chart vs diagram vs graph
Associated Articles: chart vs diagram vs graph
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate via the intriguing matter associated to chart vs diagram vs graph. Let’s weave fascinating info and provide contemporary views to the readers.
Desk of Content material
Chart vs. Diagram vs. Graph: Unveiling the Nuances of Visible Knowledge Illustration
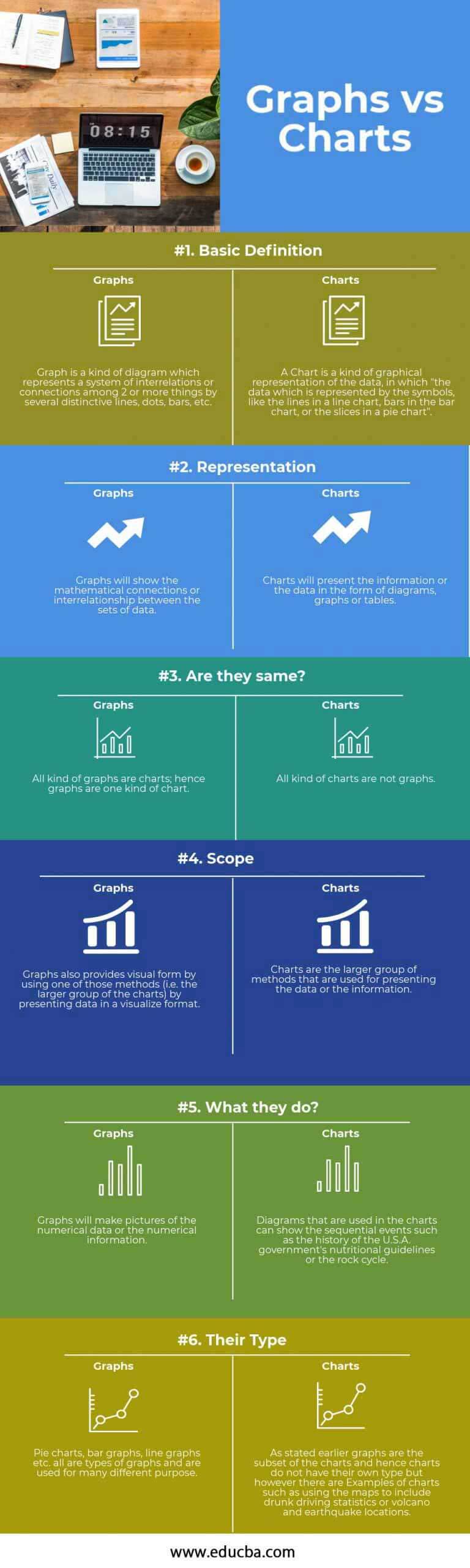
Knowledge visualization is a cornerstone of efficient communication, permitting advanced info to be understood rapidly and intuitively. Nevertheless, the phrases "chart," "diagram," and "graph" are sometimes used interchangeably, resulting in confusion about their distinct purposes and functionalities. Whereas there’s vital overlap, refined variations exist that affect the selection of visible illustration for particular datasets and communication objectives. This text delves into the nuances of every, offering clear definitions, examples, and pointers for his or her acceptable utilization.
Understanding the Elementary Variations
At their core, all three – charts, diagrams, and graphs – serve the aim of visually representing knowledge. Nevertheless, their approaches and the sorts of knowledge they greatest symbolize differ considerably:
-
Graphs: Primarily used to point out the connection between two or extra variables, typically depicting quantitative knowledge. They emphasize the traits, patterns, and correlations inside the knowledge. Graphs rely closely on numerical scales and axes to precisely symbolize knowledge factors.
-
Charts: Broader in scope than graphs, charts current knowledge in a summarized or categorized method. They’ll show each quantitative and qualitative knowledge, specializing in highlighting key options, comparisons, and distributions. Charts typically make the most of bars, slices, or different visible parts to symbolize knowledge proportions or frequencies.
-
Diagrams: Probably the most versatile of the three, diagrams are used as an instance ideas, processes, or constructions. They could incorporate quantitative knowledge however primarily deal with visible illustration of relationships, hierarchies, or workflows. Diagrams are sometimes schematic and fewer reliant on exact numerical accuracy.
A Deeper Dive into Every Visible Illustration
Let’s discover every class intimately, analyzing their particular sorts, purposes, and strengths:
1. Graphs: Unveiling Relationships and Developments
Graphs are arguably probably the most mathematically exact of the three. They make the most of coordinate programs (Cartesian or polar) to plot knowledge factors, enabling the visualization of relationships between variables. A number of widespread sorts of graphs exist:
-
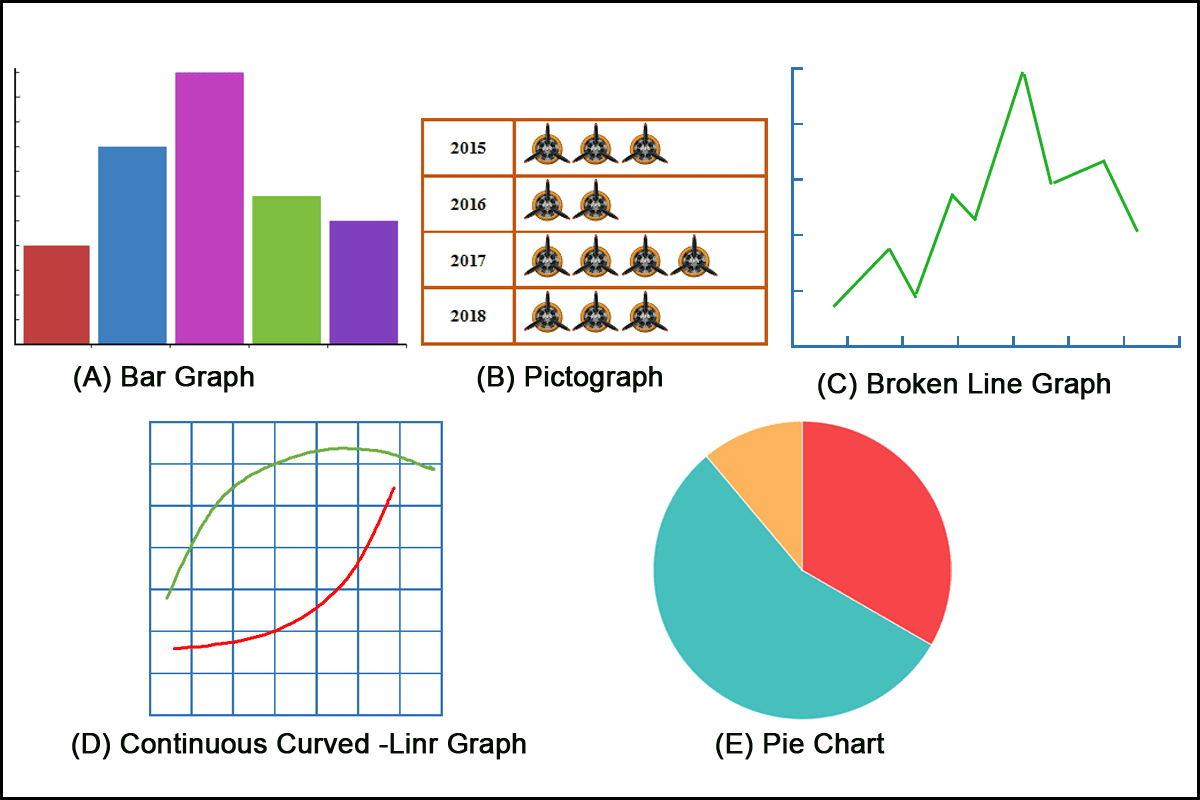
Line Graphs: Ultimate for displaying traits over time or illustrating the connection between two steady variables. They’re significantly efficient for highlighting adjustments and patterns in knowledge. Examples embrace inventory costs over time, temperature fluctuations, or inhabitants progress.
-
Scatter Plots: Used to show the connection between two variables with out implying causation. They’re helpful for figuring out correlations, clusters, and outliers within the knowledge. Examples embrace the connection between top and weight, or promoting spend and gross sales.
-
Bar Graphs (or Bar Charts): Whereas typically categorized as charts, bar graphs will also be thought-about a sort of graph once they symbolize quantitative knowledge alongside a numerical scale. They’re glorious for evaluating values throughout completely different classes. Examples embrace gross sales figures for various merchandise or the variety of college students in varied tutorial packages.
-
Space Graphs: Much like line graphs, space graphs emphasize the magnitude of change over time or throughout classes. They’re helpful for highlighting cumulative totals or proportions. Examples embrace market share over time or web site visitors sources.
-
Pie Charts: Whereas technically a chart, pie charts will also be used to symbolize proportions of an entire, visually demonstrating the relative contribution of every part. Nevertheless, they turn out to be much less efficient with many classes.
The energy of graphs lies of their capability to disclose exact quantitative relationships, traits, and patterns. Their limitations embrace potential complexity with massive datasets and issue in representing qualitative info.
2. Charts: Summarizing and Categorizing Knowledge
Charts provide a extra versatile method to knowledge visualization, encompassing varied sorts designed for particular functions:
-
Bar Charts: As talked about earlier, bar charts are versatile and efficient for evaluating categorical knowledge. They are often horizontal or vertical, and clustered bar charts permit for comparisons throughout a number of classes concurrently.
-
Pie Charts: These round charts divide an entire into proportional segments, representing the share contribution of every class. They’re greatest suited to displaying easy proportions however can turn out to be cluttered with many classes.
-
Column Charts: Much like bar charts, however with vertical bars, column charts are glorious for evaluating values throughout classes.
-
Histograms: These charts show the frequency distribution of steady knowledge, displaying the variety of knowledge factors inside particular ranges or bins. They’re helpful for understanding the form and unfold of knowledge.
-
Pictograms: These charts use icons or pictures to symbolize knowledge, making them extra partaking and simpler to grasp for non-technical audiences. Nevertheless, they could lack precision in comparison with different chart sorts.
-
Flowcharts: Whereas technically diagrams, flowcharts are sometimes thought-about charts when depicting sequential processes or workflows utilizing quantitative metrics like time or price at every step.
Charts excel at summarizing massive datasets and presenting key findings in a concise and simply digestible format. They’re significantly efficient for highlighting comparisons, distributions, and proportions. Nevertheless, they is probably not as efficient in revealing intricate relationships between variables as graphs.
3. Diagrams: Illustrating Ideas and Constructions
Diagrams transfer past the strict numerical illustration of knowledge, specializing in visible depictions of ideas, processes, and constructions. Their main objective is to make clear relationships and illustrate advanced info in a simplified method. Examples embrace:
-
Flowcharts: These diagrams illustrate the sequence of steps in a course of, typically utilizing symbols to symbolize actions, selections, and inputs/outputs.
-
Community Diagrams: These diagrams depict the connections and relationships between parts in a system, reminiscent of a pc community or social community.
-
Organizational Charts: These diagrams illustrate the hierarchical construction of a corporation, displaying reporting relationships and roles.
-
UML Diagrams: Utilized in software program engineering, UML diagrams symbolize varied facets of a software program system, together with class diagrams, sequence diagrams, and use case diagrams.
-
Venn Diagrams: These diagrams illustrate the relationships between units, displaying overlaps and distinctive parts.
-
Thoughts Maps: These diagrams visually arrange ideas and concepts, branching out from a central idea.
Diagrams are essential for speaking advanced programs, processes, and ideas visually. They prioritize readability and understanding over exact numerical accuracy. Whereas they could incorporate quantitative knowledge, their main perform is as an instance relationships and constructions.
Selecting the Proper Visible Illustration
Deciding on the suitable visible illustration relies on the kind of knowledge, the message you wish to convey, and your viewers. Contemplate the next components:
-
Kind of Knowledge: Quantitative knowledge (numerical values) is greatest represented by graphs and sure sorts of charts. Qualitative knowledge (categorical values) is healthier suited to charts and diagrams.
-
Relationship between Variables: If you wish to present the connection between two or extra variables, a graph is probably the most acceptable alternative.
-
Viewers: Contemplate the technical experience of your viewers. Easy charts and diagrams are higher suited to non-technical audiences, whereas graphs is perhaps essential for conveying extra advanced quantitative relationships to consultants.
-
Communication Objective: What would you like your viewers to grasp or take away from the visualization? This may assist decide the best visible illustration.
Conclusion: A Unified Method to Knowledge Visualization
Whereas the distinctions between charts, diagrams, and graphs are essential, they aren’t mutually unique. Efficient knowledge visualization typically includes a mix of those strategies to current a complete and compelling narrative. By understanding the strengths and limitations of every, you possibly can select the optimum visible illustration to speak your knowledge successfully and obtain your communication objectives. Keep in mind, the last word objective is evident, concise, and impactful communication, and the best visible software performs a vital function in attaining this.







Closure
Thus, we hope this text has supplied helpful insights into chart vs diagram vs graph. We thanks for taking the time to learn this text. See you in our subsequent article!