Decoding the Historical System: A Complete Information to Roman Numerals (1-1000) and Past
Associated Articles: Decoding the Historical System: A Complete Information to Roman Numerals (1-1000) and Past
Introduction
With nice pleasure, we’ll discover the intriguing subject associated to Decoding the Historical System: A Complete Information to Roman Numerals (1-1000) and Past. Let’s weave fascinating info and supply recent views to the readers.
Desk of Content material
Decoding the Historical System: A Complete Information to Roman Numerals (1-1000) and Past

Roman numerals, a system of numerical notation originating in historic Rome, proceed to carry an enchanting place in our trendy world. Whereas largely outdated by the Hindu-Arabic numeral system we use each day, Roman numerals persist in numerous contexts, from clock faces and chapter headings to copyright dates and the numbering of monarchs and Tremendous Bowls. Understanding their construction and software gives a glimpse into the historical past of arithmetic and the enduring legacy of Roman civilization. This text supplies a complete exploration of Roman numerals, specializing in the vary from 1 to 1000, and delving into the system’s underlying ideas, historic improvement, and ongoing relevance.
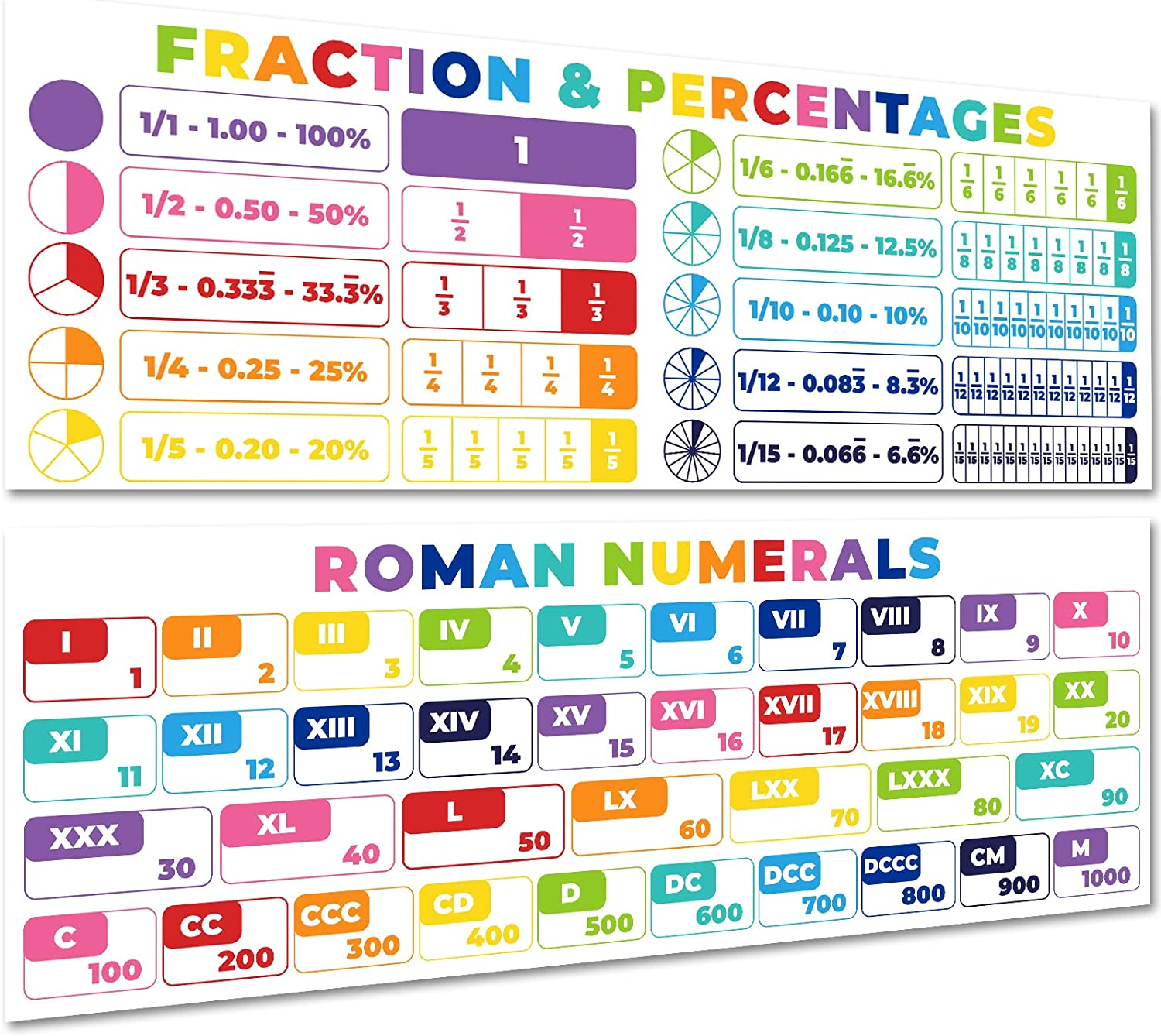
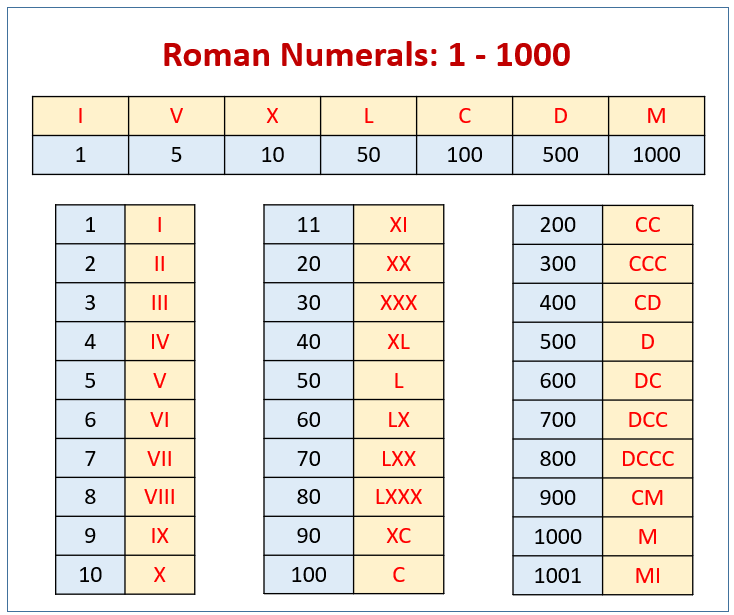
The Primary Constructing Blocks: Symbols and Their Values
The Roman numeral system employs seven fundamental symbols, every representing a particular numerical worth:
- I: 1
- V: 5
- X: 10
- L: 50
- C: 100
- D: 500
- M: 1000
These symbols, derived from Latin phrases or their abbreviations, type the inspiration upon which all different Roman numerals are constructed. As an example, "I" seemingly originated from the one stroke utilized in tallying, whereas "V" is assumed to symbolize half of "X" (ten). The origins of "L," "C," "D," and "M" are much less sure, however they’re believed to be associated to the Latin phrases for 50 ( quinquaginta), 100 (centum), 500 (quingenti), and 1000 (mille), respectively.
Developing Numbers: Addition and Subtraction
The sweetness and ease of the Roman numeral system lie in its additive and subtractive ideas. Smaller values positioned to the proper of bigger values are added. For instance:
- VI: 6 (V + I = 5 + 1)
- XII: 12 (X + II = 10 + 2)
- LXIV: 64 (L + X + IV = 50 + 10 + 4)
Nevertheless, the system additionally incorporates a subtractive precept. When a smaller worth is positioned to the left of a bigger worth, it’s subtracted. This rule applies solely to particular pairs:
- IV: 4 (V – I = 5 – 1)
- IX: 9 (X – I = 10 – 1)
- XL: 40 (L – X = 50 – 10)
- XC: 90 (C – X = 100 – 10)
- CD: 400 (D – C = 500 – 100)
- CM: 900 (M – C = 1000 – 100)
This subtractive precept prevents the extreme repetition of symbols, making the system extra concise. As an example, 99 is represented as XCIX (100 – 10 + 10 – 1) fairly than the extra cumbersome LXXXIX (50 + 10 + 10 + 10 + 9).
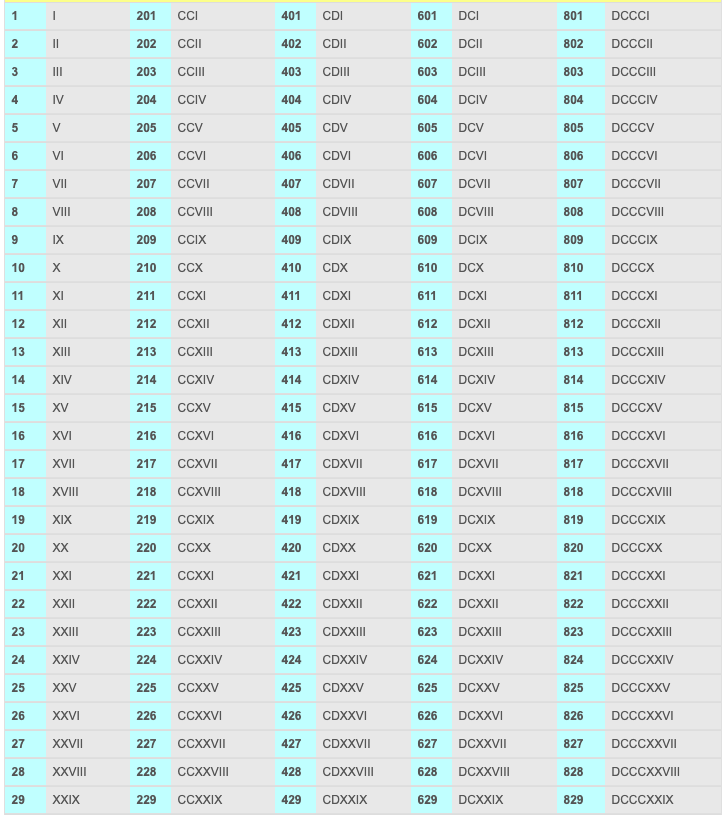
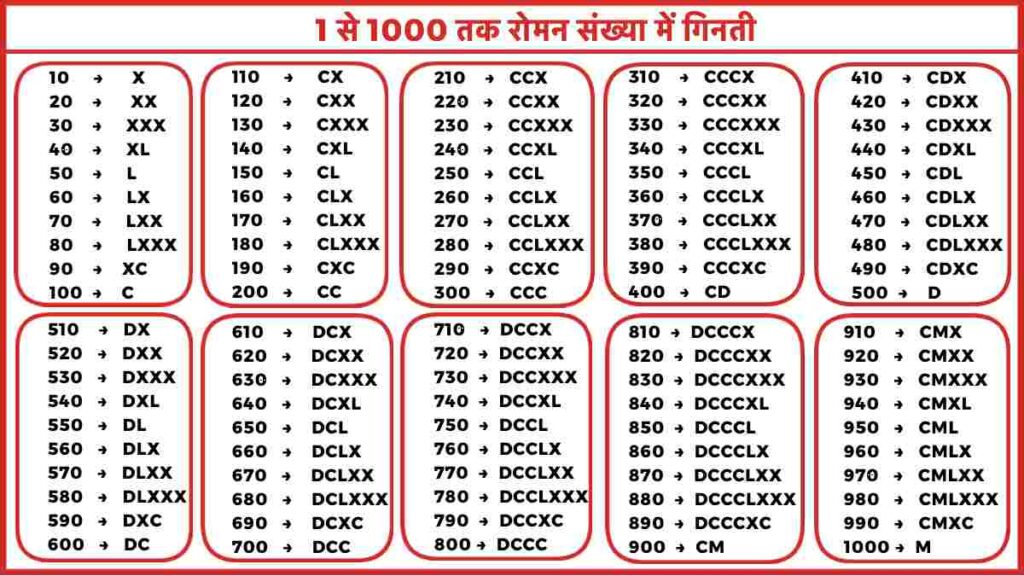
A Complete Chart of Roman Numerals (1-1000)
The next chart illustrates the Roman numeral illustration for numbers 1 to 1000, highlighting the constant software of the additive and subtractive ideas:
| Quantity | Roman Numeral | Quantity | Roman Numeral | Quantity | Roman Numeral |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | I | 334 | CCCXXXIV | 667 | DCLXVII |
| 2 | II | 335 | CCCXXXV | 668 | DCLXVIII |
| 3 | III | 336 | CCCXXXVI | 669 | DCLXIX |
| 4 | IV | 337 | CCCXXXVII | 670 | DCLXX |
| 5 | V | 338 | CCCXXXVIII | 671 | DCLXXI |
| 6 | VI | 339 | CCCXXXIX | 672 | DCLXXII |
| 7 | VII | 340 | CCCXL | 673 | DCLXXIII |
| 8 | VIII | 341 | CCCXLI | 674 | DCLXXIV |
| 9 | IX | 342 | CCCXLII | 675 | DCLXXV |
| 10 | X | 343 | CCCXLIII | 676 | DCLXXVI |
| … | … | … | … | … | … |
| 100 | C | 498 | CDXCVIII | 997 | CMLXCVII |
| 200 | CC | 499 | CDXCIX | 998 | CMLXCVIII |
| 300 | CCC | 500 | D | 999 | CMXCIX |
| 400 | CD | 600 | DC | 1000 | M |
(This chart would proceed to 1000, following the identical sample. Because of house constraints, the complete chart just isn’t included right here, however the sample is well extrapolated.)
Limitations and Extensions of the System
The Roman numeral system, whereas elegant in its simplicity, possesses limitations. Massive numbers grow to be cumbersome to write down and browse, and arithmetic operations are considerably extra advanced than with the Hindu-Arabic system. There is not any direct illustration of zero, and fractions will not be simply expressed.
To symbolize numbers bigger than 1000, the system makes use of overbars or vinculi. A bar positioned above a numeral multiplies its worth by 1000. For instance:
- V̅: 5000
- X̅: 10,000
- C̅: 100,000
- M̅: 1,000,000
Even with these extensions, the system’s limitations grow to be more and more obvious for very giant numbers.
Historic Context and Trendy Utilization
The Roman numeral system developed organically over centuries, reflecting the evolution of Roman society and its administrative wants. Its use regularly declined with the rise of the extra environment friendly Hindu-Arabic system, which supplied better ease in arithmetic and the illustration of huge numbers.
Regardless of its obsolescence in on a regular basis arithmetic, Roman numerals proceed to seek out area of interest functions:
- Clock faces: Roman numerals are sometimes used on clocks and watches, including a contact of classical class.
- Chapter and part numbering: Books and paperwork incessantly use Roman numerals for chapter or part headings.
- Outlining: Roman numerals are incessantly used for outlining, offering a hierarchical construction.
- Copyright dates: Copyright notices usually embrace Roman numerals for the 12 months, notably in additional formal or conventional contexts.
- Monarchs and Popes: Successive monarchs and Popes are historically numbered utilizing Roman numerals.
- Tremendous Bowls: The annual Tremendous Bowl video games are numbered utilizing Roman numerals.
Conclusion
The Roman numeral system, whereas not the first methodology for numerical illustration, stays a testomony to the ingenuity of historic Roman civilization. Its enduring presence in numerous points of recent life underscores its historic significance and aesthetic attraction. Understanding its construction, limitations, and continued relevance permits us to understand the wealthy tapestry of mathematical historical past and the enduring legacy of Roman tradition. Whereas the Hindu-Arabic system reigns supreme in practicality, the Roman numeral system gives a singular and enduring contribution to the world of numbers.




Closure
Thus, we hope this text has supplied useful insights into Decoding the Historical System: A Complete Information to Roman Numerals (1-1000) and Past. We thanks for taking the time to learn this text. See you in our subsequent article!