is a bar chart a histogram
Associated Articles: is a bar chart a histogram
Introduction
On this auspicious event, we’re delighted to delve into the intriguing matter associated to is a bar chart a histogram. Let’s weave attention-grabbing info and supply contemporary views to the readers.
Desk of Content material
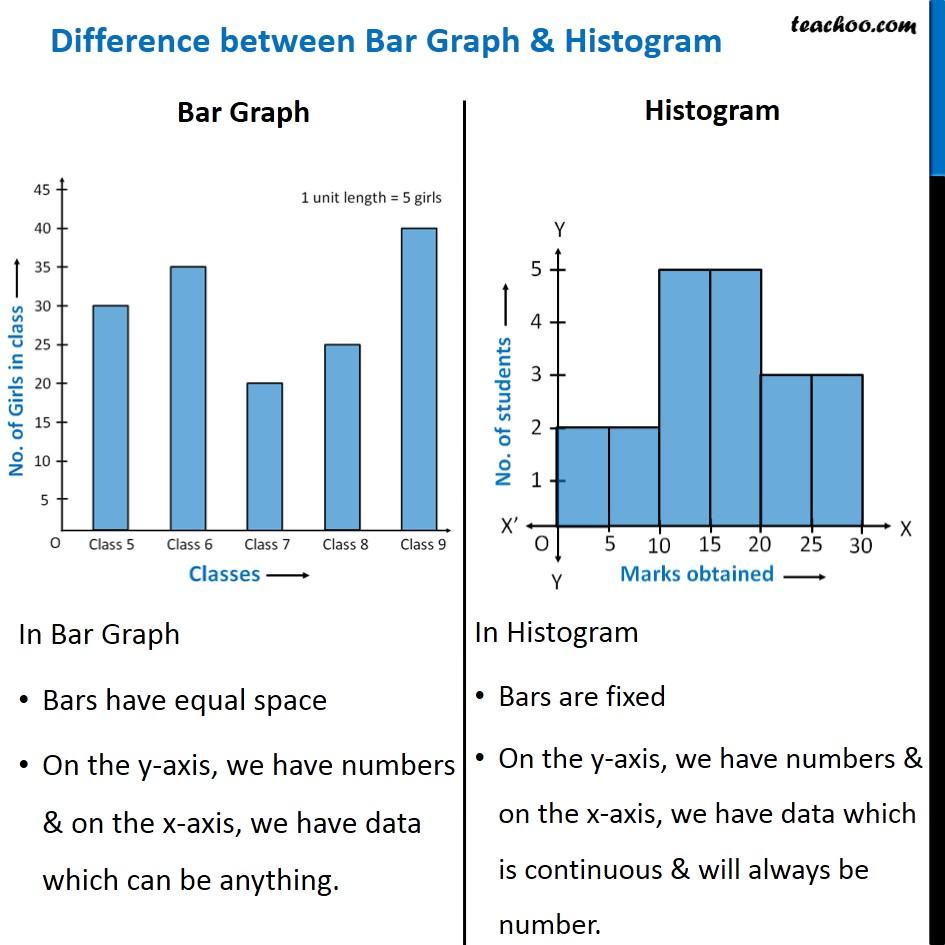
Bar Charts vs. Histograms: A Deep Dive into Knowledge Visualization

Bar charts and histograms are each highly effective instruments for visualizing information, notably when coping with categorical or numerical information displaying frequency or rely. Their visible similarity typically results in confusion, however understanding their elementary variations is essential for efficient information communication and correct interpretation. Whereas each use rectangular bars to signify information, the underlying nature of the information they signify and the inferences drawn from them differ considerably. This text will delve into the nuances of bar charts and histograms, exploring their functions, limitations, and the important thing distinctions that set them aside.
Bar Charts: Categorical Knowledge and Comparisons
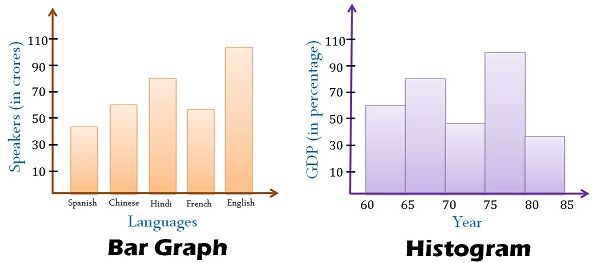
A bar chart is a visible illustration of categorical information, the place every bar corresponds to a particular class, and the peak (or size, relying on orientation) of the bar represents the frequency or magnitude of that class. The classes themselves could be qualitative (e.g., colours, kinds of fruit) or quantitative however discrete (e.g., variety of vehicles owned, age teams). The important thing attribute is that the classes are distinct and separate, not steady.
Kinds of Bar Charts:
A number of variations exist throughout the bar chart household:
-
Easy Bar Chart: This shows the frequency or magnitude of a single categorical variable. For instance, displaying the variety of college students enrolled in numerous programs.
-
Grouped Bar Chart: This compares the frequencies of a categorical variable throughout completely different teams. As an illustration, evaluating the variety of female and male college students enrolled in every course.
-
Stacked Bar Chart: Just like a grouped bar chart, however the bars are stacked on prime of one another, displaying the contribution of every subgroup to the whole for every class. That is helpful for visualizing proportions inside every class.
-
100% Stacked Bar Chart: A variation of the stacked bar chart the place the whole top of every bar is normalized to 100%, representing the proportion contribution of every subgroup.
Key Options of Bar Charts:
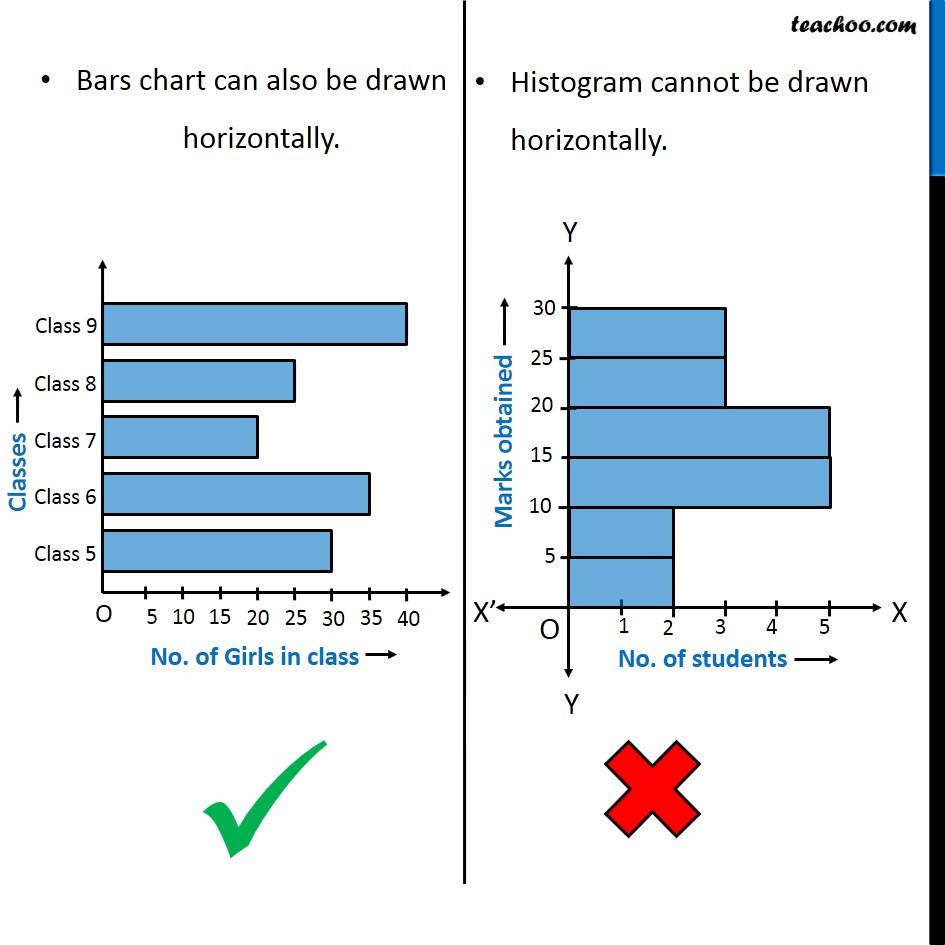
- Discrete Classes: The x-axis represents distinct, non-overlapping classes.
- Frequency or Magnitude: The y-axis represents the frequency or magnitude of every class.
- Simple Comparability: Bar charts excel at visually evaluating the frequencies or magnitudes of various classes.
- Clear Labeling: Clear labeling of classes and values is crucial for correct interpretation.
Purposes of Bar Charts:
Bar charts are extensively used throughout numerous fields:
- Enterprise: Evaluating gross sales figures throughout completely different product strains, areas, or time durations.
- Advertising: Analyzing buyer preferences, model consciousness, and marketing campaign effectiveness.
- Training: Representing pupil efficiency, enrollment statistics, and course recognition.
- Social Sciences: Displaying demographic information, survey outcomes, and public opinion polls.
Histograms: Numerical Knowledge and Distribution
Not like bar charts, histograms signify the distribution of numerical information. The info is grouped into intervals or bins, and the peak of every bar represents the frequency or rely of knowledge factors falling inside that particular bin. The essential distinction right here is that the x-axis represents steady numerical information, not discrete classes. The bins are usually of equal width, though this is not strictly obligatory.
Key Options of Histograms:
- Steady Knowledge: The x-axis represents steady numerical information divided into bins or intervals.
- Frequency Distribution: The y-axis represents the frequency or rely of knowledge factors inside every bin.
- Form of Distribution: Histograms reveal the form of the information distribution, indicating whether or not it’s symmetrical, skewed, or multimodal.
- Knowledge Density: The peak of the bars signifies the density of knowledge factors inside every bin.
Creating Histograms:
Establishing a histogram entails a number of steps:
- Decide the vary of the information: Discover the minimal and most values.
- Select the variety of bins: The variety of bins influences the visible illustration of the information’s distribution. Too few bins can obscure particulars, whereas too many can create a jagged and uninformative graph.
- Calculate the bin width: Divide the vary by the variety of bins.
- Depend the information factors in every bin: Decide what number of information factors fall inside every bin.
- Draw the histogram: Create bars with heights similar to the frequency of knowledge factors in every bin.
Purposes of Histograms:
Histograms are notably helpful in:
- Statistics: Analyzing the distribution of knowledge, figuring out outliers, and estimating parameters like imply and commonplace deviation.
- High quality Management: Monitoring course of variability and figuring out potential issues in manufacturing or different processes.
- Scientific Analysis: Visualizing experimental outcomes, analyzing measurement errors, and understanding information patterns.
- Knowledge Evaluation: Exploring information distributions earlier than making use of extra superior statistical methods.
Distinguishing Bar Charts and Histograms: A Comparative Desk
| Characteristic | Bar Chart | Histogram |
|---|---|---|
| Knowledge Sort | Categorical (qualitative or discrete) | Numerical (steady) |
| X-axis | Distinct classes | Steady numerical information (bins/intervals) |
| Y-axis | Frequency or magnitude of every class | Frequency or rely of knowledge factors in every bin |
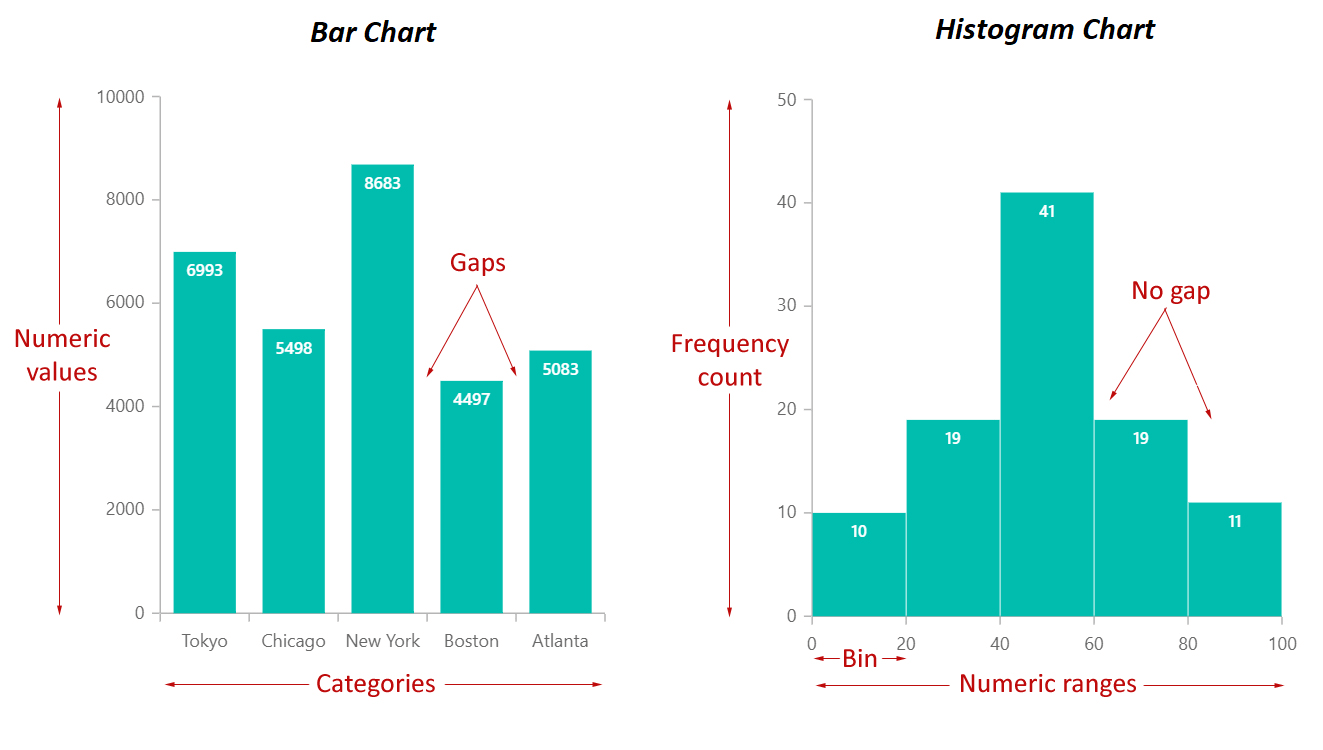
| Gaps between bars | Gaps exist between bars; bars are separated | No gaps between bars; bars are adjoining |
| Function | Examine classes; present frequencies | Present information distribution; reveal patterns |
| Order of classes | Order often arbitrary, except ordinal information | Order is set by the numerical information |
Misinterpretations and Widespread Errors:
A typical mistake is to deal with a histogram as a bar chart, notably when coping with information which may seem categorical however is definitely numerical. As an illustration, representing age teams (e.g., 18-25, 26-35) as distinct classes in a bar chart might sound acceptable, however a histogram is extra correct if the underlying information is the precise age of people. The histogram would present the distribution of ages, offering insights into the density of ages inside every group, which a easy bar chart can’t present.
One other potential error is misinterpreting the peak of the bars in a histogram. The peak represents the frequency density, not essentially absolutely the variety of information factors. If the bin widths are unequal, the peak should be adjusted to precisely mirror the frequency density.
Conclusion:
Bar charts and histograms are helpful instruments for information visualization, every serving a definite function. Bar charts are perfect for evaluating discrete classes, whereas histograms are important for understanding the distribution of steady numerical information. Understanding the basic variations between these two chart sorts is essential for selecting the suitable visualization approach and precisely deciphering the ensuing graphs. By fastidiously contemplating the kind of information and the specified insights, researchers and information analysts can successfully make the most of each bar charts and histograms to speak their findings clearly and precisely. Failing to make this distinction can result in misinterpretations and doubtlessly flawed conclusions drawn from the information. Due to this fact, a radical understanding of the underlying rules and acceptable functions of every chart sort is paramount for profitable information evaluation and communication.



Closure
Thus, we hope this text has supplied helpful insights into is a bar chart a histogram. We hope you discover this text informative and useful. See you in our subsequent article!