Navigating the Stream: A Complete Information to High quality by Design (QbD) Flowcharts
Associated Articles: Navigating the Stream: A Complete Information to High quality by Design (QbD) Flowcharts
Introduction
On this auspicious event, we’re delighted to delve into the intriguing matter associated to Navigating the Stream: A Complete Information to High quality by Design (QbD) Flowcharts. Let’s weave attention-grabbing info and supply recent views to the readers.
Desk of Content material
Navigating the Stream: A Complete Information to High quality by Design (QbD) Flowcharts
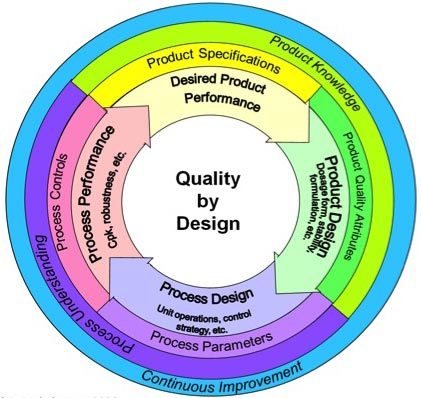
High quality by Design (QbD) is a scientific strategy to pharmaceutical improvement that goals to construct high quality right into a product from its inception, fairly than inspecting high quality into it on the finish. This proactive technique depends on a deep understanding of the product and course of, using scientific data and danger evaluation to make sure constant product high quality. Visualizing this complicated course of is essential, and flowcharts present a robust device for understanding and implementing QbD rules. This text explores varied QbD flowcharts, highlighting their key elements and demonstrating their software all through the drug improvement lifecycle.
I. The Core QbD Flowchart: A Holistic Overview
The overarching QbD course of could be represented by a central flowchart that illustrates the iterative nature of the strategy. This flowchart is not a inflexible sequence, however fairly a cyclical strategy of studying and enchancment.
(Determine 1: Core QbD Flowchart – Conceptual)
[Insert a flowchart here depicting a cyclical process with the following stages:
- Define Target Product Profile (TPP): Includes desired product attributes, performance characteristics, and quality attributes.
- Material Attributes: Characterize the raw materials and their impact on product quality.
- Process Understanding: Identify critical process parameters (CPPs) and critical quality attributes (CQAs).
- Design Space: Define the ranges of CPPs that consistently deliver the desired CQAs.
- Control Strategy: Establish methods for controlling CPPs and monitoring CQAs.
- Process Validation: Confirm that the process consistently delivers the desired product quality within the design space.
- Continuous Improvement: Monitor product and process performance, and iterate based on learnings. Feedback loops to earlier stages are crucial.]
Clarification of Levels:
-
Outline Goal Product Profile (TPP): This preliminary stage units the muse for the complete QbD course of. The TPP clearly defines the specified traits of the ultimate product, together with its meant use, efficacy, security, and high quality attributes. This kinds the benchmark in opposition to which all subsequent improvement efforts are measured.
-
Materials Attributes: A radical understanding of uncooked supplies is essential. This stage entails characterizing the properties of all uncooked supplies and their potential influence on the ultimate product’s high quality. This consists of identification of potential impurities, variability, and their affect on CQAs.
-
Course of Understanding: That is arguably probably the most essential stage. It entails conducting experiments (e.g., Design of Experiments – DOE) to know the connection between course of parameters (inputs) and product attributes (outputs). This identifies the CPPs that considerably affect the CQAs.
-
Design House: The design area is a multidimensional area, outlined by the ranges of CPPs, inside which constant product high quality is assured. It is not merely a set of optimum circumstances, however fairly a spread of acceptable circumstances that reliably ship the specified CQAs. This gives flexibility and robustness to the manufacturing course of.
-
Management Technique: This stage outlines the strategies for controlling the CPPs and monitoring the CQAs throughout manufacturing. This consists of defining course of analytical know-how (PAT) instruments, in-process controls, and high quality management testing.
-
Course of Validation: Course of validation goals to display that the manufacturing course of constantly produces a product that meets the predefined high quality requirements throughout the established design area. This sometimes entails a number of batches beneath various circumstances throughout the design area.
-
Steady Enchancment: QbD isn’t a one-time effort; it is an ongoing course of. Steady monitoring of the product and course of efficiency permits for iterative enhancements and changes to the design area and management technique primarily based on real-world knowledge.
II. Detailed Flowcharts for Particular QbD Levels:
Whereas the core flowchart gives a high-level overview, extra detailed flowcharts could be created for particular person levels. For instance:
(Determine 2: Flowchart for Defining the Goal Product Profile (TPP))
[Insert a flowchart here illustrating the steps involved in defining the TPP. This could include:
- Identify Intended Use: Define the therapeutic indication and target patient population.
- Define Efficacy Parameters: Specify the desired clinical outcomes and efficacy endpoints.
- Define Safety Parameters: Identify potential risks and define acceptable safety limits.
- Define Quality Attributes: Specify the critical quality attributes (CQAs) that must be controlled to ensure product quality and consistency.
- Develop Specifications: Set acceptable limits for the CQAs.]
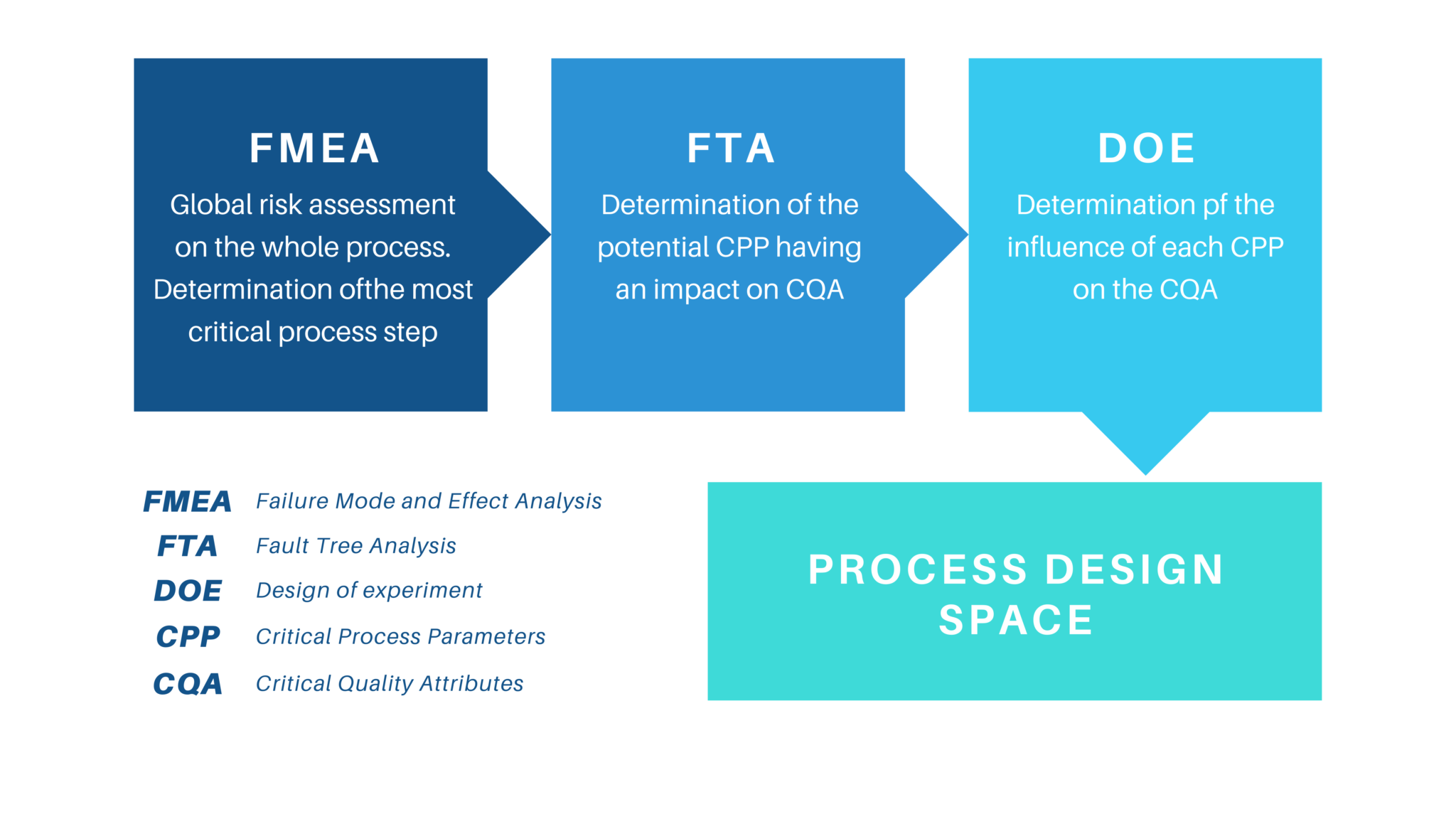
(Determine 3: Flowchart for Course of Understanding utilizing Design of Experiments (DOE))
[Insert a flowchart here illustrating a DOE approach:
- Define Objectives: Clearly state the goals of the experiment.
- Select Factors (CPPs): Identify the process parameters to be investigated.
- Select Responses (CQAs): Identify the product attributes to be measured.
- Choose Experimental Design: Select an appropriate DOE design (e.g., factorial, central composite).
- Conduct Experiments: Perform the experiments according to the chosen design.
- Analyze Data: Use statistical methods to analyze the experimental data and identify significant factors.
- Model Development: Develop mathematical models to describe the relationships between CPPs and CQAs.
- Model Validation: Validate the models using independent data.]
(Determine 4: Flowchart for establishing a Management Technique)
[Insert a flowchart here depicting the steps involved:
- Identify Critical Process Parameters (CPPs): List all CPPs identified from process understanding.
- Identify Critical Quality Attributes (CQAs): List all CQAs identified from process understanding.
- Define Control Methods for CPPs: Outline methods for controlling CPPs (e.g., automated systems, real-time monitoring).
- Define Monitoring Methods for CQAs: Outline methods for monitoring CQAs (e.g., PAT tools, in-process testing).
- Establish Acceptance Criteria: Define acceptable limits for both CPPs and CQAs.
- Develop Documentation: Document the entire control strategy for future reference.]
III. Advantages of Utilizing QbD Flowcharts:
Utilizing flowcharts in QbD provides a number of important advantages:
-
Improved Communication: Flowcharts present a transparent and concise visible illustration of the QbD course of, facilitating communication and collaboration amongst totally different groups concerned in drug improvement.
-
Enhanced Understanding: Visualizing the method helps to enhance understanding of the complicated relationships between totally different levels and parameters.
-
Danger Administration: Flowcharts assist establish potential dangers and bottlenecks early within the improvement course of, permitting for proactive mitigation methods.
-
Improved Effectivity: By offering a transparent roadmap, flowcharts can streamline the event course of, decreasing time and assets.
-
Regulatory Compliance: Properly-documented QbD flowcharts assist display compliance with regulatory necessities.
-
Steady Enchancment: Flowcharts facilitate steady monitoring and enchancment of the QbD course of, main to higher product high quality and consistency.
IV. Conclusion:
High quality by Design is an important paradigm shift in pharmaceutical improvement, prioritizing proactive high quality administration over reactive inspection. Flowcharts are invaluable instruments for visualizing and managing the complexity of the QbD course of. By using a mix of high-level and detailed flowcharts, pharmaceutical firms can successfully implement QbD rules, resulting in improved product high quality, decreased danger, and enhanced regulatory compliance. The iterative nature of the method, emphasised by the cyclical flowcharts, underscores the continual studying and enchancment which might be central to a profitable QbD implementation. The detailed flowcharts for particular levels additional improve the understanding and sensible software of QbD rules, making it a sturdy and efficient framework for drug improvement and manufacturing.







Closure
Thus, we hope this text has supplied precious insights into Navigating the Stream: A Complete Information to High quality by Design (QbD) Flowcharts. We thanks for taking the time to learn this text. See you in our subsequent article!