distinction in bar chart and histogram
Associated Articles: distinction in bar chart and histogram
Introduction
On this auspicious event, we’re delighted to delve into the intriguing subject associated to distinction in bar chart and histogram. Let’s weave attention-grabbing info and provide contemporary views to the readers.
Desk of Content material
Bar Charts vs. Histograms: Unveiling the Variations in Information Visualization

Bar charts and histograms are each highly effective instruments for visualizing information, notably when coping with categorical or numerical information distributions. Nonetheless, they serve distinct functions and make use of totally different methodologies, resulting in variations of their interpretation and utility. Whereas each use rectangular bars to symbolize information, understanding their elementary variations is essential for efficient information communication and evaluation. This text delves deep into the nuances of bar charts and histograms, clarifying their distinctions and guiding readers on when to make the most of every.
Understanding Bar Charts: Categorical Information at a Look
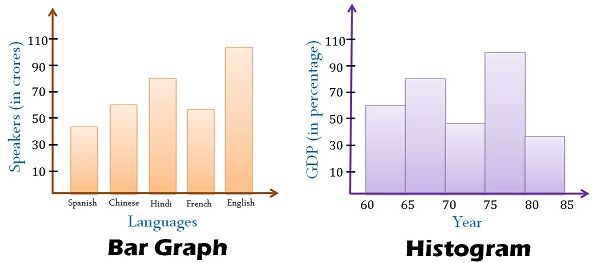
Bar charts are primarily used to match totally different classes of information. Every bar represents a single class, and its size corresponds to the worth or frequency related to that class. The classes themselves might be something from geographical areas and product sorts to time intervals and demographic teams. The important thing attribute of a bar chart is the categorical nature of the information it presents. The classes are distinct and impartial, with no inherent order or numerical relationship between them.
Sorts of Bar Charts:
A number of variations of bar charts exist, every tailor-made to particular information illustration wants:
-
Easy Bar Chart: That is essentially the most fundamental sort, displaying the frequency or worth of a single variable throughout totally different classes. For instance, a easy bar chart may examine the gross sales figures of various product traces in an organization.
-
Grouped Bar Chart: Used to match a number of variables throughout the identical classes. As an illustration, it may show the gross sales figures of various product traces throughout numerous areas, permitting for a direct comparability of regional efficiency for every product.
-
Stacked Bar Chart: Just like a grouped bar chart, however the bars representing totally different variables are stacked on high of one another inside every class. This visualization is useful in displaying the contribution of every variable to the whole worth inside every class.
-
100% Stacked Bar Chart: A variation of the stacked bar chart the place the peak of every stacked bar represents 100%, displaying the proportion of every variable inside every class. That is helpful for highlighting relative contributions.
Key Options of Bar Charts:
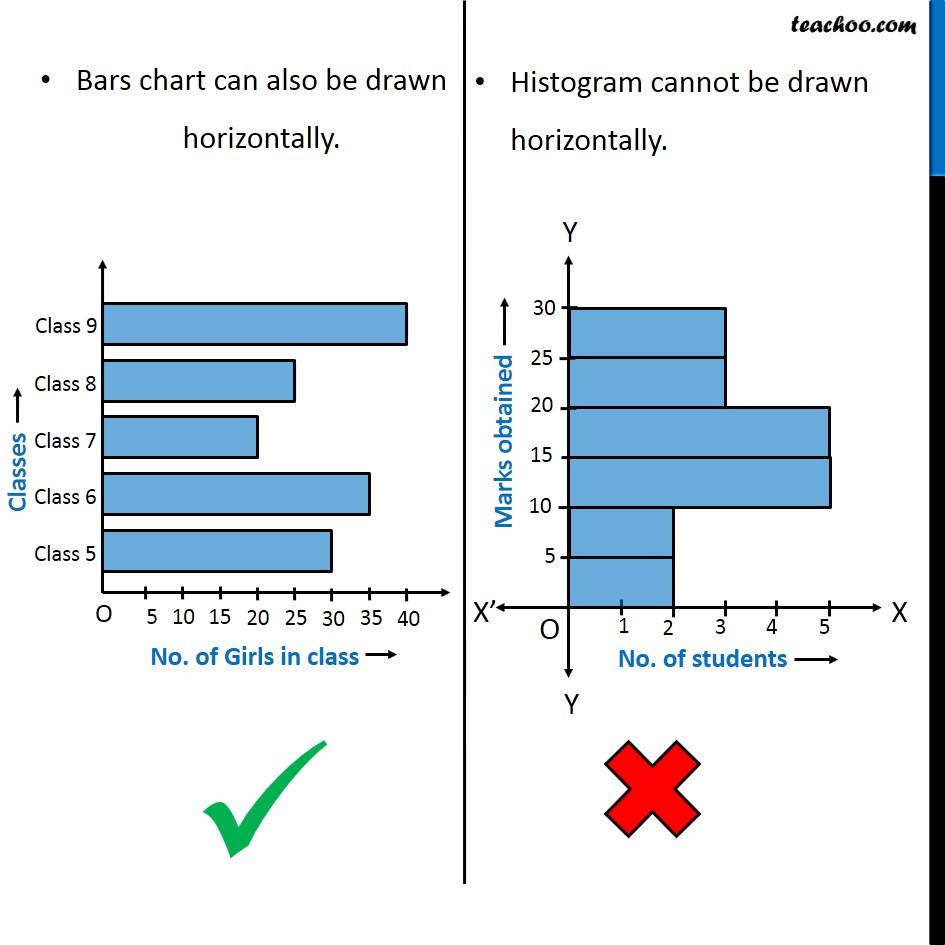
- Categorical X-axis: The horizontal axis (x-axis) shows distinct, unordered classes.
- Numerical Y-axis: The vertical axis (y-axis) represents the frequency, depend, or worth related to every class.
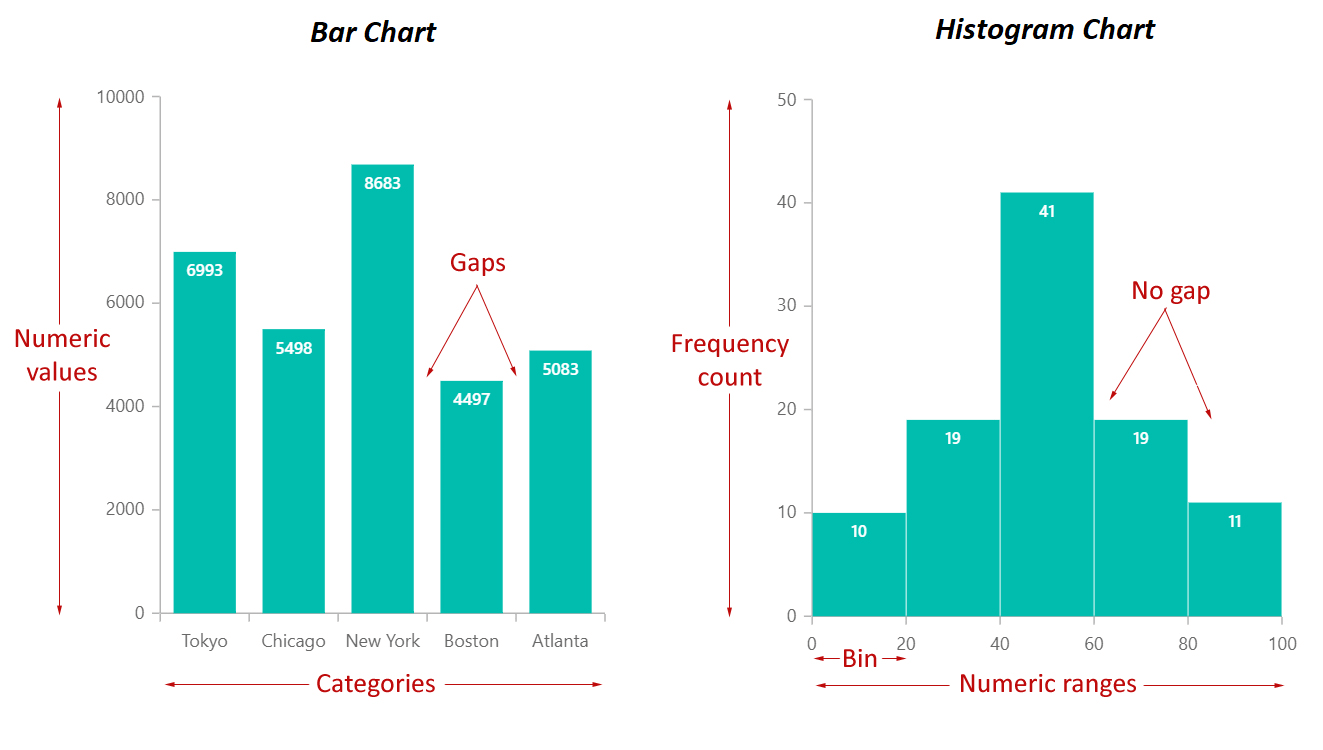
- Discrete Bars: Bars are separated by gaps, emphasizing the distinctness of the classes.
- Straightforward Comparability: Facilitates simple visible comparability of values throughout totally different classes.
Understanding Histograms: Unveiling the Distribution of Numerical Information
Histograms, not like bar charts, are particularly designed to show the distribution of numerical information. They depict the frequency or relative frequency of information factors falling inside particular ranges or intervals (bins). The important thing distinction lies within the nature of the information: histograms cope with steady or discrete numerical information, whereas bar charts deal with categorical information.
Setting up a Histogram:
Making a histogram entails dividing the vary of the numerical information into a number of equal-width intervals or bins. The peak of every bar within the histogram represents the variety of information factors that fall inside that particular bin. The bins are contiguous, that means there aren’t any gaps between them, reflecting the continual nature of the underlying information.
Key Options of Histograms:
- Numerical X-axis: The horizontal axis represents the vary of numerical values, divided into bins.
- Frequency/Relative Frequency Y-axis: The vertical axis represents the frequency or relative frequency (proportion) of information factors inside every bin.
- Steady Bars: Bars are adjoining to one another, reflecting the continual nature of the information.
- Information Distribution: Histograms reveal the form of the information distribution, indicating whether or not it is symmetric, skewed, or multimodal.
Distinguishing Bar Charts and Histograms: A Comparative Evaluation
The next desk summarizes the important thing variations between bar charts and histograms:
| Characteristic | Bar Chart | Histogram |
|---|---|---|
| Information Kind | Categorical | Numerical (steady or discrete) |
| X-axis | Classes | Numerical ranges (bins) |
| Y-axis | Frequency, Depend, or Worth | Frequency or Relative Frequency |
| Bar Spacing | Gaps between bars | No gaps between bars |
| Function | Evaluate classes | Present information distribution and establish patterns |
| Order of X-axis | Order is unfair or significant | Order is inherent (numerical) |
| Interpretation | Direct comparability of class values | Interpretation of distribution form, central tendency, unfold |
When to Use Which:
The selection between a bar chart and a histogram relies upon completely on the character of your information and the insights you goal to convey:
-
Use a bar chart when:
- You wish to examine totally different classes.
- Your information is categorical (e.g., colours, manufacturers, nations).
- You might want to present the frequency or worth of every class clearly.
-
Use a histogram when:
- You wish to visualize the distribution of numerical information.
- You wish to establish patterns, equivalent to skewness, symmetry, or modality in your information.
- You might want to perceive the frequency of information factors inside particular ranges.
Past the Fundamentals: Superior Concerns
Whereas the elemental variations are clear, a number of nuances can additional differentiate the applying of bar charts and histograms:
-
Bin Dimension in Histograms: The selection of bin measurement considerably impacts the looks and interpretation of a histogram. Too few bins might obscure vital particulars, whereas too many bins might create a jagged and uninformative visualization. Experimentation and cautious consideration are important.
-
Information Transformation: Each bar charts and histograms might be enhanced by information transformations (e.g., logarithmic scales) to raised visualize information with a variety or skewed distributions.
-
Including Context: Each visualizations profit from clear labels, titles, and legends to reinforce understanding and interpretation. Contextual info considerably improves the effectiveness of information visualization.
-
Software program and Instruments: Quite a few software program packages and instruments (e.g., Excel, R, Python with Matplotlib/Seaborn) present functionalities to create each bar charts and histograms simply and effectively.
Conclusion:
Bar charts and histograms, although visually related, are distinct instruments for information visualization. Understanding their elementary variations – primarily the specific vs. numerical nature of the information they symbolize – is essential for selecting the suitable visualization method. By fastidiously choosing the best chart sort and contemplating the nuances of information illustration, researchers and analysts can successfully talk insights and facilitate data-driven decision-making. Selecting the improper chart can result in misinterpretations and hinder the efficient communication of information. Due to this fact, a transparent understanding of the strengths and limitations of every visualization method is paramount for efficient information evaluation and communication.




Closure
Thus, we hope this text has supplied helpful insights into distinction in bar chart and histogram. We hope you discover this text informative and useful. See you in our subsequent article!