Sample
Let’s illustrate with a head and shoulders sample. Assume a bearish head and shoulders sample varieties, with the neckline at $100. A break beneath the neckline confirms the sample. A stop-loss may very well be positioned barely above the neckline, maybe at $102, to restrict losses if the sample fails. The goal may very well be calculated by measuring the space between the top ($110) and the neckline ($100), which is $10. Projecting this distance downwards from the neckline breakout provides a goal of $90 ($100 – $10).
Elements Influencing Goal and Cease Loss Placement:
A number of elements affect the optimum placement of targets and cease losses:
-
Volatility: Greater volatility requires wider cease losses to keep away from untimely triggering.
-
Pattern Power: A robust pattern may justify extra aggressive goal ranges, whereas a weak pattern necessitates extra cautious targets and tighter cease losses.
-
Danger Tolerance: Particular person danger tolerance considerably impacts stop-loss placement. Conservative merchants favor tighter cease losses, whereas extra aggressive merchants may settle for wider cease losses for bigger potential good points.
-
Time Horizon: Longer-term trades often permit for wider cease losses and targets.
-
Market Context: Total market circumstances, financial information, and geopolitical occasions can affect the accuracy of chart patterns and the effectiveness of goal and stop-loss ranges.
Conclusion:
Chart patterns provide a beneficial instrument for merchants to research market sentiment and predict potential value actions. Nevertheless, they don’t seem to be infallible. The mixture of chart sample recognition with strategic goal and stop-loss placement is essential for efficient danger administration and maximizing profitability. Do not forget that thorough evaluation, contemplating different technical indicators and elementary elements, is important earlier than getting into any commerce. Constantly refining your understanding of chart patterns and danger administration strategies will improve your buying and selling expertise and enhance your probabilities of success. At all times keep in mind that buying and selling includes inherent danger, and losses are a chance. Self-discipline, persistence, and steady studying are key to long-term success within the markets.



:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/dotdash_Final_Market_Sentiment_Nov_2020-01-0b3907c75fdd4e9e9d05c82851465244.jpg)


Closure
Thus, we hope this text has supplied beneficial insights into Chart Patterns: Decoding Market Sentiment and Defining Danger with Targets and Cease Losses. We hope you discover this text informative and helpful. See you in our subsequent article!