Mastering Chart Information Ranges: A Complete Information to Efficient Information Visualization
Associated Articles: Mastering Chart Information Ranges: A Complete Information to Efficient Information Visualization
Introduction
With nice pleasure, we are going to discover the intriguing matter associated to Mastering Chart Information Ranges: A Complete Information to Efficient Information Visualization. Let’s weave attention-grabbing data and provide contemporary views to the readers.
Desk of Content material
Mastering Chart Information Ranges: A Complete Information to Efficient Information Visualization
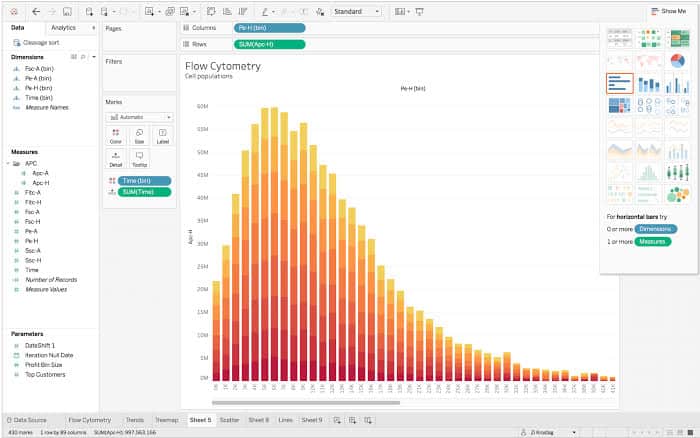
Information visualization is essential for successfully speaking insights derived from knowledge. Charts, a cornerstone of information visualization, rely closely on the suitable choice and presentation of information ranges. Selecting the best knowledge vary considerably impacts the readability, accuracy, and general effectiveness of your chart. A poorly chosen vary can mislead the viewers, obscuring essential traits or exaggerating minor fluctuations. This text delves into the nuances of chart knowledge ranges, exploring greatest practices, frequent pitfalls, and superior methods for optimizing your visualizations.
Understanding the Significance of Information Vary Choice
The information vary, encompassing the minimal and most values displayed on a chart’s axes, defines the scope of the visualized knowledge. This seemingly easy facet considerably influences how the viewers perceives the information. An improperly chosen vary can result in a number of issues:
- Misrepresentation of Tendencies: A slim vary can exaggerate small variations, making insignificant modifications seem dramatic. Conversely, a variety can decrease important traits, making substantial modifications seem negligible.
- Distorted Proportions: Incorrect scaling can distort the visible illustration of information factors, resulting in inaccurate comparisons and interpretations.
- Lack of Context: An inappropriately chosen vary can take away essential context, making it tough for the viewers to grasp the information’s significance inside a bigger image.
- Diminished Readability: A cluttered chart with an excessively wide selection or an excessively zoomed-in vary may be tough to interpret, decreasing the effectiveness of the visualization.
Widespread Chart Sorts and Vary Concerns
Totally different chart varieties have particular concerns relating to knowledge vary choice. Let’s look at some fashionable chart varieties:
-
Line Charts: Line charts successfully showcase traits over time. The vary ought to be fastidiously chosen to focus on the general pattern whereas avoiding pointless magnification of minor fluctuations. Think about using logarithmic scales for knowledge spanning a number of orders of magnitude.
-
Bar Charts: Bar charts evaluate discrete classes. The vary ought to be certain that all bars are clearly distinguishable and that the variations between them are simply perceivable. Contemplate beginning the y-axis at zero to keep away from deceptive visible comparisons.
-
Scatter Plots: Scatter plots show the connection between two variables. The vary for each axes ought to be fastidiously chosen to embody all knowledge factors whereas sustaining readability. Think about using completely different colours or symbols to group knowledge factors primarily based on further variables.
-
Pie Charts: Pie charts characterize proportions of a complete. The vary is inherently outlined by the full sum, however the visible illustration may be improved by highlighting particular segments or utilizing annotations to make clear percentages.
-
Histograms: Histograms show the distribution of a steady variable. The vary ought to embody all knowledge factors, with bin sizes fastidiously chosen to disclose the underlying distribution with out being overly granular or too coarse.
Finest Practices for Deciding on Information Ranges
A number of greatest practices can information you in selecting applicable knowledge ranges to your charts:
-
Begin at Zero (Typically): For bar charts and different charts evaluating portions, beginning the y-axis at zero is essential for correct visible illustration. Deviating from this observe can considerably distort the notion of variations.
-
Contemplate the Viewers: Tailor the vary to your viewers’s understanding and expectations. A technical viewers would possibly admire a wider vary and extra granular element, whereas a non-technical viewers would possibly profit from a narrower vary specializing in key traits.
-
Analyze Information Distribution: Look at the information’s distribution (e.g., utilizing histograms) to grasp its vary and determine outliers. Outliers can considerably affect the selection of vary. Contemplate whether or not to incorporate or exclude them primarily based on the context and function of the visualization.
-
Use Logarithmic Scales: When coping with knowledge spanning a number of orders of magnitude, a logarithmic scale can successfully compress the vary and reveal patterns that may be obscured on a linear scale.
-
Make use of Information Breaks: For charts with a wide variety and a small portion of information clustered close to the minimal or most, knowledge breaks can enhance readability by visually separating the clustered knowledge from the remainder.
-
Iterate and Refine: The perfect knowledge vary is commonly discovered by way of experimentation. Create a number of charts with completely different ranges and evaluate their effectiveness in conveying the specified message.
Superior Strategies for Information Vary Administration
Past primary vary choice, a number of superior methods can improve the effectiveness of your chart visualizations:
-
Dynamic Vary Adjustment: For interactive charts, think about implementing dynamic vary adjustment primarily based on consumer interactions (e.g., zooming, panning).
-
Adaptive Binning: For histograms, adaptive binning algorithms can robotically modify bin sizes primarily based on the information distribution, guaranteeing optimum visualization.
-
A number of Axes: In some circumstances, utilizing a number of axes can successfully show knowledge with vastly completely different ranges on a single chart, enhancing readability.
-
Information Transformation: Remodeling the information (e.g., utilizing logarithmic transformations) can enhance the visible illustration by compressing the vary or stabilizing variance.
-
Annotation and Callouts: Use annotations and callouts to focus on particular knowledge factors or ranges of curiosity, offering further context and clarification.
Widespread Pitfalls to Keep away from
A number of frequent pitfalls can result in deceptive or ineffective visualizations:
-
Cherry-picking Information: Deciding on a variety that solely consists of knowledge supporting a selected narrative is unethical and deceptive.
-
Ignoring Outliers: Outliers can present worthwhile insights, and ignoring them can result in an incomplete or inaccurate image.
-
Over-zooming: Excessively zooming in on a small portion of the information can obscure the general pattern and context.
-
Utilizing the Flawed Scale: Utilizing a linear scale when a logarithmic scale is extra applicable can distort the notion of traits.
-
Lack of Context: Failing to supply adequate context, corresponding to models of measurement or related background data, can render the chart meaningless.
Conclusion:
Deciding on the suitable knowledge vary is a crucial step in creating efficient and correct chart visualizations. By understanding the rules of vary choice, using greatest practices, and avoiding frequent pitfalls, you’ll be able to considerably improve the readability, accuracy, and affect of your knowledge visualizations. Do not forget that the aim just isn’t merely to show knowledge however to speak insights clearly and successfully. By cautious consideration of information vary, you’ll be able to guarantee your charts successfully serve this function. Constantly refine your method by way of iteration and experimentation to grasp the artwork of information vary administration and unlock the complete potential of your knowledge visualizations.





Closure
Thus, we hope this text has offered worthwhile insights into Mastering Chart Information Ranges: A Complete Information to Efficient Information Visualization. We thanks for taking the time to learn this text. See you in our subsequent article!