Decoding the I-Beam Measurement and Weight Chart: A Complete Information
Associated Articles: Decoding the I-Beam Measurement and Weight Chart: A Complete Information
Introduction
On this auspicious event, we’re delighted to delve into the intriguing matter associated to Decoding the I-Beam Measurement and Weight Chart: A Complete Information. Let’s weave fascinating data and provide contemporary views to the readers.
Desk of Content material
Decoding the I-Beam Measurement and Weight Chart: A Complete Information
I-beams, often known as H-beams or wide-flange beams, are ubiquitous in building and engineering tasks on account of their excessive strength-to-weight ratio and versatile design. Understanding their dimensions and weights is essential for correct structural calculations, materials ordering, and undertaking value estimation. This text delves into the intricacies of I-beam measurement and weight charts, explaining their interpretation, purposes, and the significance of choosing the suitable beam for a given activity.
Understanding I-Beam Nomenclature and Dimensions
Earlier than diving into weight charts, it is important to understand the usual nomenclature used to establish I-beams. Completely different international locations and requirements organizations (like ASTM within the US, BS within the UK, and DIN in Germany) make use of barely various techniques, however the core ideas stay constant. Sometimes, an I-beam is recognized by a designation that features:
-
Depth (or Peak): That is the general vertical dimension of the beam, often expressed in inches or millimeters. A bigger depth usually signifies a better load-bearing capability.
-
Flange Width: This refers back to the horizontal dimension of the beam’s flanges (the horizontal sections on the prime and backside). Wider flanges present elevated resistance to bending.
-
Net Thickness: That is the thickness of the vertical part of the beam, connecting the flanges. A thicker internet contributes to elevated shear energy.
-
Flange Thickness: That is the thickness of the horizontal flanges. Just like internet thickness, a better flange thickness will increase energy.
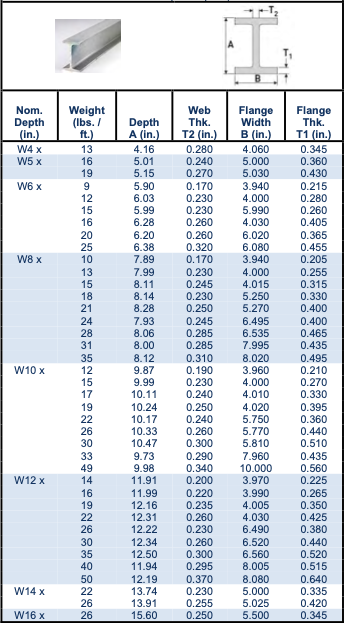
The designation usually combines these dimensions, typically with further letters or numbers indicating the fabric grade (e.g., metal grade) and manufacturing course of. For instance, a designation like "W12x26" (a typical North American designation) signifies a wide-flange beam with a nominal depth of 12 inches and a weight of 26 kilos per linear foot. Different techniques would possibly use completely different codecs, equivalent to a mix of depth and weight or a extra detailed description incorporating all of the related dimensions.
Accessing and Deciphering I-Beam Measurement and Weight Charts (PDFs)
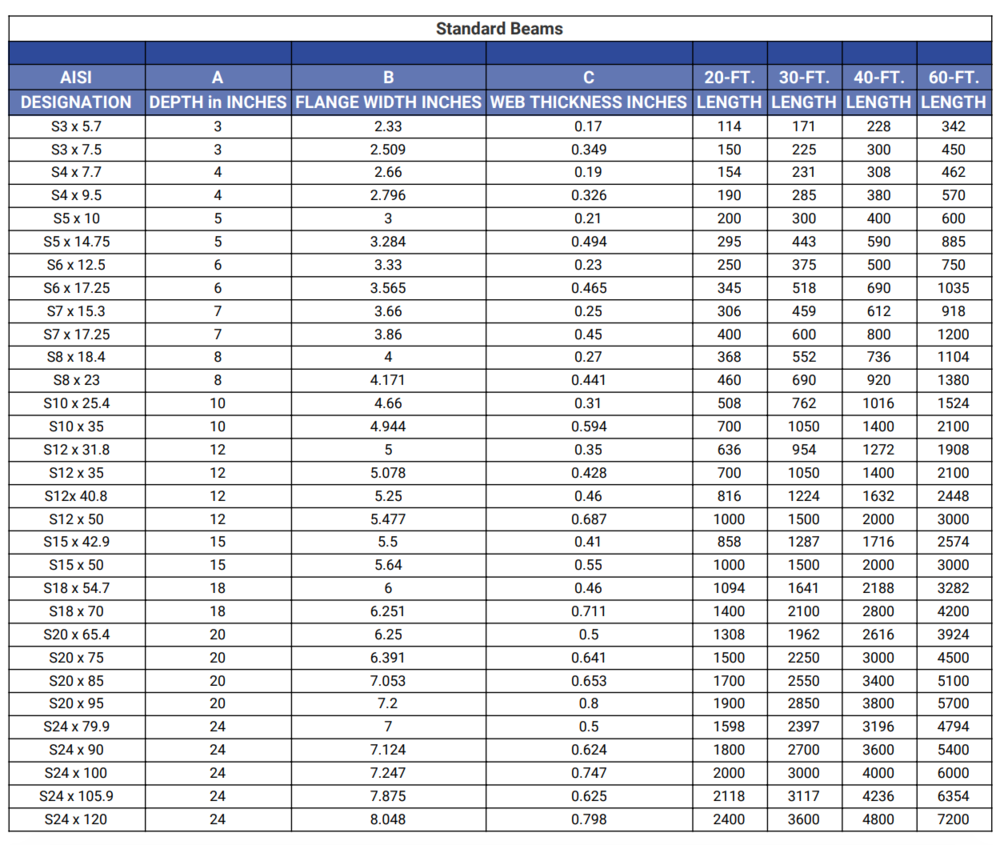
I-beam measurement and weight charts are available on-line and in numerous engineering handbooks. These charts sometimes current the size and weight per unit size (e.g., kilos per foot, kilograms per meter) for a variety of I-beam sizes. The charts are often organized by depth, making it straightforward to find beams with a desired peak. A typical PDF chart will embody columns for:
-
Designation: The distinctive identifier for the I-beam (e.g., W12x26, HEA 160).
-
Depth: The general peak of the beam.
-
Flange Width: The width of the horizontal flanges.
-
Net Thickness: The thickness of the vertical internet.
-
Flange Thickness: The thickness of the flanges.
-
Weight per Unit Size: The load of the beam per unit size, often in kilos per foot or kilograms per meter.
-
Space: The cross-sectional space of the beam.
-
Part Modulus: A measure of the beam’s resistance to bending.
-
Second of Inertia: A measure of the beam’s resistance to bending and twisting.
-
Radius of Gyration: A measure of the beam’s stiffness.
Understanding these parameters is essential for correct beam choice. The load per unit size is crucial for calculating the whole weight of the beam required for a undertaking, influencing transportation prices and basis design. Part modulus, second of inertia, and radius of gyration are vital for structural evaluation, making certain the beam can face up to the anticipated hundreds with out failure.
Components Influencing I-Beam Choice Past Weight and Measurement
Whereas weight and dimensions are main issues, a number of different elements affect the number of an acceptable I-beam:
-
Materials Grade: The metal grade used within the I-beam considerably impacts its energy and ductility. Greater-grade metal gives elevated yield energy and supreme tensile energy, permitting for the usage of smaller beams for a similar load capability.
-
Span Size: The gap the beam must span between helps immediately impacts the required beam measurement. Longer spans necessitate bigger, stronger beams.
-
Loading Circumstances: The sort and magnitude of the masses (useless hundreds, dwell hundreds, dynamic hundreds) the beam will help are essential elements. Uniformly distributed hundreds, concentrated hundreds, and moments all have an effect on the required beam measurement.
-
Deflection Limits: Extreme deflection (bending) can have an effect on the performance and aesthetics of a construction. Design codes specify allowable deflection limits, which should be thought-about throughout beam choice.
-
Buckling Resistance: Slender beams are vulnerable to buckling underneath compressive hundreds. The beam’s slenderness ratio (ratio of size to cross-sectional dimensions) influences its buckling resistance.
-
Hearth Resistance: In sure purposes, hearth resistance is a vital issue. Hearth-resistant coatings or specialised I-beams is likely to be mandatory.
-
Corrosion Resistance: Relying on the setting, corrosion resistance is likely to be an important issue, doubtlessly necessitating the usage of galvanized or coated I-beams.
Utilizing I-Beam Measurement and Weight Charts in Apply
The method of choosing an I-beam sometimes entails:
-
Figuring out the masses: Calculate the useless hundreds (weight of the beam itself and different everlasting parts) and dwell hundreds (variable hundreds like individuals, gear, and snow).
-
Performing structural evaluation: Use engineering software program or hand calculations to find out the required part modulus, second of inertia, and different parameters based mostly on the masses and span size.
-
Consulting the I-beam chart: Use the calculated parameters to seek out an acceptable I-beam from the chart that meets or exceeds the required energy and stiffness.
-
Checking deflection limits: Confirm that the chosen I-beam’s deflection underneath the anticipated hundreds stays inside acceptable limits.
-
Contemplating different elements: Consider the fabric grade, corrosion resistance, and different related elements based mostly on the particular utility.
Conclusion
I-beam measurement and weight charts are invaluable instruments for engineers and building professionals. Understanding their contents and the assorted elements influencing I-beam choice is essential for making certain structural integrity, security, and cost-effectiveness. Whereas the charts present important information, it is crucial to do not forget that correct structural evaluation and consideration of all related elements are important for choosing the suitable I-beam for any given undertaking. All the time seek the advice of related constructing codes and requirements to make sure compliance and security. The knowledge supplied on this article serves as a information and shouldn’t be thought-about an alternative to skilled engineering recommendation.






Closure
Thus, we hope this text has supplied beneficial insights into Decoding the I-Beam Measurement and Weight Chart: A Complete Information. We hope you discover this text informative and useful. See you in our subsequent article!
