Mastering Gantt Charts in Excel: A Deep Dive into Formulation and Strategies
Associated Articles: Mastering Gantt Charts in Excel: A Deep Dive into Formulation and Strategies
Introduction
With nice pleasure, we are going to discover the intriguing subject associated to Mastering Gantt Charts in Excel: A Deep Dive into Formulation and Strategies. Let’s weave fascinating info and provide recent views to the readers.
Desk of Content material
Mastering Gantt Charts in Excel: A Deep Dive into Formulation and Strategies

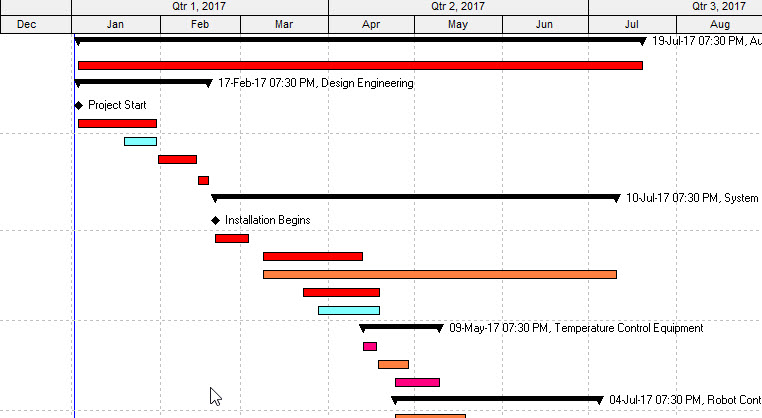
Gantt charts are invaluable instruments for challenge administration, offering a visible illustration of duties, their durations, and dependencies over time. Whereas devoted challenge administration software program gives strong Gantt chart performance, Excel, with its highly effective system capabilities, permits for surprisingly subtle Gantt chart creation. This text delves into the formulation and methods required to construct and customise efficient Gantt charts straight inside Excel. We’ll discover numerous strategies, from easy bar charts to extra superior methods incorporating dependencies and milestones.
Understanding the Fundamentals: The Constructing Blocks of a Gantt Chart
Earlier than diving into formulation, let’s set up the elemental elements of a Gantt chart inside an Excel spreadsheet:
- Duties: An inventory of particular person challenge actions (e.g., "Write proposal," "Design web site," "Conduct testing"). These are usually listed in a column.
- Begin Date: The date every activity begins. That is one other column in your spreadsheet.
- Period: The size of time every activity is predicted to take (in days, weeks, or months). That is essential for figuring out the top date and the size of the bars in your chart.
- Finish Date: The date every activity is predicted to finish. That is calculated primarily based on the beginning date and period.
- Dependencies: Relationships between duties (e.g., "Process B can’t begin till Process A is full"). These are sometimes represented by means of predecessor/successor relationships or visible hyperlinks within the Gantt chart.
Method 1: Calculating the Finish Date
Probably the most elementary system for constructing a Gantt chart in Excel is calculating the top date of every activity. Assuming your begin date is in column B and period in column C, the top date in column D could be calculated utilizing the next system:
=B2+C2
This system merely provides the period (in days) to the beginning date. In case your period is in weeks or months, you may want to regulate the system accordingly:
-
Weeks:
=B2+C2*7 -
Months: That is extra advanced as months have various lengths. You’d seemingly use a extra subtle method involving the
EDATEperform:=EDATE(B2,C2)
Method 2: Creating the Gantt Chart Bars (Easy Method)
The visible illustration of the Gantt chart depends on creating bars representing the duty period. A easy method makes use of stacked bars. We’ll want a helper column (for instance column E) to signify the size of the bar in days. That is merely the period:
=C2
Now, we will use a bar chart. Choose the columns containing the duty names (A), begin dates (B), and bar lengths (E). Insert a bar chart. You will want to regulate the chart’s horizontal axis to signify dates. This creates a fundamental Gantt chart. The bars will signify the duty period, however they will not be appropriately positioned towards the timeline.
Method 3: Exact Gantt Chart Bar Positioning (Superior Method)
The straightforward stacked bar chart would not precisely place bars towards the beginning date. For correct positioning, we want a special method. We’ll use a clustered column chart and manipulate the information.
We’d like two helper columns:
-
Begin Date Quantity: This column converts the beginning date right into a sequential quantity representing the variety of days since a selected base date. Use the
TODAY()perform as a base date or select a selected date. The system in column F can be:
=B2-TODAY() (Regulate TODAY() in case you favor a special base date)
- Finish Date Quantity: This column converts the top date into an analogous sequential quantity. The system in column G can be:
=D2-TODAY() (Regulate TODAY() persistently with the earlier system)
Now, create a clustered column chart utilizing columns A (Process Identify), F (Begin Date Quantity), and G (Finish Date Quantity). The chart will now appropriately place the bars primarily based on the beginning and finish dates. You will want to regulate the horizontal axis to signify days or perhaps weeks, probably utilizing customized axis labels to indicate dates.
Incorporating Dependencies:
Dealing with dependencies considerably will increase the complexity. One method is to make use of the NETWORKDAYS perform to calculate the variety of working days between duties. This requires a extra structured knowledge setup. You will want columns for predecessors and successors.
For instance, for instance column H comprises the predecessor activity identify. If a activity has no predecessor, depart it clean. To calculate the beginning date of a activity contemplating its dependency, you may want a extra advanced system involving VLOOKUP and NETWORKDAYS:
=IF(ISBLANK(H2),B2,VLOOKUP(H2,A:D,4,FALSE)+1)
This system checks if there is a predecessor. If not, it makes use of the unique begin date. If there’s a predecessor, it finds the top date of the predecessor utilizing VLOOKUP and provides 1 (assuming a one-day hole between duties). You will then have to recalculate the top date and bar lengths primarily based on this adjusted begin date.
Superior Strategies and Issues:
- Conditional Formatting: Spotlight duties which might be not on time or nearing completion utilizing conditional formatting primarily based on the beginning and finish dates.
- Knowledge Validation: Use knowledge validation to make sure constant date codecs and forestall incorrect knowledge entry.
- Macros (VBA): For terribly advanced Gantt charts with many dependencies and dynamic updates, VBA macros can automate chart technology and updates.
- Pivot Charts: For big initiatives, pivot charts can provide a summarized view of the Gantt chart, grouping duties by classes or phases.
- Customizing the Chart Look: Regulate chart colours, fonts, and labels to enhance readability and visible attraction.
Limitations of Excel Gantt Charts:
Whereas Excel permits for creating Gantt charts, it has limitations in comparison with devoted challenge administration software program:
- Useful resource Administration: Excel would not inherently assist useful resource allocation and administration options.
- Collaboration: Sharing and collaboratively modifying an Excel Gantt chart could be difficult in comparison with cloud-based challenge administration instruments.
- Complexity: Managing extremely advanced initiatives with quite a few dependencies and sources can change into unwieldy in Excel.
Conclusion:
Creating Gantt charts in Excel, whereas requiring a deeper understanding of formulation and probably some handbook changes, gives a robust and versatile resolution for visualizing challenge timelines. Beginning with the essential formulation and progressively incorporating extra superior methods like dependency administration and conditional formatting permits for creating more and more subtle and informative Gantt charts straight inside your Excel spreadsheet. Keep in mind to decide on the method that most accurately fits your challenge’s complexity and your individual Excel proficiency. For terribly giant or advanced initiatives, devoted challenge administration software program stays the extra strong and environment friendly resolution.





Closure
Thus, we hope this text has supplied beneficial insights into Mastering Gantt Charts in Excel: A Deep Dive into Formulation and Strategies. We thanks for taking the time to learn this text. See you in our subsequent article!