ser chart and estar chart
Associated Articles: ser chart and estar chart
Introduction
On this auspicious event, we’re delighted to delve into the intriguing subject associated to ser chart and estar chart. Let’s weave attention-grabbing info and provide recent views to the readers.
Desk of Content material
Ser vs. Estar: Unraveling the Nuances of Spanish Verbs of Being

Spanish, like many languages, possesses a number of verbs that translate to "to be" in English. This seemingly easy distinction results in important complexities for learners. The 2 commonest verbs, ser and estar, are incessantly the supply of a lot confusion. Whereas each categorical a state of being, they differ considerably of their utilization, conveying completely different features of existence and referring to distinct grammatical ideas. Mastering the excellence between ser and estar is essential for attaining fluency and accuracy in Spanish. This text will delve deep into the nuances of those two verbs, offering a complete information with examples to light up their utilization.
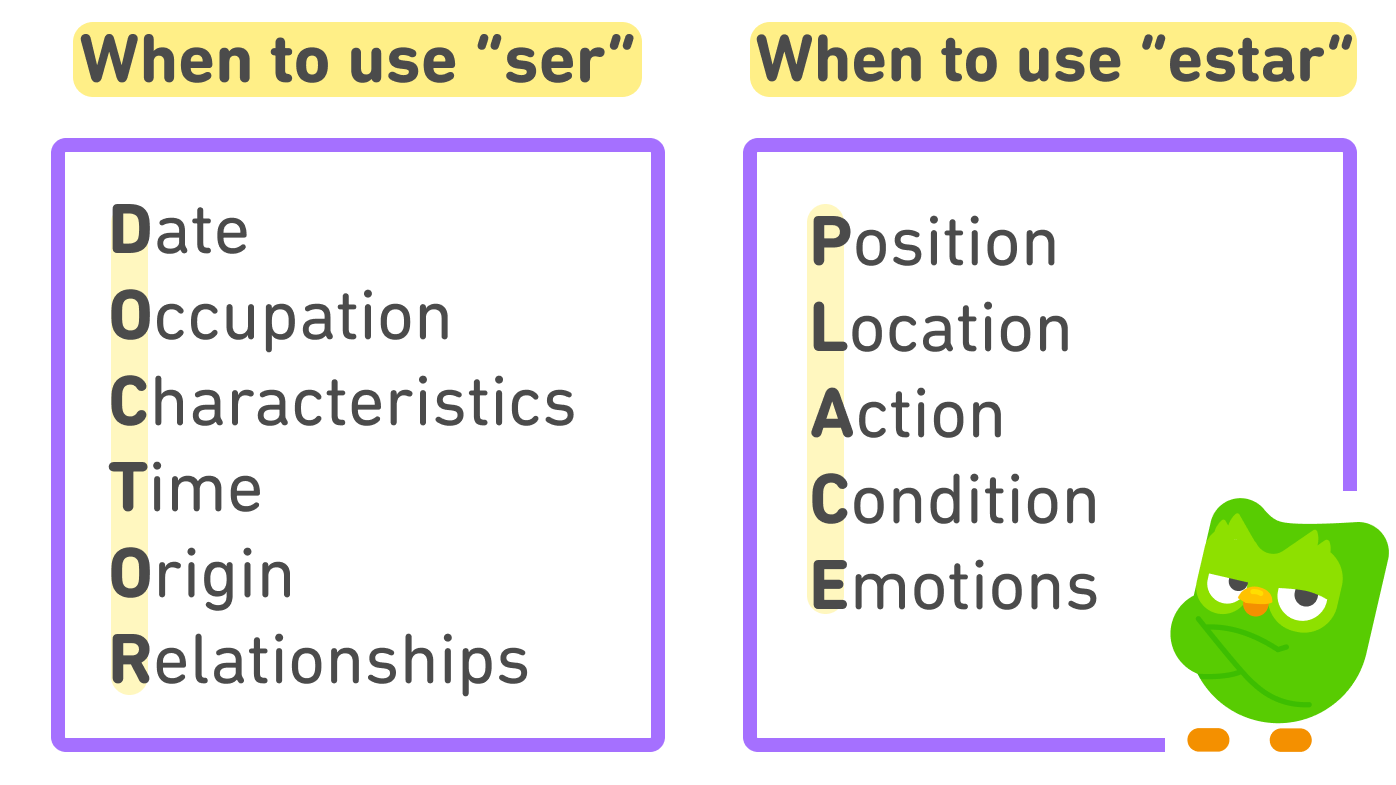
Ser: The Verb of Essence and Inherent Qualities
Ser describes inherent qualities, everlasting traits, identification, origin, composition, and time or date. Consider it because the verb defining what one thing is at its core. Its implications are typically unchanging and everlasting, or not less than long-lasting.
Key Makes use of of Ser:
-
Identification and Origin: That is maybe probably the most easy use of ser. It describes who or what one thing is.
- Instance: Yo soy médico. (I am a physician.) – This describes a occupation, a defining attribute of the speaker.
- Instance: Ella es de México. (She is from Mexico.) – This means her origin, a everlasting facet of her identification.
- Instance: Mi casa es grande. (My home is large.) – Whereas a home might be altered, its inherent dimension is described by ser.
-
Traits and Qualities: Ser describes inherent and lasting traits.
- Instance: Él es alto y delgado. (He is tall and skinny.) – These are bodily traits, comparatively everlasting options.
- Instance: El agua es incolora. (Water is colorless.) – This describes an intrinsic property of water.
- Instance: Ella es inteligente. (She is clever.) – Intelligence is taken into account a comparatively steady private attribute.
-
Possession (with de): Whereas not as frequent as different makes use of, ser can categorical possession when used with the preposition de.
- Instance: Este libro es de Juan. (This e-book is Juan’s.) – This means possession. Be aware that estar isn’t used on this context.
-
Time and Date: Ser signifies the time or date.
- Instance: Son las tres de la tarde. (It is three o’clock within the afternoon.)
- Instance: Hoy es lunes. (As we speak is Monday.)
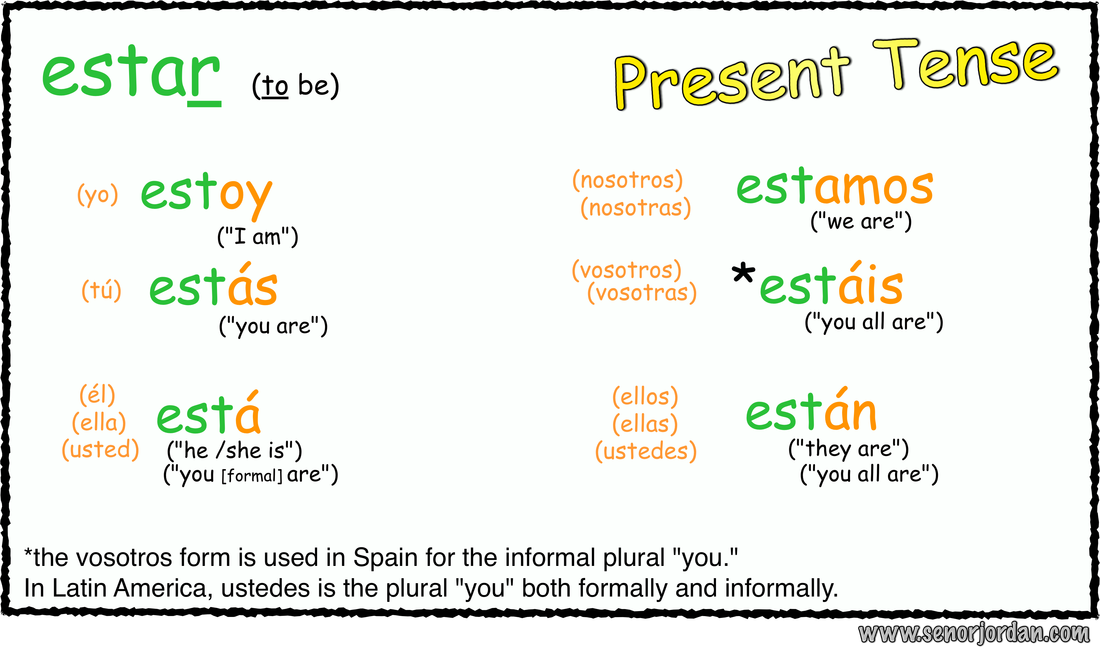
Estar: The Verb of Location, Situation, and Short-term States
Estar describes momentary states, location, circumstances, and feelings. It signifies how one thing is at a specific second. Its implications are sometimes fleeting or topic to alter.
Key Makes use of of Estar:
-
Location: Estar specifies the situation of one thing.
- Instance: El libro está en la mesa. (The e-book is on the desk.) – This describes the e-book’s momentary place.
- Instance: Estamos en España. (We are in Spain.) – This describes a brief location.
-
Situation: Estar describes the situation or state of one thing.
- Instance: Estoy cansado. (I am drained.) – This describes a brief state.
- Instance: La puerta está abierta. (The door is open.) – This describes a present situation, which might change.
- Instance: La comida está fría. (The meals is chilly.) – This describes a present situation, topic to alter (it could possibly be warmed).
-
Feelings and Emotions: Estar expresses feelings and emotions, that are inherently momentary.
- Instance: Estoy feliz. (I am completely satisfied.) – Happiness is a sense that fluctuates.
- Instance: Está triste. (He/She is unhappy.) – Disappointment is a brief emotional state.
-
Progressive Tense (with the gerund): Estar is used to type the progressive tenses in Spanish (e.g., estar + gerund).
- Instance: Estoy comiendo. (I am consuming.)
- Instance: Están hablando. (They are speaking.)
Widespread Pitfalls and Additional Nuances:
The excellence between ser and estar might be refined and difficult, particularly for newcomers. Listed here are some frequent pitfalls and additional nuances to think about:
-
"To be" + adjective: The selection between ser and estar with adjectives relies upon closely on whether or not the adjective describes an inherent high quality (ser) or a brief state (estar). For instance: Ella es bonita (She is gorgeous – inherent high quality) vs. Ella está bonita hoy (She is fairly in the present day – momentary state).
-
Ser and estar with loco/a (loopy): Loco/a can be utilized with each verbs. Ser loco/a implies a everlasting state of insanity, whereas estar loco/a signifies momentary craziness or eccentricity.
-
Regional Variations: Whereas the overall guidelines outlined above maintain true, refined regional variations in utilization might exist.
-
Figurative Language: The excellence might be blurred in figurative language. For instance, Estoy loca por ti (I am loopy about you) makes use of estar to precise intense feeling, not literal insanity.
Sensible Workout routines for Mastering Ser and Estar
The easiest way to grasp the distinction between ser and estar is thru constant observe. Listed here are some workouts:
-
Sentence Completion: Fill within the blanks with both ser or estar:
- El gato __ en el sofá. (The cat is on the couch.)
- Mi amigo __ physician. (My pal is a physician.)
- Yo __ muy feliz. (I’m very completely satisfied.)
- La película __ aburrida. (The film is boring.)
- Hoy __ viernes. (As we speak is Friday.)
-
Sentence Transformation: Rewrite sentences utilizing the alternative verb:
- Ella está cansada. (She is drained.) Rewrite utilizing ser.
- El libro es interesante. (The e-book is attention-grabbing.) Rewrite utilizing estar.
-
Contextual Utilization: Analyze sentences in context and decide the suitable verb: Learn brief tales or information articles and determine situations of ser and estar, paying shut consideration to the context to know the supposed that means.
-
Immersion: The best option to study is thru immersion. Have interaction with native Spanish audio system, watch Spanish-language media, and actively observe talking and writing.
Conclusion:
The excellence between ser and estar represents a big hurdle for a lot of Spanish learners. Nevertheless, by understanding the core ideas of inherent qualities versus momentary states, and by diligently working towards, one can overcome this problem and obtain a higher degree of fluency and accuracy. Do not forget that constant observe, contextual understanding, and immersion are key to mastering this significant facet of Spanish grammar. By diligently working by way of the examples and workouts supplied, learners can construct a powerful basis for utilizing ser and estar accurately and confidently. The reward for mastering this difficult however rewarding facet of Spanish is a big step in direction of true fluency.






Closure
Thus, we hope this text has supplied helpful insights into ser chart and estar chart. We hope you discover this text informative and helpful. See you in our subsequent article!