Mastering the Chart of Accounts in Sage: A Complete Information
Associated Articles: Mastering the Chart of Accounts in Sage: A Complete Information
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate by way of the intriguing subject associated to Mastering the Chart of Accounts in Sage: A Complete Information. Let’s weave fascinating data and provide contemporary views to the readers.
Desk of Content material
Mastering the Chart of Accounts in Sage: A Complete Information
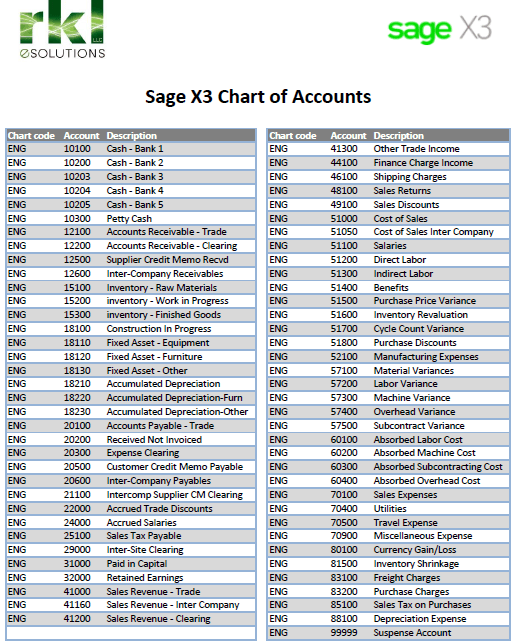
Sage accounting software program, a preferred selection for companies of all sizes, depends closely on a well-structured Chart of Accounts (COA). This basic component dictates how monetary transactions are categorized, tracked, and reported. A correctly configured COA is essential for correct monetary statements, environment friendly tax preparation, and knowledgeable enterprise decision-making. This text delves into the intricacies of the Sage Chart of Accounts, exploring its construction, greatest practices for creation and upkeep, and leverage it for optimum monetary administration.
Understanding the Chart of Accounts in Sage
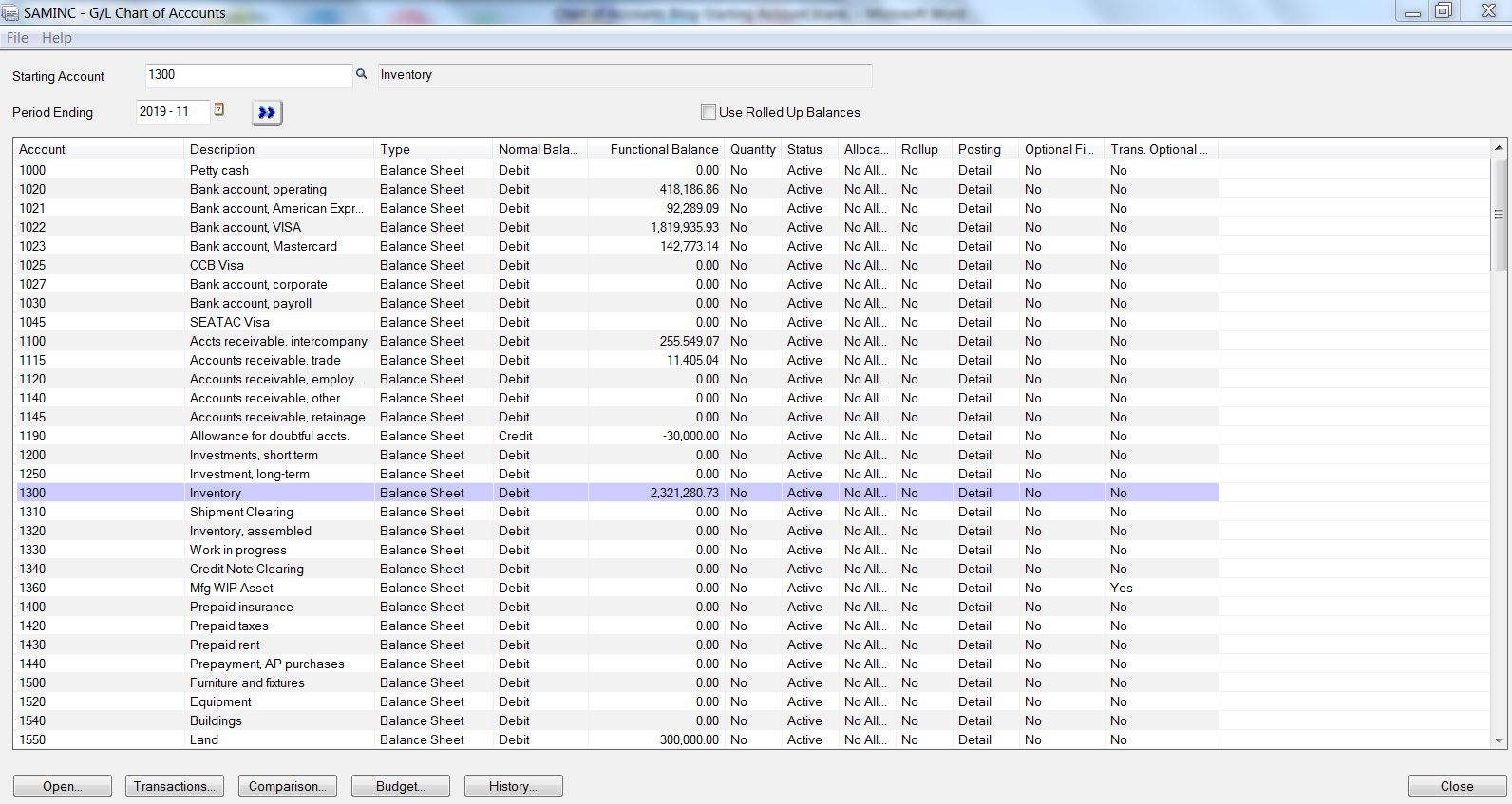
The Chart of Accounts in Sage is a hierarchical checklist of all of the accounts used to report monetary transactions. Every account represents a particular class of property, liabilities, fairness, income, or bills. This structured system permits for detailed monitoring of monetary exercise, offering a transparent image of a enterprise’s monetary well being. The COA is just not merely an inventory; it is a system of classification that facilitates correct bookkeeping and reporting.
Key Elements of a Sage Chart of Accounts:
-
Account Numbering System: Sage makes use of a numerical system to arrange accounts. This sometimes entails a hierarchical construction, utilizing a constant variety of digits for every stage. For example, a typical construction may use:
- 1000-1999: Property
- 2000-2999: Liabilities
- 3000-3999: Fairness
- 4000-4999: Income
- 5000-5999: Bills
The particular numbering system is customizable, however sustaining a logical and constant construction is important for readability and effectivity.
-
Account Names: Clear and concise account names are important. They need to precisely replicate the character of the account’s function. Keep away from ambiguous phrases and guarantee consistency in naming conventions.
-
Account Varieties: Sage categorizes accounts into differing kinds, together with property, liabilities, fairness, income, and bills. Understanding these classes is significant for correct monetary reporting. Every sort performs a definite position within the accounting equation (Property = Liabilities + Fairness).
-
Account Sub-accounts: The hierarchical nature of the COA permits for the creation of sub-accounts inside essential accounts. This supplies the next stage of element and permits for granular monitoring of particular facets of a enterprise’s funds. For instance, below the "Bills" class, you may need sub-accounts for "Lease Expense," "Salaries Expense," and "Utilities Expense."
Making a Chart of Accounts in Sage:
Organising a COA in Sage entails a number of steps:
-
Planning: Earlier than beginning, rigorously plan the construction of your COA. Take into account what you are promoting’s particular wants and the extent of element required for correct monetary reporting. Seek the advice of with an accountant if essential.
-
Selecting a Chart of Accounts Template: Sage typically supplies pre-built templates that may be tailored to what you are promoting. These templates provide a place to begin, saving effort and time. Nonetheless, customization is usually essential to replicate your particular enterprise wants.
-
Including Accounts: Manually add accounts to the COA, guaranteeing correct naming and correct categorization. Pay shut consideration to the account numbering system to take care of consistency.
-
Defining Account Varieties: Specify the kind of every account (asset, legal responsibility, and so forth.) to make sure appropriate classification in monetary experiences.
-
Organising Sub-accounts: Create sub-accounts as wanted to offer a extra detailed breakdown of monetary exercise.
-
Evaluation and Testing: Completely evaluate the finished COA to make sure accuracy and completeness. Take a look at the system by recording pattern transactions to confirm that accounts are appropriately categorised and that experiences are generated precisely.
Finest Practices for Sustaining a Sage Chart of Accounts:
-
Common Evaluation: Periodically evaluate your COA to make sure it stays related to what you are promoting’s actions. Adjustments in enterprise operations could necessitate changes to the COA.
-
Consistency: Keep consistency in naming conventions and account numbering all through the COA. This ensures accuracy and simplifies monetary reporting.
-
Documentation: Keep thorough documentation of your COA, together with account descriptions and any adjustments revamped time. That is essential for auditing functions and for onboarding new staff.
-
Account Reconciliation: Repeatedly reconcile your accounts to make sure that the stability in your accounting software program matches your financial institution statements and different monetary information. This helps determine and proper errors early on.
-
Use of Segmented Reporting: Leverage Sage’s reporting capabilities to research information primarily based on totally different segments, resembling departments, tasks, or areas. This supplies helpful insights into the efficiency of various facets of what you are promoting.
Widespread Chart of Accounts Errors and How one can Keep away from Them:
-
Inconsistent Naming Conventions: Utilizing inconsistent naming conventions can result in confusion and errors in reporting. Set up clear pointers and follow them.
-
Incorrect Account Classifications: Misclassifying accounts can distort monetary statements and result in inaccurate monetary evaluation. Be certain that every account is appropriately categorized as an asset, legal responsibility, fairness, income, or expense.
-
Lacking Accounts: Failing to incorporate essential accounts can lead to incomplete monetary reporting. Repeatedly evaluate your COA to make sure it consists of all related accounts.
-
Duplicate Accounts: Having duplicate accounts can result in double-counting and inaccurate monetary data. Keep a novel account quantity for every account.
-
Pointless Complexity: An excessively advanced COA will be tough to handle and may result in errors. Try for a stability between element and ease.
Integrating the Chart of Accounts with Different Sage Modules:
The COA is just not an remoted component inside Sage. It integrates seamlessly with different modules, resembling stock administration, payroll, and venture accounting. This integration ensures consistency throughout totally different areas of the enterprise and supplies a holistic view of monetary efficiency. For instance, gross sales transactions routinely replace the income accounts within the COA, whereas buy transactions replace the expense accounts.
Conclusion:
The Chart of Accounts in Sage is a important element of any profitable accounting system. A well-designed and maintained COA is important for correct monetary reporting, environment friendly tax preparation, and knowledgeable decision-making. By following greatest practices and understanding the intricacies of COA construction and upkeep, companies can leverage Sage’s capabilities to optimize their monetary administration and achieve helpful insights into their monetary efficiency. Keep in mind that common evaluate, constant software of guidelines, and clear documentation are key to sustaining a strong and dependable Chart of Accounts inside your Sage system. Searching for skilled recommendation from an accountant is at all times really helpful, particularly when coping with advanced enterprise constructions or particular business necessities.




:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/chart-accounts-4117638b1b6246d7847ca4f2030d4ee8.jpg)


Closure
Thus, we hope this text has offered helpful insights into Mastering the Chart of Accounts in Sage: A Complete Information. We thanks for taking the time to learn this text. See you in our subsequent article!