chart vs diagram
Associated Articles: chart vs diagram
Introduction
On this auspicious event, we’re delighted to delve into the intriguing matter associated to chart vs diagram. Let’s weave attention-grabbing data and supply recent views to the readers.
Desk of Content material
Charts vs. Diagrams: Unveiling the Nuances of Visible Communication
Visible communication is paramount in in the present day’s information-saturated world. We depend on charts and diagrams to condense complicated information, illustrate intricate processes, and convey multifaceted concepts in a readily digestible format. Whereas each serve the aim of visible illustration, charts and diagrams possess distinct traits and are finest suited to completely different functions. Understanding these variations is essential for efficient communication and information visualization.
This text delves into the intricacies of charts and diagrams, exploring their definitions, key distinctions, numerous varieties, acceptable utilization situations, and the essential function they play in efficient communication. We’ll look at the strengths and weaknesses of every, guiding you in selecting essentially the most acceptable visible support in your particular wants.
Defining Charts and Diagrams:
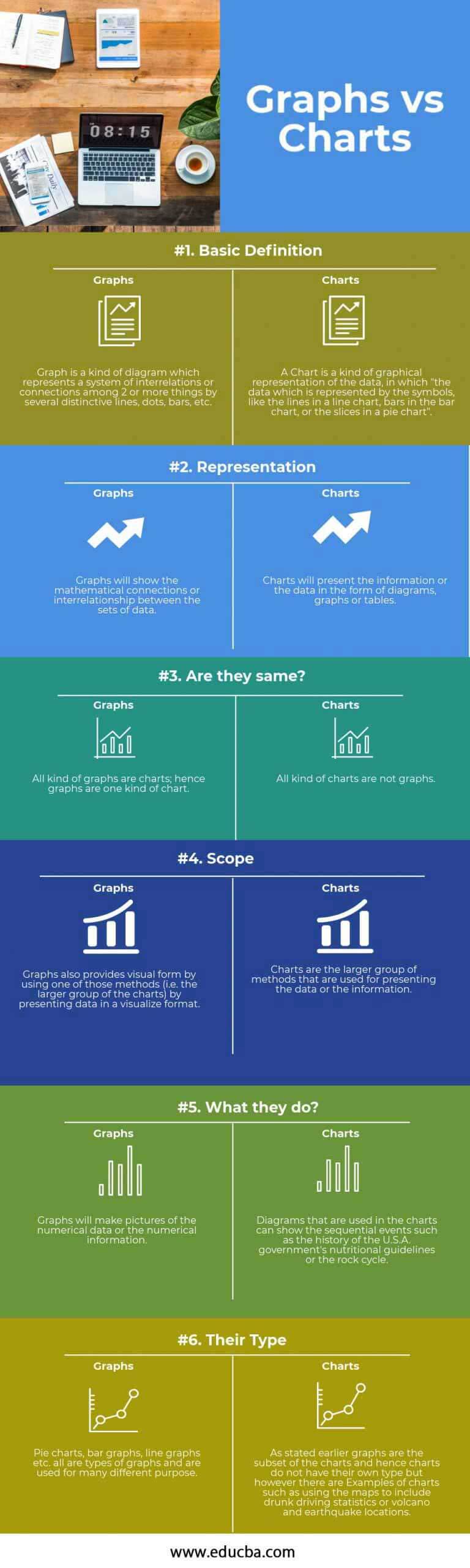
A chart is a graphical illustration of knowledge, usually numerical, designed for instance relationships, developments, and patterns inside that information. Charts primarily concentrate on quantitative data, utilizing visible components like bars, strains, or slices to signify numerical values and their adjustments over time or throughout classes. The first purpose of a chart is to disclose insights hidden inside the numbers, making complicated datasets extra comprehensible and actionable.
A diagram, however, is a simplified visible illustration of an idea, system, or course of. Whereas diagrams can incorporate numerical information, their major focus is on illustrating the construction, relationships, or circulate of data, relatively than solely on quantitative evaluation. Diagrams emphasize qualitative features, displaying how issues are linked, organized, or perform. They usually make the most of symbols, labels, and arrows to depict relationships and processes.
Key Distinctions: A Comparative Evaluation
The basic distinction between charts and diagrams lies of their major objective and the kind of data they signify:
| Function | Chart | Diagram |
|---|---|---|
| Main Objective | Present quantitative information and developments | Illustrate ideas, processes, constructions |
| Knowledge Kind | Primarily numerical information | Numerical information (generally), however primarily qualitative |
| Focus | Relationships between numerical values | Relationships between components, steps, or elements |
| Emphasis | Quantitative evaluation and comparisons | Qualitative understanding and illustration |
| Visible Parts | Bars, strains, pie slices, areas | Shapes, arrows, strains, symbols, labels |
| Interpretation | Based mostly on numerical values and their adjustments | Based mostly on visible relationships and circulate |
Forms of Charts:
The world of charts is huge and different, every sort designed to spotlight particular features of knowledge:
-
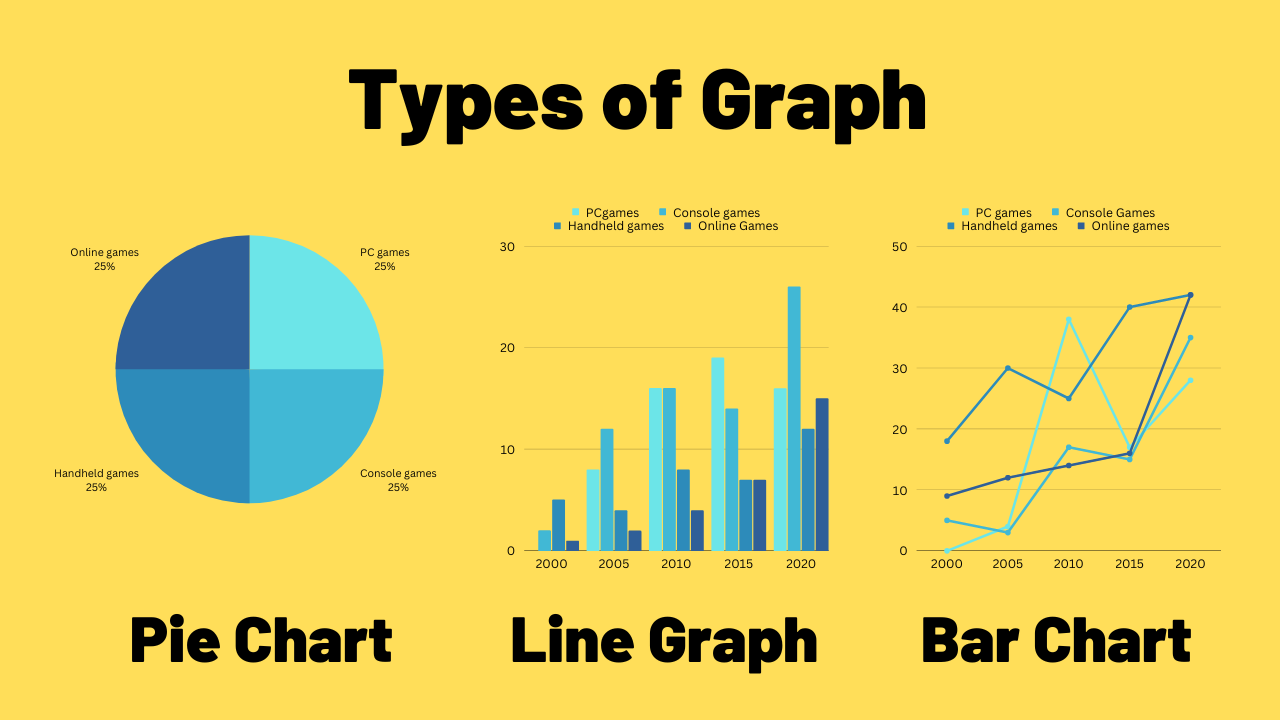
Bar Charts: Preferrred for evaluating discrete classes or teams. They use rectangular bars of various lengths to signify the magnitude of every class. Variations embrace clustered bar charts (evaluating a number of variables inside classes) and stacked bar charts (displaying components of a complete inside classes).
-
Line Charts: Wonderful for displaying developments and adjustments over time. They join information factors with strains, revealing patterns of development, decline, or stability. A number of strains can be utilized to check completely different variables over time.
-
Pie Charts: Successfully present the proportion of components to an entire. They divide a circle into segments, every representing a proportion of the overall. Greatest used when the variety of classes is comparatively small.
-
Space Charts: Much like line charts, however the space underneath the road is crammed, emphasizing the magnitude of the values over time. They’re efficient for visualizing cumulative information or displaying the relative contribution of various elements.
-
Scatter Plots: Used to indicate the connection between two variables. Every information level is represented as a dot on a graph, revealing correlations, clusters, and outliers.
-
Histograms: Show the frequency distribution of a steady variable. They use bars to signify the variety of information factors falling inside particular ranges or intervals.
Forms of Diagrams:
The realm of diagrams is equally numerous, catering to a variety of visualization wants:
-
Flowcharts: Illustrate the sequence of steps in a course of or workflow. They use standardized symbols (rectangles, diamonds, arrows) to signify actions, selections, and information circulate.
-
UML Diagrams (Unified Modeling Language): Utilized in software program engineering to visualise the construction and habits of software program techniques. Varied varieties exist, together with class diagrams, sequence diagrams, and use case diagrams.
-
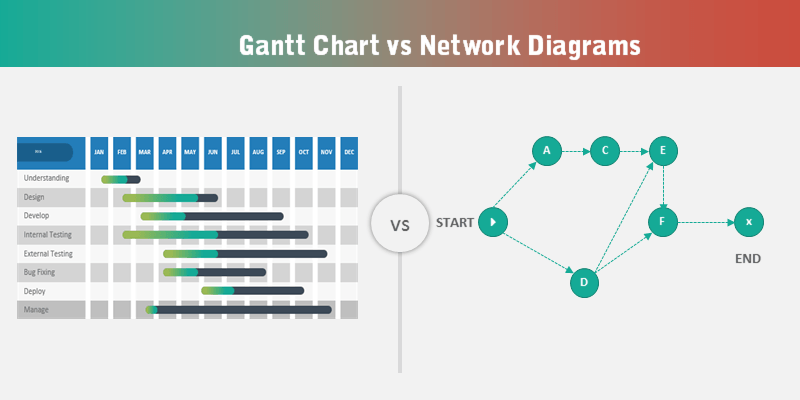
Community Diagrams: Present the connections and relationships between completely different components in a community, corresponding to pc networks or organizational constructions.
-
Thoughts Maps: Used for brainstorming and organizing concepts. They radiate from a central matter, with branches representing subtopics and associated ideas.
-
Venn Diagrams: Illustrate the relationships between units of knowledge, displaying overlaps and variations.
-
Organizational Charts: Depict the hierarchical construction of a corporation, displaying reporting relationships and positions.
-
Knowledge Move Diagrams (DFD): Illustrate the circulate of knowledge inside a system, displaying how information is reworked and moved between completely different processes.
Selecting the Proper Visible Help:
The number of a chart or diagram relies upon closely on the character of the knowledge being introduced and the specified consequence. Take into account the next elements:
-
Kind of Knowledge: Numerical information typically requires charts, whereas qualitative data advantages from diagrams.
-
Goal: Are you aiming to indicate developments, comparisons, proportions, or relationships? Totally different chart and diagram varieties excel in numerous areas.
-
Viewers: Take into account your viewers’s familiarity with completely different visible representations. Select a format that’s simply understood and interpreted.
-
Complexity: For complicated datasets, contemplate breaking them down into a number of less complicated charts or diagrams.
-
Readability and Simplicity: Prioritize readability and keep away from overwhelming your viewers with an excessive amount of data or overly complicated visuals.
Strengths and Weaknesses:
Charts:
Strengths: Successfully talk numerical information, reveal patterns and developments, facilitate comparisons, and help quantitative evaluation.
Weaknesses: Might be troublesome to interpret with giant datasets, will not be appropriate for qualitative data, and might be deceptive if not designed fastidiously.
Diagrams:
Strengths: Present a transparent visible illustration of complicated ideas, processes, and techniques, facilitate understanding of relationships and constructions, and are sometimes simpler to grasp than complicated numerical information.
Weaknesses: Is probably not appropriate for detailed quantitative evaluation, might be much less exact than charts, and require cautious design to keep away from ambiguity.
Conclusion:
Charts and diagrams are highly effective instruments for visible communication, every serving a novel objective. Understanding their distinctions, recognizing their strengths and weaknesses, and punctiliously contemplating the context of their software are essential for creating efficient and impactful visualizations. By deciding on the suitable visible support, you possibly can rework complicated data into readily comprehensible insights, fostering clearer communication and knowledgeable decision-making. The hot button is to match the visible illustration to the knowledge and the meant message, guaranteeing that the chosen chart or diagram enhances understanding relatively than obscuring it.





Closure
Thus, we hope this text has offered helpful insights into chart vs diagram. We thanks for taking the time to learn this text. See you in our subsequent article!