Decoding Japan’s GDP Chart: A Two-Decade Journey of Stagnation and Resilience
Associated Articles: Decoding Japan’s GDP Chart: A Two-Decade Journey of Stagnation and Resilience
Introduction
With nice pleasure, we’ll discover the intriguing subject associated to Decoding Japan’s GDP Chart: A Two-Decade Journey of Stagnation and Resilience. Let’s weave fascinating data and supply recent views to the readers.
Desk of Content material
Decoding Japan’s GDP Chart: A Two-Decade Journey of Stagnation and Resilience

Japan’s Gross Home Product (GDP) chart over the previous 20 years presents a posh narrative of financial stagnation punctuated by durations of development and decline. Whereas as soon as a worldwide financial powerhouse, Japan has grappled with persistent deflation, demographic challenges, and structural points which have hindered its skill to attain sustained, sturdy development. Understanding the traits depicted within the GDP chart requires inspecting a mess of interconnected components, from authorities insurance policies and technological innovation to world financial shocks and inner demographic shifts.
The Lengthy Stagnation: A Have a look at the Broad Tendencies (2000-2023)
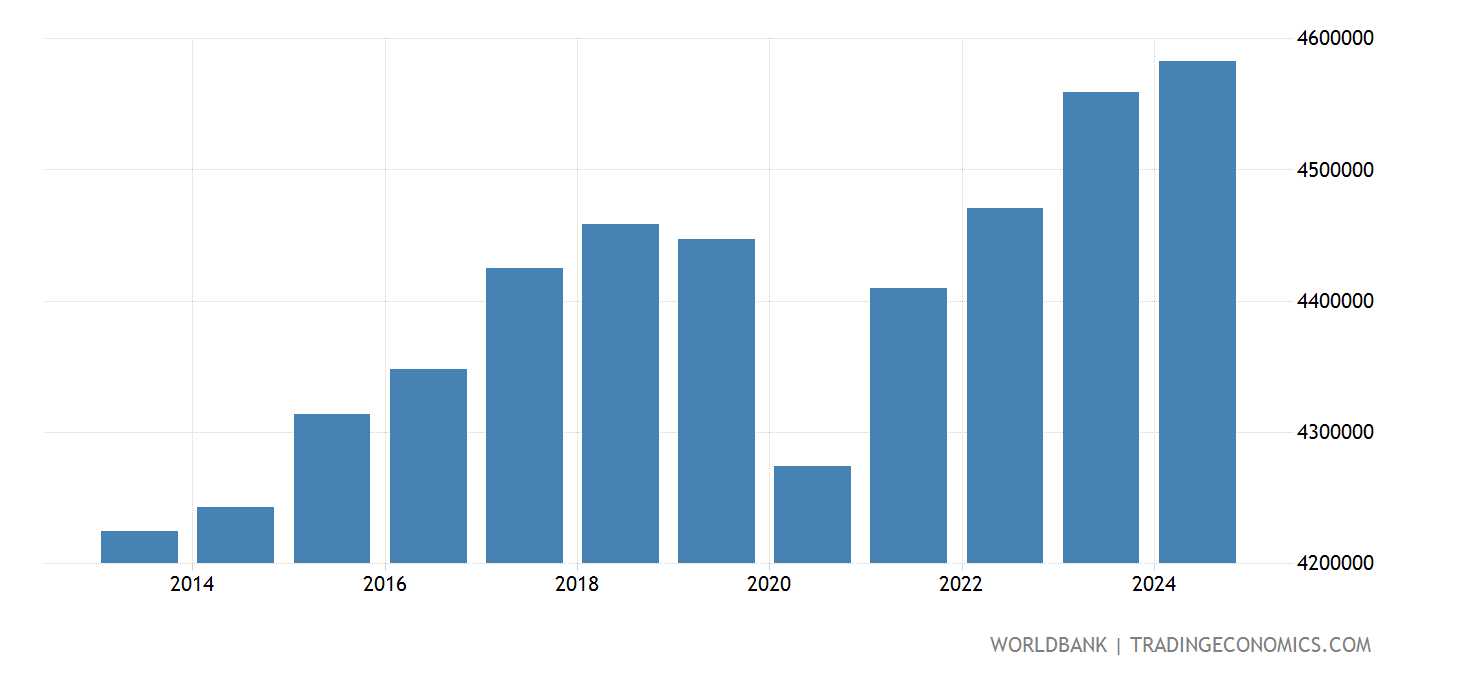
A visible illustration of Japan’s GDP from 2000 to 2023 would reveal a comparatively flat trajectory, a stark distinction to the speedy development skilled in earlier a long time. Whereas there have been durations of enlargement, they’ve been comparatively short-lived and sometimes adopted by durations of contraction or stagnation. This extended interval of low development, also known as "Japan’s Misplaced A long time," is a defining attribute of its current financial historical past. The chart would seemingly present a gradual improve in nominal GDP, however when adjusted for inflation (actual GDP), the expansion would seem much more subdued.
A number of key durations stand out:
-
The Dot-Com Bubble Burst (early 2000s): The bursting of the dot-com bubble globally impacted Japan, contributing to a slowdown in its already decelerating economic system. The chart would replicate a noticeable dip round this era.
-
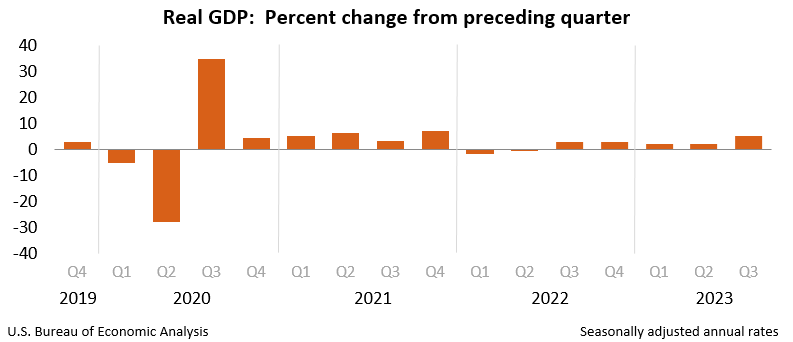
The International Monetary Disaster (2008-2009): The worldwide monetary disaster severely impacted Japan, resulting in a pointy contraction in GDP. The chart would present a major downturn, highlighting the nation’s vulnerability to world financial shocks. The following restoration was sluggish and uneven.
-
The Abenomics Period (2013-2020): Prime Minister Shinzo Abe’s financial insurance policies, often known as Abenomics, aimed to revitalize the Japanese economic system by means of financial easing, fiscal stimulus, and structural reforms. Whereas the chart would possibly present a brief increase in GDP development throughout this era, the general influence was arguably much less transformative than initially hoped. The effectiveness of Abenomics stays a topic of ongoing debate.
-
The COVID-19 Pandemic (2020-2022): The COVID-19 pandemic dealt a major blow to the Japanese economic system, resulting in a pointy contraction in GDP. The chart would replicate a dramatic drop, adopted by a gradual, uneven restoration. The pandemic uncovered vulnerabilities in Japan’s tourism-dependent sectors and highlighted the necessity for better financial diversification.
Components Contributing to Japan’s Stagnant GDP:
Analyzing the GDP chart requires understanding the underlying components contributing to Japan’s financial challenges:
-
Deflation: Japan has struggled with deflation for a protracted interval, characterised by falling costs. This discourages spending and funding as customers postpone purchases anticipating additional worth reductions, making a vicious cycle of low demand and financial stagnation. The chart would possibly present durations the place inflation stays stubbornly low and even destructive.
-
Demographic Challenges: Japan faces a quickly ageing inhabitants and declining birthrate, resulting in a shrinking workforce and rising pressure on social safety programs. This demographic shift reduces shopper demand and limits the potential for financial development. The chart displays this not directly, displaying slower development in comparison with nations with youthful and increasing populations.
-
Structural Rigidities: Japan’s economic system has been criticized for its inflexible labor market, lack of competitors in sure sectors, and resistance to structural reforms. These rigidities hinder innovation, productiveness development, and the environment friendly allocation of assets. The long-term influence of those structural points is seen within the sluggish tempo of GDP development.
-
Technological Innovation: Whereas Japan is a technological chief in particular areas, its total charge of technological innovation and adoption has been slower in comparison with different superior economies. This has restricted its skill to drive productiveness development and create new financial alternatives. The GDP chart might replicate durations the place technological developments fail to translate into substantial financial good points.
-
International Financial Circumstances: Japan’s export-oriented economic system is extremely delicate to world financial fluctuations. Recessions and slowdowns in main buying and selling companions immediately influence Japan’s GDP, as proven by the numerous dips through the world monetary disaster and the COVID-19 pandemic.
-
Authorities Insurance policies: Authorities insurance policies play an important position in shaping financial outcomes. The effectiveness of fiscal and financial insurance policies in stimulating development has been a topic of ongoing debate in Japan. The chart displays the influence (or lack thereof) of varied authorities interventions over time.
Deciphering the Nuances of the GDP Chart:
A easy line graph of Japan’s GDP won’t totally seize the complexities of the financial scenario. A extra complete evaluation requires contemplating:
-
Nominal vs. Actual GDP: Evaluating nominal GDP (unadjusted for inflation) to actual GDP (adjusted for inflation) gives a clearer image of the underlying financial development.
-
GDP per Capita: Analyzing GDP per capita gives insights into the common earnings ranges and lifestyle. This metric helps to know the influence of financial development on the well-being of the Japanese inhabitants.
-
Sectoral Contributions to GDP: Analyzing the contribution of various sectors (e.g., manufacturing, providers, agriculture) to GDP reveals the structural shifts inside the economic system.
-
Comparability with Different Economies: Evaluating Japan’s GDP development to that of different superior economies gives useful context and highlights its relative efficiency.
Wanting Forward: Challenges and Alternatives
Japan’s financial future stays unsure. Addressing the challenges of deflation, demographic change, and structural rigidities requires daring and complete coverage reforms. Nonetheless, there are additionally alternatives:
-
Technological developments: Funding in rising applied sciences, similar to synthetic intelligence, robotics, and renewable vitality, may increase productiveness and create new financial alternatives.
-
Elevated feminine participation within the workforce: Encouraging better participation of girls within the workforce may assist alleviate the labor scarcity.
-
Structural reforms: Implementing reforms to boost competitors, enhance labor market flexibility, and promote innovation may unlock vital financial potential.
-
Globalization: Additional integration into the worldwide economic system and strategic partnerships may present entry to new markets and applied sciences.
The Japanese GDP chart over the previous 20 years tells a narrative of persistent challenges and restricted development. Nonetheless, it additionally hints on the resilience of the Japanese economic system and its potential for future development. By addressing the underlying structural points and embracing innovation, Japan can probably navigate its financial challenges and obtain a extra sustainable and affluent future. The following chapter of Japan’s financial story, as mirrored in its GDP chart, will rely critically on the success of those efforts.





Closure
Thus, we hope this text has offered useful insights into Decoding Japan’s GDP Chart: A Two-Decade Journey of Stagnation and Resilience. We hope you discover this text informative and helpful. See you in our subsequent article!