Mastering the Pareto Chart: A Complete Information to Figuring out and Prioritizing Key Points
Associated Articles: Mastering the Pareto Chart: A Complete Information to Figuring out and Prioritizing Key Points
Introduction
With nice pleasure, we are going to discover the intriguing matter associated to Mastering the Pareto Chart: A Complete Information to Figuring out and Prioritizing Key Points. Let’s weave fascinating info and supply contemporary views to the readers.
Desk of Content material
Mastering the Pareto Chart: A Complete Information to Figuring out and Prioritizing Key Points

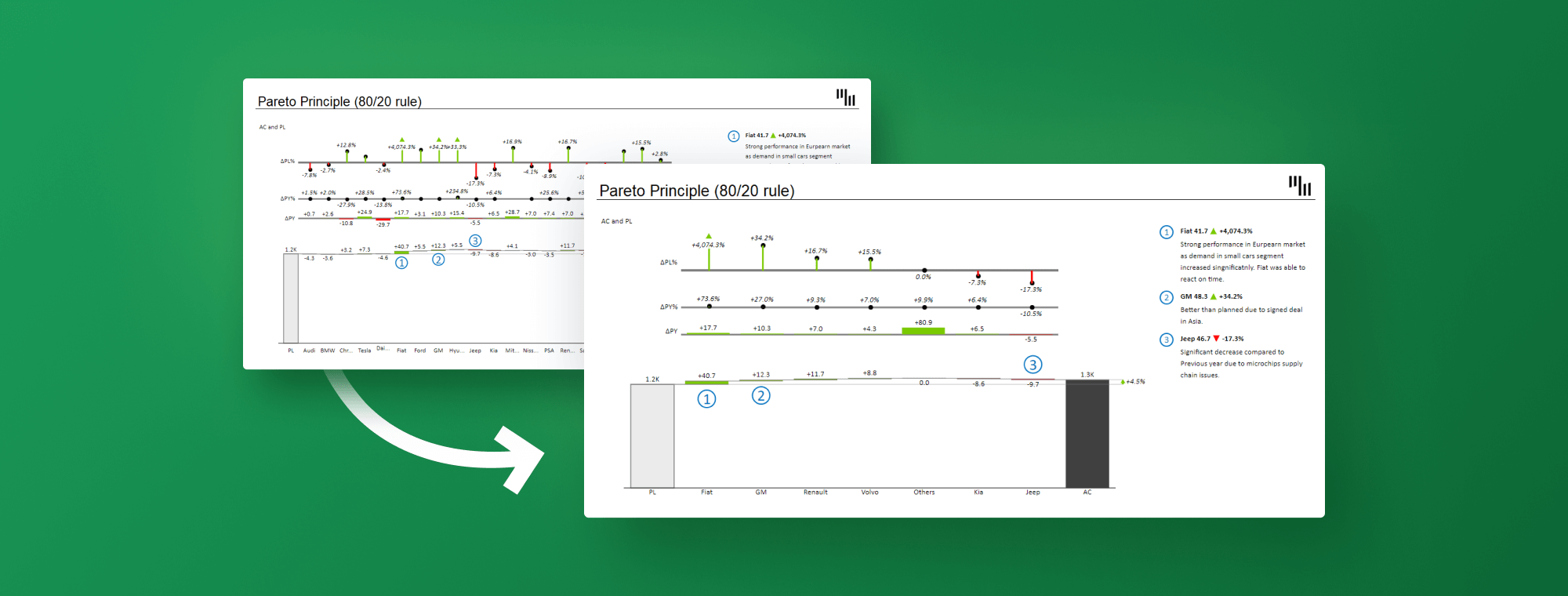
The Pareto precept, also called the 80/20 rule, means that roughly 80% of results come from 20% of causes. Whereas not a strict mathematical legislation, it is a highly effective heuristic relevant throughout numerous fields, from enterprise administration and high quality management to private productiveness and healthcare. Visualizing this precept successfully is essential for figuring out and addressing probably the most impactful points, and that is the place the Pareto chart is available in. This complete information will delve into the creation and interpretation of Pareto charts, equipping you with the abilities to leverage this worthwhile instrument for improved decision-making.
Understanding the Fundamentals: What’s a Pareto Chart?
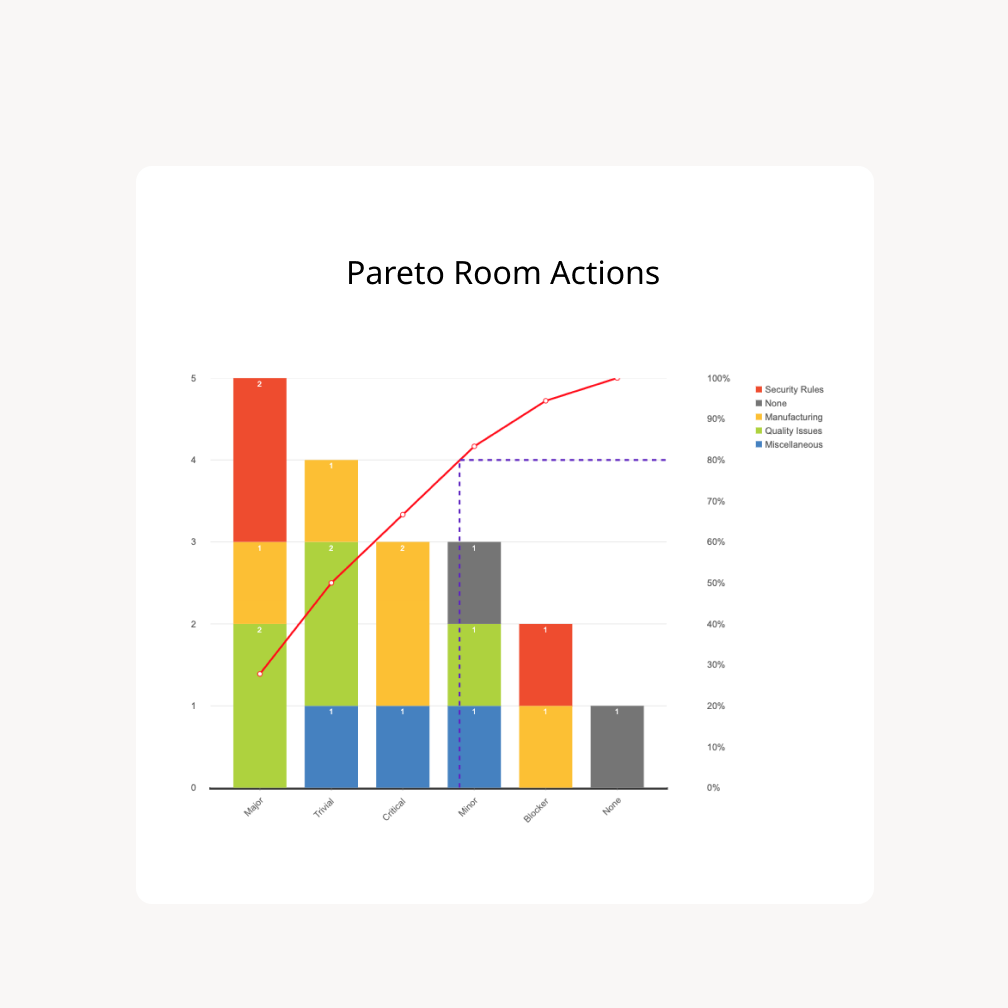
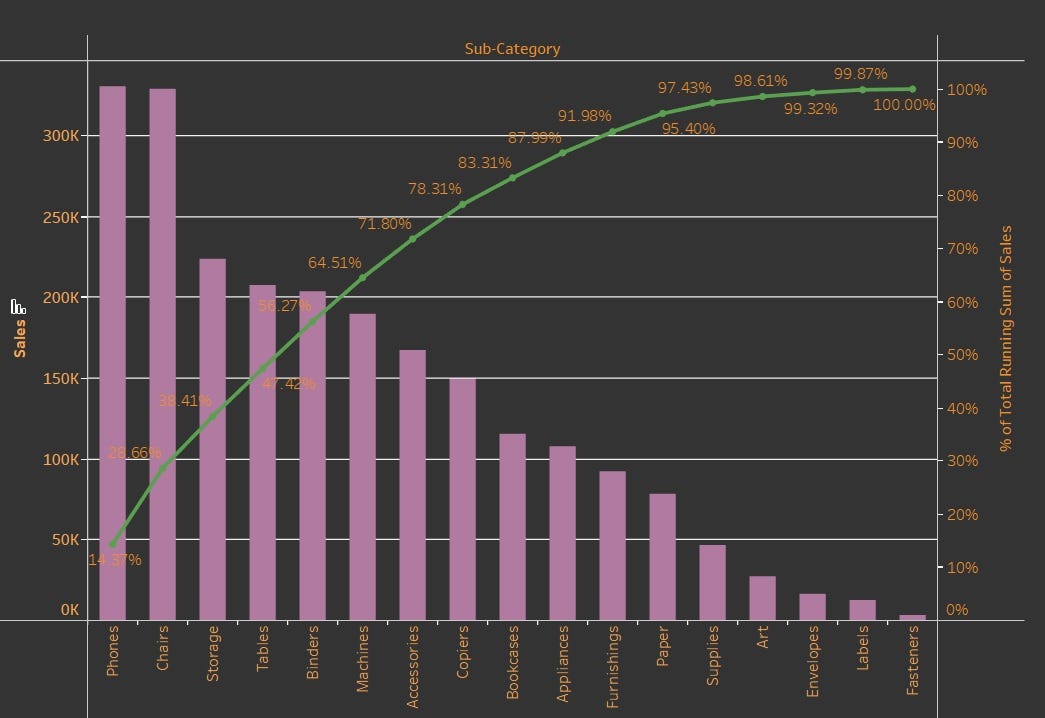
A Pareto chart is a mixed bar and line graph that visually represents the Pareto precept. It concurrently shows the frequency of various classes (represented by bars) and their cumulative contribution to the entire (represented by a line). The classes are usually organized in descending order of frequency, highlighting the "very important few" that contribute considerably to the general downside. This twin illustration permits for a fast and intuitive understanding of which components deserve probably the most consideration.
Key Elements of a Pareto Chart:
-
Horizontal Axis (X-axis): This axis lists the classes of information, normally ranked from highest frequency to lowest. These classes symbolize the potential causes or sources of an issue. For instance, in a producing context, classes may embody particular kinds of defects; in a customer support setting, they could symbolize various kinds of buyer complaints.
-
Vertical Axis (Y-axis): The left vertical axis shows the frequency or depend of every class. That is represented by the peak of the bars. The appropriate vertical axis shows the cumulative proportion of the entire. That is represented by the road graph.
-
Bar Graph: Every bar represents the frequency of a selected class. The taller the bar, the upper the frequency of that class.
-
Line Graph: This line exhibits the cumulative proportion of the entire frequency as you progress from left to proper throughout the classes. It visually emphasizes the cumulative affect of probably the most frequent classes.
Steps to Create a Pareto Chart:
Making a Pareto chart entails a number of key steps:
1. Knowledge Assortment and Categorization:
Step one is to collect related knowledge associated to the issue you are analyzing. This knowledge needs to be categorized into distinct teams or classes. The selection of classes is essential and needs to be primarily based on the precise downside you are attempting to resolve. Think about the next:
- Outline the Drawback Clearly: What particular concern are you making an attempt to handle? It will information your knowledge assortment and categorization.
- Determine Potential Causes: Brainstorm potential causes or contributing components associated to the issue.
- Set up Classes: Group related causes collectively into distinct classes. Guarantee classes are mutually unique and collectively exhaustive (which means each knowledge level suits into one and just one class).
- Knowledge Accuracy: Guarantee the information you accumulate is correct and dependable. Inconsistent or inaccurate knowledge will result in deceptive conclusions.
Instance: For instance an organization desires to research buyer complaints. They could categorize complaints as: "Product Defects," "Delivery Points," "Buyer Service," "Billing Errors," and "Different."
2. Knowledge Tabulation and Calculation:
As soon as the information is categorized, tabulate the frequency of every class. Then, calculate the proportion of every class relative to the entire variety of observations. Lastly, calculate the cumulative proportion for every class by including the proportion of the present class to the cumulative proportion of the previous classes.
Instance (Persevering with the Buyer Criticism Instance):
| Class | Frequency | Share | Cumulative Share |
|---|---|---|---|
| Product Defects | 500 | 40% | 40% |
| Delivery Points | 300 | 24% | 64% |
| Buyer Service | 200 | 16% | 80% |
| Billing Errors | 100 | 8% | 88% |
| Different | 100 | 8% | 96% |
| Complete | 1200 | 100% |
3. Chart Building:
With the information tabulated, you possibly can start establishing the Pareto chart. This may be accomplished manually utilizing graph paper or utilizing software program equivalent to Microsoft Excel, Google Sheets, or specialised statistical software program.
- Organize Classes: Checklist the classes on the horizontal axis in descending order of frequency (from highest to lowest).
- Draw Bar Graph: Draw a bar for every class, with the peak of the bar equivalent to its frequency.
- Draw Cumulative Share Line: Plot the cumulative proportion for every class on the correct vertical axis. Join these factors with a line.
- Label Axes and Chart: Clearly label each axes, together with items of measurement. Add a title to the chart that precisely displays the information being introduced.
4. Chart Interpretation and Evaluation:
The Pareto chart permits for a fast visible identification of the "very important few" classes that contribute most importantly to the issue. Focus your consideration on addressing these high-impact classes first.
- Determine the 80/20 Rule: Observe which classes contribute to the bulk (roughly 80%) of the entire frequency. These are the important thing areas to prioritize.
- Prioritize Actions: Develop methods to handle the high-impact classes first. This centered method will yield the best return in your efforts.
- Steady Enchancment: Frequently monitor and replace the Pareto chart to trace progress and establish new rising tendencies.
Software program Instruments for Creating Pareto Charts:
A number of software program instruments simplify the method of making Pareto charts:
- Microsoft Excel: Excel’s charting capabilities enable for simple creation of Pareto charts utilizing its built-in chart choices or by means of add-ins.
- Google Sheets: Much like Excel, Google Sheets gives instruments for creating Pareto charts.
- Statistical Software program (R, SPSS, Minitab): These specialised software program packages supply superior statistical evaluation and charting capabilities, together with the creation of refined Pareto charts.
- Specialised Enterprise Intelligence Instruments (Tableau, Energy BI): These instruments supply highly effective visualization capabilities, making the creation and evaluation of Pareto charts extremely environment friendly.
Functions of Pareto Charts:
Pareto charts discover functions throughout a broad spectrum of fields:
- High quality Management: Figuring out probably the most frequent kinds of defects in manufacturing processes.
- Buyer Service: Analyzing buyer complaints to pinpoint areas for enchancment.
- Venture Administration: Figuring out the essential duties that contribute most to challenge delays.
- Healthcare: Analyzing the causes of hospital readmissions or affected person falls.
- Private Productiveness: Figuring out probably the most time-consuming duties to prioritize time administration.
- Gross sales and Advertising: Figuring out the best advertising and marketing channels or product strains.
Limitations of Pareto Charts:
Whereas Pareto charts are a robust instrument, it is essential to grasp their limitations:
- Arbitrary 80/20 Rule: The 80/20 rule is a tenet, not a strict legislation. The precise proportions could fluctuate.
- Class Choice Bias: The selection of classes considerably impacts the outcomes. Cautious consideration is required.
- Ignoring Underlying Relationships: Pareto charts could not reveal the underlying relationships between totally different classes. Additional investigation is perhaps required.
- Oversimplification: Focusing solely on the "very important few" could neglect vital, albeit much less frequent, components.
Conclusion:
The Pareto chart is a worthwhile instrument for figuring out and prioritizing key points throughout numerous fields. By following the steps outlined on this information and understanding its limitations, you possibly can successfully leverage this instrument to enhance decision-making and obtain vital enhancements in effectivity and effectiveness. Keep in mind that the Pareto chart just isn’t a standalone resolution however a robust visible support that enhances different analytical strategies in driving optimistic change. By combining the visible readability of the Pareto chart with sound judgment and additional investigation, you possibly can unlock the potential for vital enhancements in your chosen subject.




Closure
Thus, we hope this text has supplied worthwhile insights into Mastering the Pareto Chart: A Complete Information to Figuring out and Prioritizing Key Points. We hope you discover this text informative and helpful. See you in our subsequent article!