histogram vs bar chart
Associated Articles: histogram vs bar chart
Introduction
With nice pleasure, we are going to discover the intriguing matter associated to histogram vs bar chart. Let’s weave attention-grabbing data and supply contemporary views to the readers.
Desk of Content material
Histograms vs. Bar Charts: Unveiling the Variations and Selecting the Proper Software
Information visualization is essential for successfully speaking insights from datasets. Two standard selections for representing knowledge are histograms and bar charts. Whereas each make use of rectangular bars to show data, their underlying functions and the kind of knowledge they symbolize differ considerably. Misunderstanding these variations can result in misinterpretations and inaccurate conclusions. This text delves into the nuances of histograms and bar charts, clarifying their purposes, benefits, and limitations that can assist you select the suitable instrument on your knowledge.
Understanding Bar Charts: Categorical Information Illustration
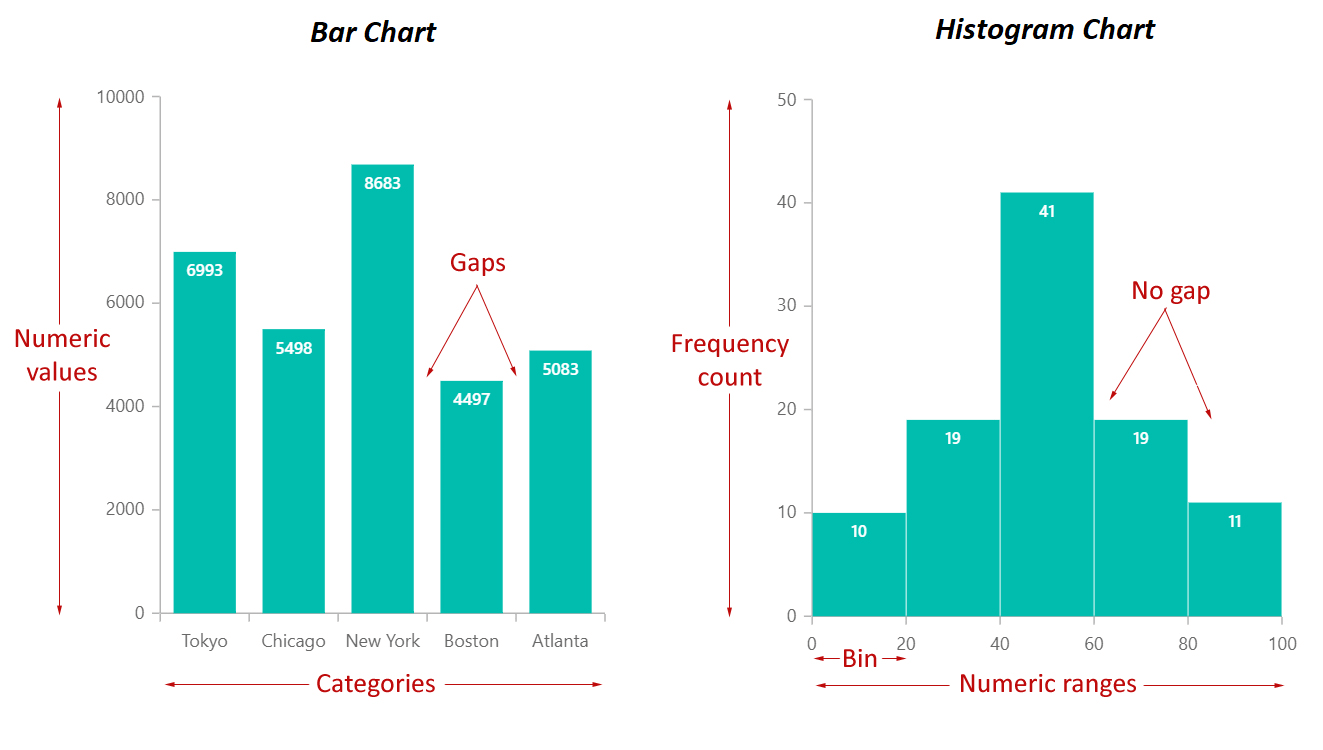
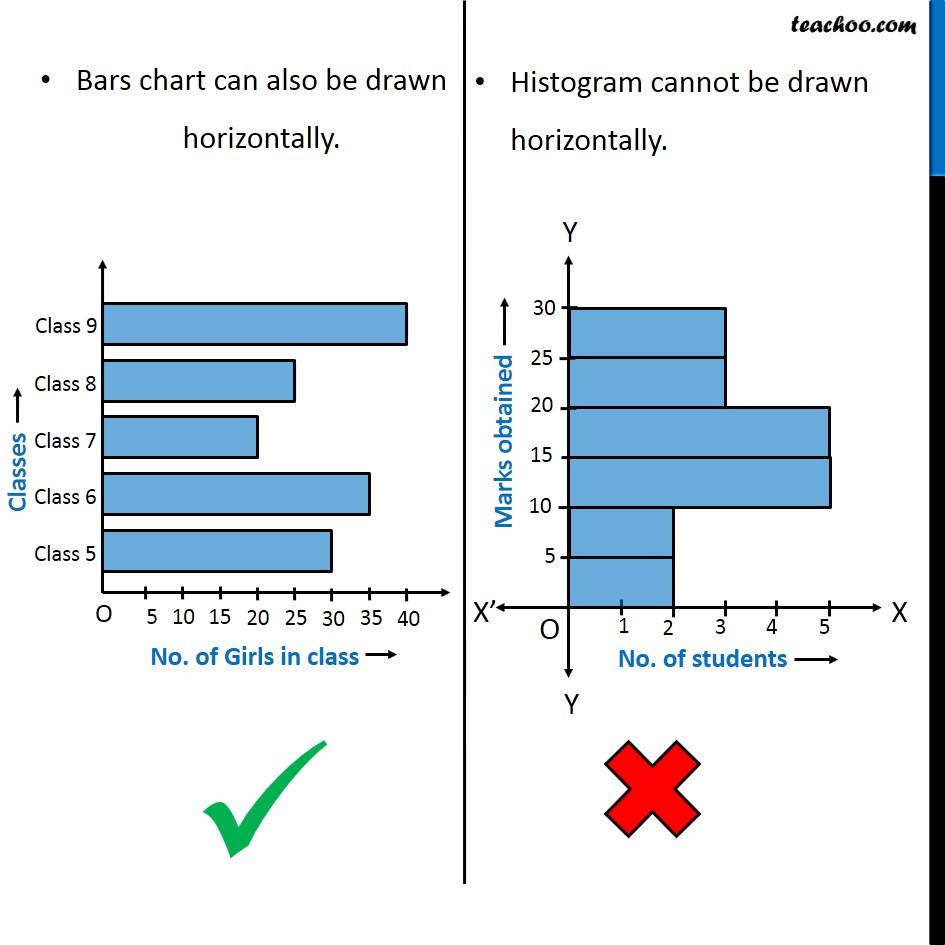
Bar charts are versatile instruments primarily used to check completely different classes of knowledge. Every bar represents a particular class, and its size corresponds to the worth related to that class. The classes may be something from product gross sales figures to survey responses or geographical areas. The important thing attribute of a bar chart is that the classes on the horizontal axis are discrete and unbiased of one another. There isn’t any inherent order or numerical relationship between the classes; they’re merely distinct teams.
Sorts of Bar Charts:
Bar charts are available in numerous types, every designed to emphasise completely different features of the information:
-
Easy Bar Chart: This shows the frequency or magnitude of every class utilizing vertical or horizontal bars. It is probably the most fundamental kind and very best for simple comparisons.
-
Grouped Bar Chart: This compares a number of classes inside completely different teams. For instance, you might evaluate gross sales of various merchandise throughout numerous areas utilizing grouped bars.
-
Stacked Bar Chart: Just like grouped bar charts, stacked bar charts show a number of classes inside a gaggle, however the bars are stacked on prime of one another. This enables for visualizing the contribution of every sub-category to the whole.
-
100% Stacked Bar Chart: This variation of the stacked bar chart normalizes the information to 100%, making it simpler to check the proportions of various classes inside every group.
Benefits of Bar Charts:
-
Simple to grasp and interpret: Their easy visible illustration makes them accessible to a large viewers, no matter their statistical background.
-
Efficient for evaluating classes: They clearly present variations in magnitudes or frequencies between completely different classes.
-
Versatile: They’ll accommodate numerous forms of categorical knowledge and may be personalized with completely different colours, labels, and titles to reinforce readability.
-
Appropriate for presenting discrete knowledge: Their inherent construction completely matches the character of discrete, unordered classes.
Limitations of Bar Charts:
-
Not appropriate for steady knowledge: Bar charts aren’t designed to deal with steady knowledge, the place values can fall wherever inside a spread. Trying to make use of them for steady knowledge can result in misrepresentation.
-
Can change into cluttered with many classes: In case you have a lot of classes, the bar chart can change into tough to learn and interpret.
-
Does not reveal the distribution of knowledge: Bar charts primarily concentrate on evaluating classes; they do not present details about the distribution of knowledge inside every class.
Understanding Histograms: Steady Information Distribution
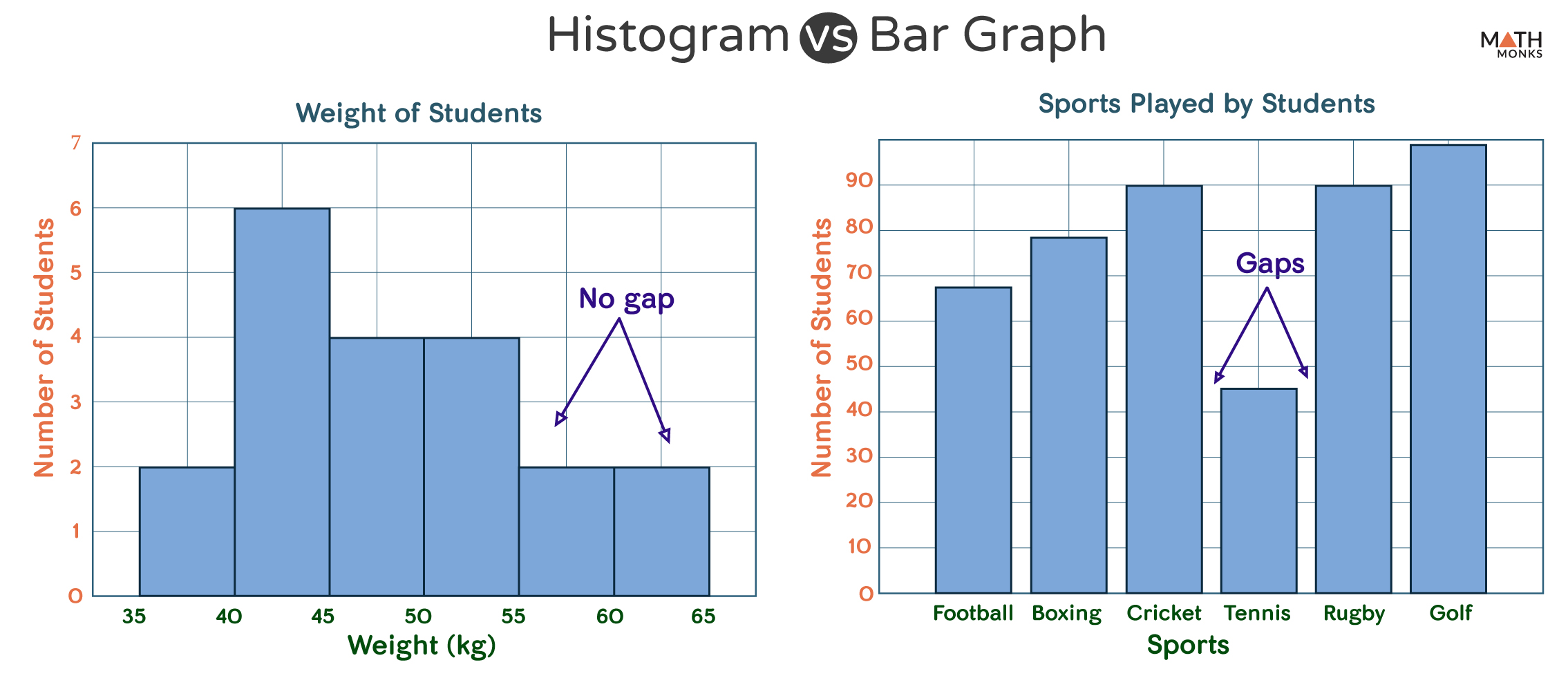
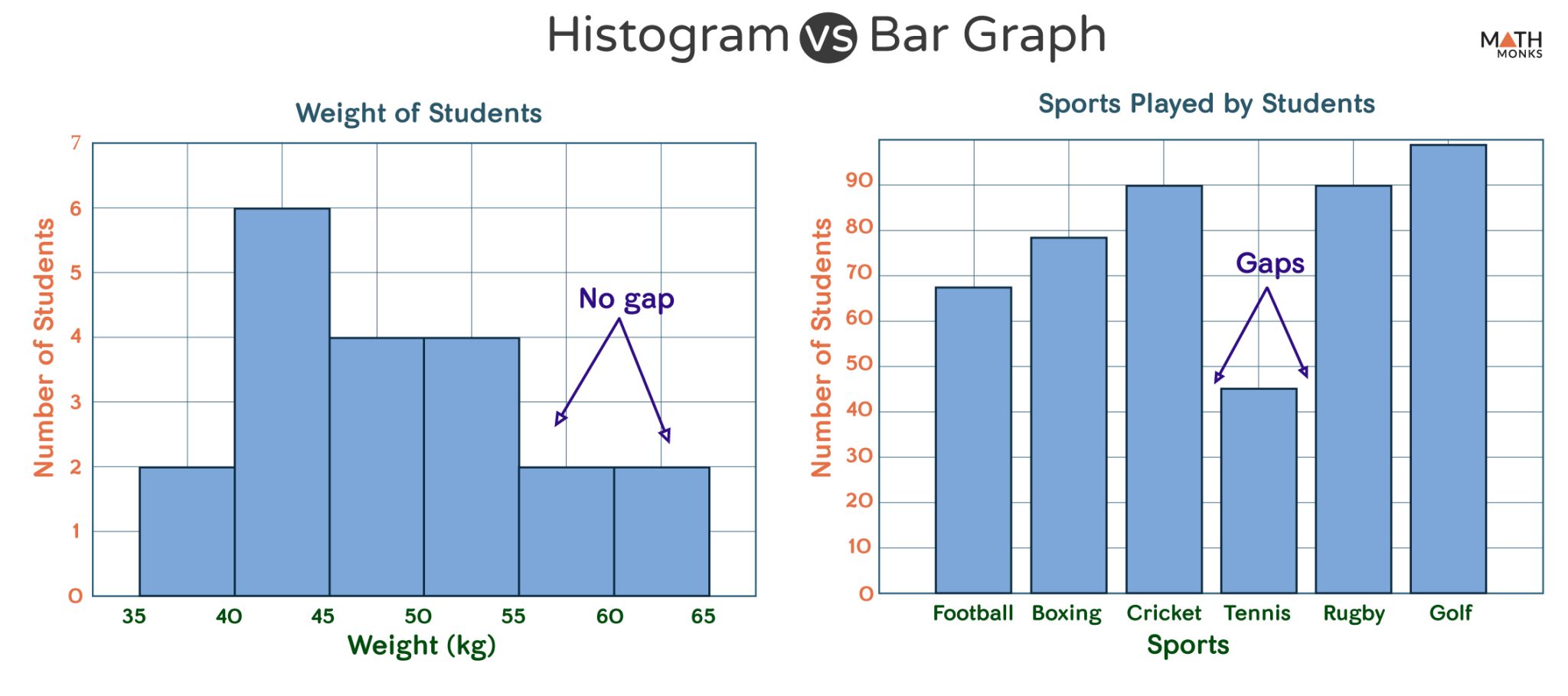
Histograms, in contrast to bar charts, are designed to symbolize the distribution of steady knowledge. They present the frequency or depend of knowledge factors falling inside particular intervals or bins alongside a steady scale. The horizontal axis represents the vary of the continual variable, divided into intervals (bins), and the vertical axis represents the frequency or density of knowledge factors inside every bin. The width of every bar represents the vary of the bin, and the peak represents the frequency or density. The important thing distinction is that the bars in a histogram are adjoining, signifying the continual nature of the information. There are not any gaps between the bars until a bin has zero knowledge factors.
Making a Histogram:
Setting up a histogram entails a number of steps:
-
Decide the vary of your knowledge: Discover the minimal and most values.
-
Select the variety of bins: The variety of bins influences the looks of the histogram. Too few bins can obscure particulars, whereas too many can create a jagged and uninformative graph. Widespread guidelines of thumb exist, equivalent to Sturges’ rule or the sq. root rule, however the optimum quantity typically will depend on the particular dataset and desired stage of element.
-
Decide the bin width: Divide the vary by the variety of bins to get the width of every bin.
-
Depend the information factors in every bin: Assign every knowledge level to the suitable bin based mostly on its worth.
-
Create the histogram: Draw the bars, with the peak of every bar representing the frequency (or density) of knowledge factors inside that bin.
Benefits of Histograms:
-
Visualizes the distribution of steady knowledge: Histograms successfully reveal the form, heart, and unfold of the information, permitting for the identification of patterns like skewness, symmetry, and modality.
-
Identifies outliers: Outliers, that are knowledge factors considerably completely different from the remainder, are sometimes simply noticed in histograms.
-
Helpful for exploratory knowledge evaluation: They supply a fast overview of the information’s traits, serving to in speculation formulation and additional evaluation.
-
Supplies insights into knowledge density: The peak of the bars reveals the focus of knowledge factors inside particular ranges.
Limitations of Histograms:
-
Delicate to bin width: The selection of bin width considerably impacts the looks of the histogram. Completely different bin widths can result in completely different interpretations of the information.
-
Can obscure particulars with massive datasets: With extraordinarily massive datasets, the main points of the distribution is likely to be misplaced if the bins are too vast.
-
Not very best for evaluating completely different classes: Histograms aren’t designed for evaluating completely different classes; they concentrate on the distribution inside a single steady variable.
Selecting Between Histograms and Bar Charts:
The selection between a histogram and a bar chart relies upon solely on the character of your knowledge:
-
Use a bar chart when:
- Your knowledge is categorical (e.g., colours, manufacturers, international locations).
- You wish to evaluate the frequencies or magnitudes of various classes.
- You have got a comparatively small variety of classes.
-
Use a histogram when:
- Your knowledge is steady (e.g., top, weight, temperature).
- You wish to visualize the distribution of your knowledge.
- You wish to establish patterns like skewness, symmetry, or modality.
Illustrative Examples:
Let’s contemplate two examples to additional illustrate the variations:
Instance 1: Evaluating Gross sales of Completely different Merchandise
If you wish to evaluate the gross sales figures of various merchandise (e.g., Product A, Product B, Product C), a bar chart is the suitable selection. Every bar would symbolize a product, and its top would correspond to its gross sales figures.
Instance 2: Analyzing the Distribution of Pupil Heights
In case you have a dataset of scholar heights, a histogram is the higher possibility. You’ll divide the vary of heights into bins (e.g., 5-foot intervals) and depend the variety of college students falling into every bin. The ensuing histogram would present the distribution of scholar heights, revealing whether or not the distribution is regular, skewed, or multimodal.
Conclusion:
Histograms and bar charts are precious instruments for knowledge visualization, however they serve completely different functions. Understanding their strengths and limitations is essential for successfully speaking knowledge insights. By rigorously contemplating the kind of knowledge and the knowledge you want to convey, you possibly can select probably the most applicable chart to precisely and clearly symbolize your findings. Selecting the mistaken chart can result in misinterpretations, so cautious consideration of the information’s nature is paramount to efficient knowledge visualization and communication. Do not forget that efficient knowledge visualization is not only about choosing the proper chart; it is about presenting the knowledge in a transparent, concise, and simply comprehensible method on your supposed viewers.





Closure
Thus, we hope this text has supplied precious insights into histogram vs bar chart. We thanks for taking the time to learn this text. See you in our subsequent article!