Decoding the R-410A Working Strain Chart: A Complete Information for HVAC Technicians
Associated Articles: Decoding the R-410A Working Strain Chart: A Complete Information for HVAC Technicians
Introduction
On this auspicious event, we’re delighted to delve into the intriguing matter associated to Decoding the R-410A Working Strain Chart: A Complete Information for HVAC Technicians. Let’s weave fascinating info and supply contemporary views to the readers.
Desk of Content material
Decoding the R-410A Working Strain Chart: A Complete Information for HVAC Technicians

R-410A, a hydrofluoroolefin (HFO) refrigerant, is a broadly used different to R-22 in air con and refrigeration programs. Understanding its working pressures is essential for secure and environment friendly system operation, troubleshooting, and upkeep. This text supplies an in depth rationalization of R-410A working stress charts, their interpretation, components influencing stress readings, and the significance of correct stress measurements in HVAC functions.
Understanding the Fundamentals: Strain-Temperature Relationship in R-410A Programs
R-410A, like all refrigerants, reveals a direct relationship between stress and temperature. This relationship is ruled by the refrigerant’s thermodynamic properties and is essential for understanding its habits inside a refrigeration cycle. A better temperature corresponds to a better stress, and vice versa, at a given saturation level. This relationship is graphically represented in pressure-temperature (P-T) charts particular to R-410A.
These charts usually current two key stress strains:
- Excessive-Facet Strain: This represents the stress throughout the high-pressure aspect of the refrigeration cycle, encompassing the condenser and liquid line. It is considerably larger than the low-side stress.
- Low-Facet Strain: This represents the stress throughout the low-pressure aspect of the refrigeration cycle, encompassing the evaporator and suction line. It is considerably decrease than the high-side stress.
The charts usually show these pressures as capabilities of temperature, permitting technicians to find out the anticipated stress primarily based on the system’s working temperature. Deviations from these anticipated pressures can point out potential issues throughout the system.
Decoding the R-410A Strain-Temperature Chart
R-410A P-T charts are usually offered as graphs or tables. The horizontal axis normally represents temperature (usually in levels Fahrenheit or Celsius), whereas the vertical axis represents stress (normally in kilos per sq. inch [psi] or kilopascals [kPa]). Two distinct curves are normally current: one for the saturation stress on the liquid state and one other for the saturation stress on the gaseous state. The realm between these curves represents the two-phase area, the place each liquid and gaseous refrigerant coexist.
Key Info Derived from the Chart:
- Anticipated Strain at a Given Temperature: The chart permits technicians to find out the anticipated high-side and low-side pressures primarily based on the system’s working temperature. This supplies a benchmark for evaluating precise stress readings.
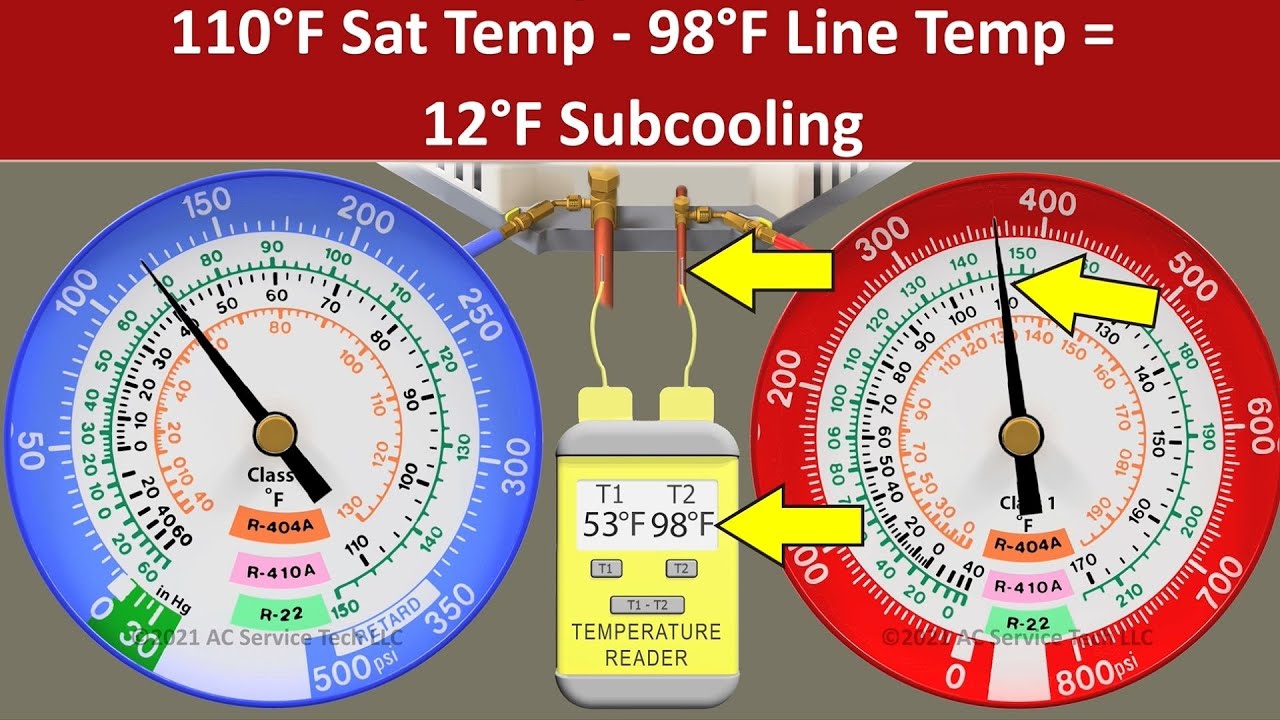
- Superheat and Subcooling: The chart can be utilized to calculate superheat and subcooling, essential parameters for assessing system efficiency and refrigerant cost. Superheat is the distinction between the precise temperature of the refrigerant fuel leaving the evaporator and its saturation temperature at that stress. Subcooling is the distinction between the precise temperature of the refrigerant liquid leaving the condenser and its saturation temperature at that stress. Optimum superheat and subcooling values guarantee environment friendly system operation and stop compressor harm.
- Troubleshooting System Points: Deviations from the anticipated pressures indicated on the chart can level to potential issues resembling refrigerant leaks, compressor malfunctions, condenser fouling, or restricted airflow.
Components Influencing R-410A Working Pressures
A number of components can affect the precise working pressures in an R-410A system, even at a given temperature:
- Ambient Temperature: Larger ambient temperatures result in larger condensing pressures, because the condenser struggles to reject warmth effectively.
- Refrigerant Cost: An undercharged system may have decrease pressures than anticipated, whereas an overcharged system will exhibit larger pressures.
- Airflow: Inadequate airflow throughout the condenser coils can result in larger condensing pressures. Equally, restricted airflow over the evaporator coils can result in decrease evaporating pressures.
- Compressor Effectivity: A malfunctioning compressor can have an effect on each high-side and low-side pressures.
- Condenser and Evaporator Fouling: Soiled condenser or evaporator coils can impede warmth switch, resulting in stress deviations.
- Altitude: Larger altitudes end in decrease atmospheric stress, which might affect the working pressures of the system.
- System Design and Parts: The design of the system, together with the kind of compressor, condenser, and evaporator, also can barely have an effect on the working pressures.
Sensible Purposes and Significance of Correct Strain Measurements
Correct stress measurements are important for numerous features of R-410A system upkeep and troubleshooting:
- Refrigerant Charging: Strain readings are important for precisely charging the system with the right amount of refrigerant. Overcharging or undercharging can result in lowered effectivity and potential harm to the system.
- Troubleshooting: Evaluating precise stress readings with these anticipated primarily based on the P-T chart helps establish potential issues throughout the system. For example, persistently excessive high-side stress may point out a restricted condenser, whereas low low-side stress may recommend a refrigerant leak.
- Efficiency Analysis: Strain measurements, along side temperature readings, permit technicians to evaluate the system’s efficiency and establish areas for enchancment.
- Security: Correct stress readings are essential for making certain the secure operation of the system. Excessively excessive pressures can result in system failure and potential security hazards.
Utilizing Strain Gauges and Manifold Units
Correct stress measurements require using calibrated stress gauges and manifold units. Manifold units permit technicians to measure each high-side and low-side pressures concurrently. Common calibration of those devices is important to make sure correct readings. It is also essential to make sure the gauges are appropriate with R-410A, as some refrigerants can harm sure gauge supplies.
Conclusion:
The R-410A working stress chart is an indispensable device for HVAC technicians. Understanding its interpretation, the components influencing stress readings, and the significance of correct stress measurements is essential for environment friendly system operation, efficient troubleshooting, and making certain secure dealing with of R-410A programs. By mastering using the pressure-temperature chart and using correct measurement methods, technicians can considerably enhance the efficiency, longevity, and security of R-410A refrigeration and air con programs. Common coaching and updates on refrigerant dealing with and system diagnostics are important for sustaining proficiency on this important space of HVAC know-how.







Closure
Thus, we hope this text has offered worthwhile insights into Decoding the R-410A Working Strain Chart: A Complete Information for HVAC Technicians. We respect your consideration to our article. See you in our subsequent article!