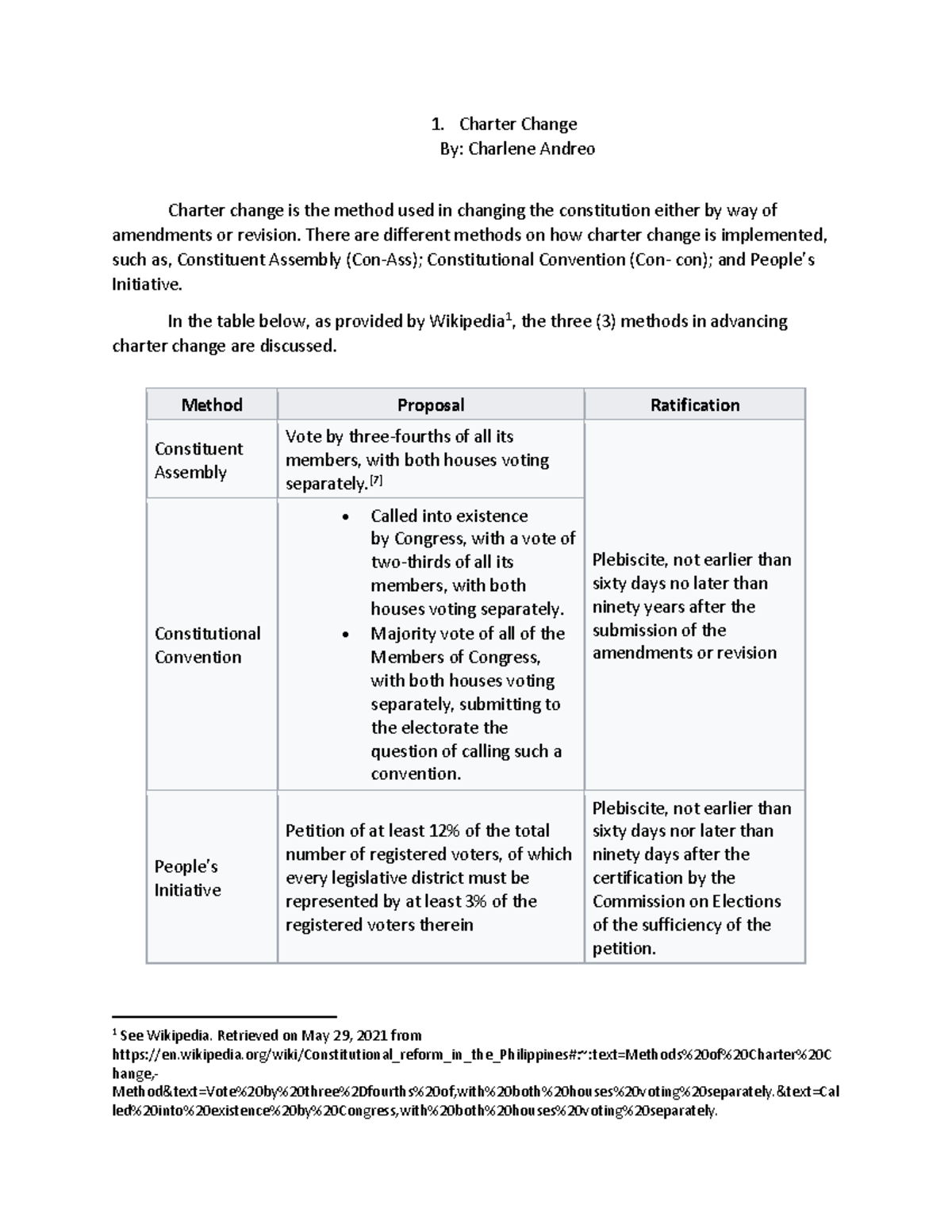
Constitution Change: A Deep Dive into Constitutional Reform By Examples
Associated Articles: Constitution Change: A Deep Dive into Constitutional Reform By Examples
Introduction
With nice pleasure, we’ll discover the intriguing subject associated to Constitution Change: A Deep Dive into Constitutional Reform By Examples. Let’s weave attention-grabbing data and provide contemporary views to the readers.
Desk of Content material
Constitution Change: A Deep Dive into Constitutional Reform By Examples

Constitutional reform, also known as constitution change, is a posh and multifaceted course of that entails altering a nation’s basic regulation. It is a highly effective instrument for adapting a nation’s governance construction to evolving societal wants, addressing historic injustices, or just bettering effectivity. Nevertheless, it is also a fragile endeavor, fraught with potential pitfalls and requiring cautious consideration of its affect on the political panorama and the citizenry. This text explores the idea of constitution change by means of numerous examples, inspecting the motivations, processes, and penalties of those important alterations.
Understanding the Course of: A Spectrum of Approaches
The mechanisms for constitutional modification differ considerably throughout nations. Some international locations, like the USA, make use of a comparatively inflexible course of requiring supermajorities in each legislative homes and, usually, ratification on the state stage. Others, comparable to the UK, have a extra versatile method, with amendments handed by means of bizarre legislative processes. Nonetheless others could make the most of referendums, permitting residents direct enter into the method. The particular method adopted displays a nation’s historical past, political tradition, and the specified stage of stability versus adaptability in its constitutional framework.
Examples of Constitution Change: Numerous Motivations and Outcomes
Let’s look at a number of examples of constitution change from around the globe, highlighting the varied motivations and penalties:
1. South Africa’s Submit-Apartheid Structure (1996): South Africa’s transition from apartheid to a democratic society necessitated a basic overhaul of its constitutional framework. The 1996 structure, drafted by means of a technique of broad-based session and negotiation, aimed to deal with the injustices of the previous and set up a simply and equitable society. Key adjustments included enshrining basic human rights, establishing an unbiased judiciary, and implementing mechanisms for affirmative motion to redress historic inequalities. This instance demonstrates constitution change pushed by the necessity for societal transformation and reconciliation. Whereas largely profitable, ongoing debates about redress and the tempo of transformation proceed to focus on the complexities of such profound change.
2. Canada’s Constitutional Amendments (Varied): Canada’s constitutional historical past is punctuated by a sequence of amendments, usually reflecting the evolving relationship between the federal authorities and the provinces. The 1982 patriation of the structure, which severed its dependence on the British Parliament, was a landmark second. Subsequent amendments have addressed points comparable to Aboriginal rights, equalization funds between provinces, and language rights. These amendments showcase a extra incremental method to constitution change, reflecting the necessity to stability nationwide unity with provincial autonomy. Nevertheless, the method has usually been contentious, highlighting the challenges of reaching consensus in a federal system.
3. The European Union’s Treaties: The European Union’s evolution from a primarily financial alliance to a political entity has concerned quite a few treaty revisions. These treaties have expanded the EU’s powers, launched new establishments, and redefined the connection between member states. The Maastricht Treaty (1993), the Amsterdam Treaty (1999), and the Lisbon Treaty (2007) are prime examples, demonstrating how constitution change can replicate the dynamic nature of worldwide relations and the necessity for adaptation to altering world circumstances. The method, nevertheless, has been marked by durations of intense negotiation and infrequently near-failure, reflecting the inherent difficulties of balancing the pursuits of various member states.
4. India’s Constitutional Amendments (Quite a few): India’s structure has undergone quite a few amendments since its adoption in 1950. These amendments have addressed a variety of points, together with land reforms, social justice initiatives, and the growth of basic rights. Nevertheless, some amendments have additionally been criticized for undermining democratic ideas or concentrating energy. This highlights the potential dangers related to frequent or poorly conceived constitutional amendments. The continued debate concerning the stability between judicial evaluation and legislative supremacy illustrates the enduring challenges of managing constitutional change in a big and various democracy.
5. America’ Invoice of Rights and Subsequent Amendments: The US Structure, whereas comparatively secure, has additionally seen important change by means of its modification course of. The Invoice of Rights, added shortly after ratification, considerably expanded particular person liberties. Subsequent amendments have addressed points comparable to slavery (thirteenth Modification), suffrage (nineteenth Modification), and presidential succession (twenty fifth Modification). This demonstrates how constitution change could be a gradual course of, responding to evolving societal values and addressing persistent injustices over time. Nevertheless, the rigorous modification course of has additionally restricted the frequency of change, reflecting a deliberate effort to make sure stability and stop impulsive alterations.
Challenges and Issues in Constitution Change
A number of challenges are inherent within the technique of constitution change:
- Political Polarization: Constitutional reform usually turns into extremely politicized, resulting in deep divisions inside society. Compromise and consensus-building are essential, however usually troublesome to attain.
- Public Opinion: The general public’s understanding and help for proposed adjustments are very important for profitable implementation. Lack of public engagement can result in instability and resentment.
- Judicial Evaluate: The position of the judiciary in deciphering and imposing constitutional amendments can considerably affect their effectiveness and implementation.
- Unintended Penalties: Constitutional adjustments can have unexpected and unintended penalties, requiring cautious evaluation and threat administration.
- Implementation Challenges: Even after a constitutional modification is adopted, its efficient implementation requires important assets and political will.
Conclusion:
Constitution change is a strong however delicate instrument of governance. The examples mentioned illustrate the varied motivations, processes, and penalties of constitutional reform. Profitable constitution change requires cautious consideration of its potential affect, broad-based participation, and a dedication to addressing the underlying societal wants that necessitate such basic alterations. It is a course of that calls for each imaginative and prescient and pragmatism, balancing the necessity for stability with the capability for adaptation in a always evolving world. The continued debates and challenges surrounding constitutional reform throughout the globe spotlight the persevering with relevance and complexity of this basic side of governance. Understanding these challenges and studying from previous experiences is essential for navigating the complexities of constitutional change and guaranteeing its success in fostering a extra simply and equitable society.

![[OPINION] Here we go again with charter change](https://www.rappler.com/tachyon/2023/03/TL-chacha.jpg)





Closure
Thus, we hope this text has offered priceless insights into Constitution Change: A Deep Dive into Constitutional Reform By Examples. We thanks for taking the time to learn this text. See you in our subsequent article!