NP Chart Instance Issues with Options: Mastering Nonconformity Management
Associated Articles: NP Chart Instance Issues with Options: Mastering Nonconformity Management
Introduction
With nice pleasure, we’ll discover the intriguing matter associated to NP Chart Instance Issues with Options: Mastering Nonconformity Management. Let’s weave attention-grabbing info and supply contemporary views to the readers.
Desk of Content material
NP Chart Instance Issues with Options: Mastering Nonconformity Management

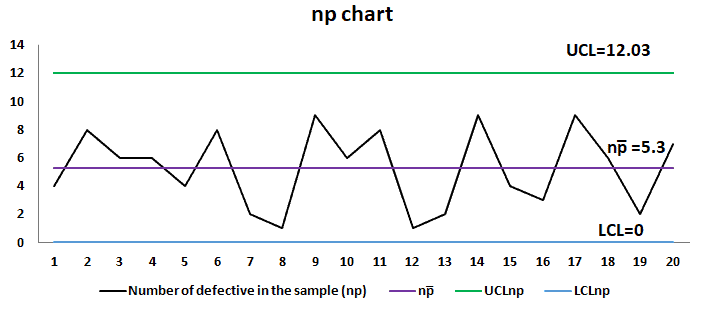
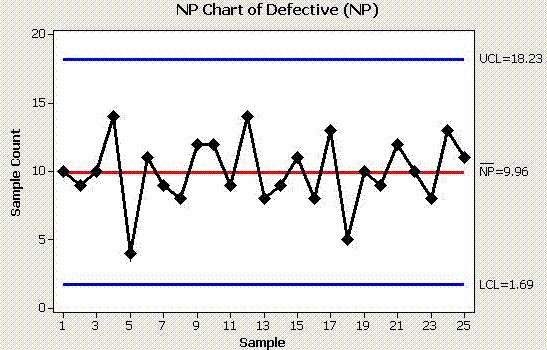
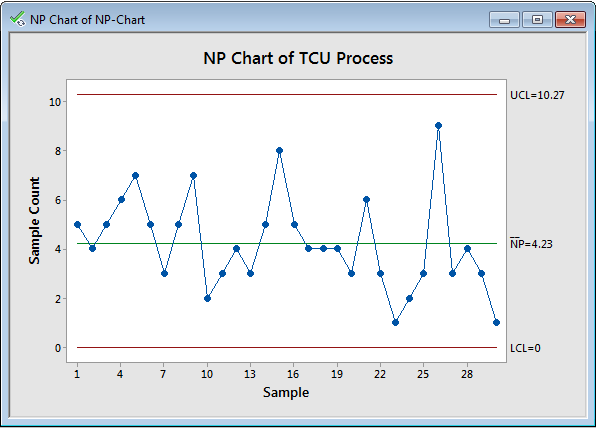
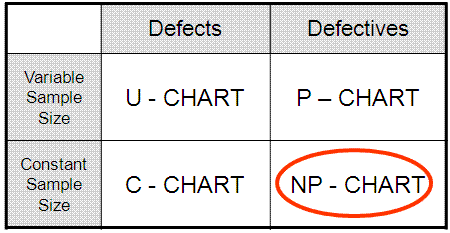
The np chart, a robust statistical course of management (SPC) instrument, is used to observe the variety of nonconforming models in a pattern of fixed measurement. Understanding the best way to assemble and interpret an np chart is essential for sustaining constant product high quality and figuring out potential course of shifts. This text will delve into a number of instance issues, offering detailed options and explanations to solidify your understanding of np chart software.
Understanding the Fundamentals of np Charts
Earlier than tackling the examples, let’s briefly assessment the important thing elements of an np chart:
- n: The fixed pattern measurement. That is the variety of models examined in every pattern.
- p̂ (p-hat): The pattern proportion of nonconforming models. That is calculated because the variety of nonconforming models (np) divided by the pattern measurement (n). p̂ = np/n
- p̄ (p-bar): The typical proportion of nonconforming models over all samples. That is the central line of the np chart.
- Management Limits: These are the higher management restrict (UCL) and decrease management restrict (LCL) that outline the appropriate vary of variation within the variety of nonconforming models. Factors falling exterior these limits recommend a possible course of shift.
The formulation for calculating the management limits are:
- UCL = n p̄ + 3 √(n p̄ (1 – p̄))
- LCL = n p̄ – 3 √(n p̄ (1 – p̄))
Nevertheless, if the calculated LCL is unfavourable, it is conventionally set to 0, as you can not have a unfavourable variety of nonconforming models.
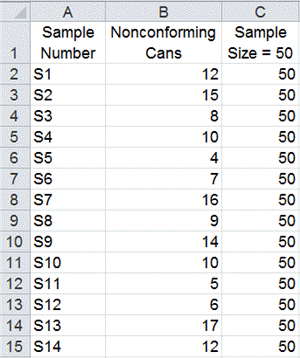
Instance Downside 1: Manufacturing Bolts
A producer produces bolts in batches of 100 (n=100). Twenty samples are taken, and the variety of faulty bolts in every pattern is recorded: 2, 3, 1, 0, 2, 4, 3, 2, 1, 0, 2, 3, 1, 2, 4, 3, 2, 1, 0, 3. Assemble an np chart and analyze the outcomes.
Answer:
-
Calculate p̄: Sum the variety of faulty bolts (2+3+1+…+3 = 36) and divide by the entire variety of bolts inspected (20 samples * 100 bolts/pattern = 2000 bolts). p̄ = 36/2000 = 0.018
-
Calculate the management limits:
- UCL = 100 0.018 + 3 √(100 0.018 (1 – 0.018)) ≈ 8.26
- LCL = 100 0.018 – 3 √(100 0.018 (1 – 0.018)) ≈ -2.26 (Set to 0)
-
Assemble the np chart: Plot the variety of faulty bolts for every pattern towards the pattern quantity. Draw the central line at n*p̄ = 1.8 and the UCL at 8.26 and LCL at 0.
-
Evaluation: Study the chart for any factors exterior the management limits or patterns indicating a course of shift. On this instance, all factors fall inside the management limits, suggesting the method is steady and below management.
Instance Downside 2: Packaging Defects
An organization packages cookies in packing containers of fifty (n=50). They take 25 samples and discover the next variety of faulty packages: 3, 2, 1, 0, 2, 3, 4, 2, 1, 0, 2, 3, 1, 2, 4, 3, 2, 1, 0, 2, 3, 1, 2, 0, 1. Assemble an np chart and interpret the outcomes.
Answer:
Observe the identical steps as in Instance 1:
-
Calculate p̄: Sum of defects = 41; Complete inspected = 1250; p̄ = 41/1250 = 0.0328
-
Calculate management limits:
- UCL = 50 0.0328 + 3 √(50 0.0328 (1 – 0.0328)) ≈ 7.23
- LCL = 50 0.0328 – 3 √(50 0.0328 (1 – 0.0328)) ≈ -0.67 (Set to 0)
-
Assemble the np chart: Plot the information and draw the central line at n*p̄ = 1.64 and the UCL and LCL.
-
Evaluation: Analyze the chart for out-of-control factors or patterns. If any factors fall exterior the management limits, examine the causes of the elevated defects.
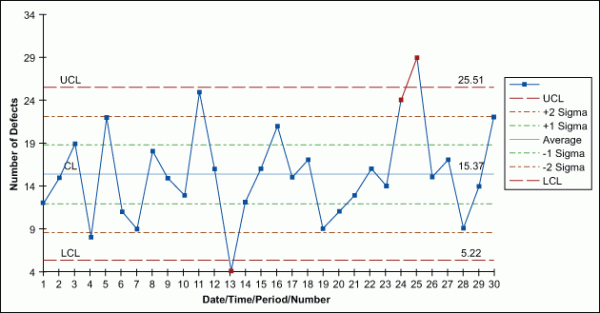
Instance Downside 3: Figuring out a Course of Shift
Let’s modify Instance 2. Suppose pattern 15 exhibits 10 faulty packages. How does this have an effect on the chart and interpretation?
Answer:
-
Recalculate p̄: The sum of defects now contains the extra 10, leading to a brand new sum of 51. p̄ = 51/1250 = 0.0408
-
Recalculate management limits: The brand new management limits will shift barely upwards.
- UCL ≈ 8.04
- LCL ≈ 0
-
Assemble the up to date np chart: Plot the information, together with the outlier at pattern 15.
-
Evaluation: The purpose at pattern 15 is now considerably above the UCL. This means a possible course of shift. An investigation must be launched to determine the basis explanation for the elevated variety of defects in that pattern. Doable causes could possibly be a machine malfunction, a change in uncooked supplies, or operator error. Additional investigation would possibly contain inspecting the particular circumstances surrounding pattern 15.
Instance Downside 4: Small Pattern Sizes and the Downside of Zero Defects
An organization inspects 10 objects (n=10) in every pattern. Over 20 samples, they document the next variety of defects: 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0. Assemble an np chart.
Answer:
-
Calculate p̄: The sum of defects is 3; Complete inspected is 200; p̄ = 3/200 = 0.015
-
Calculate management limits:
- UCL = 10 0.015 + 3 √(10 0.015 (1 – 0.015)) ≈ 1.89
- LCL = 10 0.015 – 3 √(10 0.015 (1 – 0.015)) ≈ -1.49 (Set to 0)
-
Assemble the np chart: Notice the excessive frequency of zero defects.
-
Evaluation: With small pattern sizes and a low defect price, the LCL would possibly incessantly be zero. This does not essentially point out an issue, nevertheless it highlights the constraints of the np chart in such eventualities. Think about growing the pattern measurement to acquire extra significant management limits.
Conclusion
The np chart is a helpful instrument for monitoring the variety of nonconforming models in a course of. By rigorously setting up and deciphering the chart, producers can determine potential course of shifts and take corrective motion to take care of constant product high quality. Nevertheless, it is essential to grasp the constraints of the np chart, notably when coping with small pattern sizes or extraordinarily low defect charges. In such instances, different management charts or changes to the sampling technique could also be vital. Do not forget that the np chart is best when used along with thorough course of understanding and root trigger evaluation.


Closure
Thus, we hope this text has offered helpful insights into NP Chart Instance Issues with Options: Mastering Nonconformity Management. We recognize your consideration to our article. See you in our subsequent article!