The Artwork and Science of Bar Chart Shade Palettes: Selecting Colours for Efficient Knowledge Visualization
Associated Articles: The Artwork and Science of Bar Chart Shade Palettes: Selecting Colours for Efficient Knowledge Visualization
Introduction
With nice pleasure, we are going to discover the intriguing matter associated to The Artwork and Science of Bar Chart Shade Palettes: Selecting Colours for Efficient Knowledge Visualization. Let’s weave fascinating info and supply recent views to the readers.
Desk of Content material
The Artwork and Science of Bar Chart Shade Palettes: Selecting Colours for Efficient Knowledge Visualization

Bar charts, a cornerstone of information visualization, supply an easy strategy to examine completely different classes or teams. Nevertheless, the effectiveness of a bar chart hinges not solely on the info itself but in addition on the cautious number of its colour palette. A poorly chosen palette can obscure essential info, mislead the viewers, and detract from the general impression of the visualization. Conversely, a well-chosen palette can improve readability, spotlight key developments, and create a visually interesting and memorable chart. This text delves into the artwork and science of choosing efficient colour palettes for bar charts, exploring varied concerns, finest practices, and instruments that can assist you create compelling visualizations.
Understanding the Function of Shade in Bar Charts:
Shade in bar charts serves a number of essential functions:
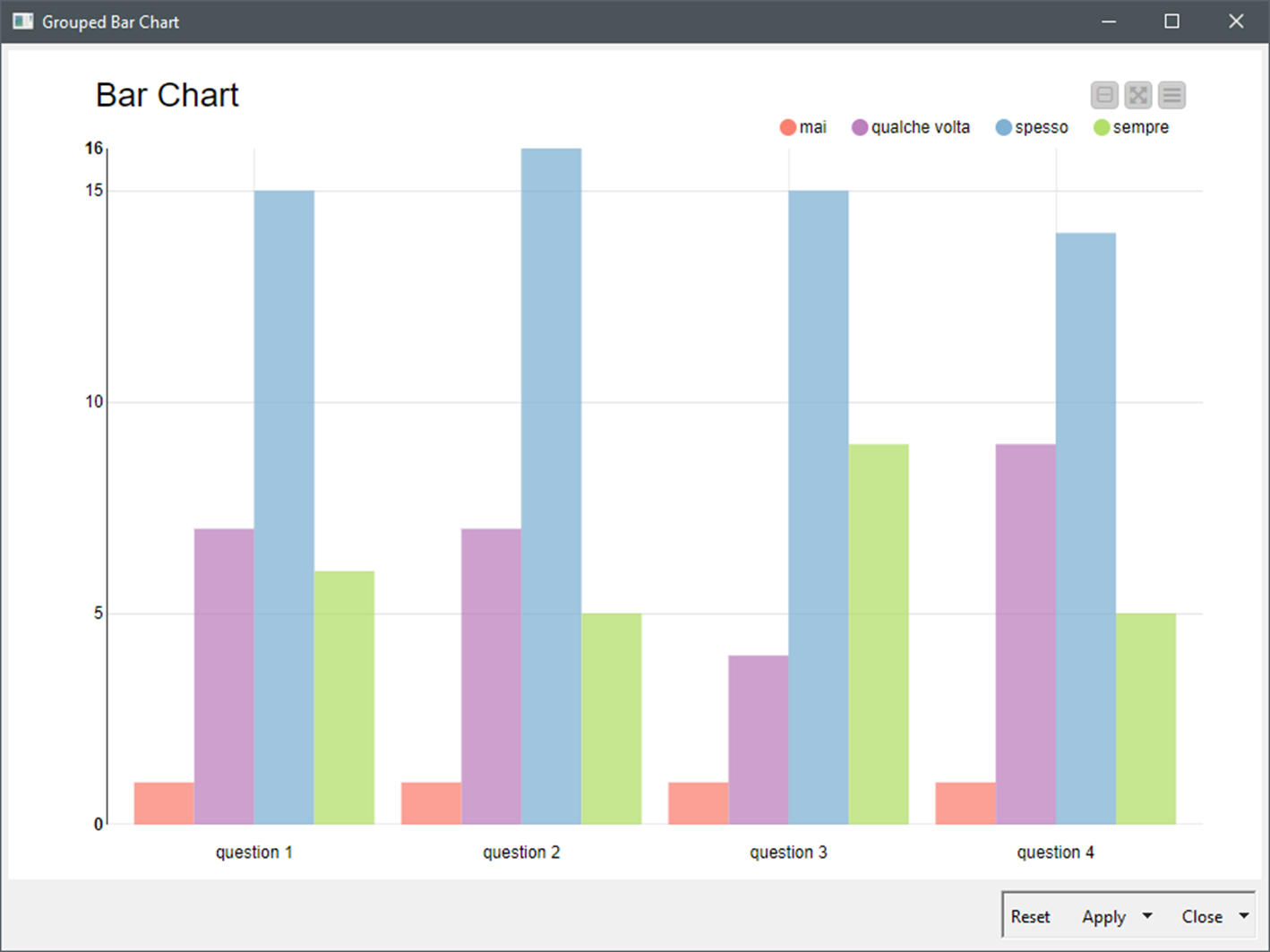
- Categorical Distinction: The first operate is to visually differentiate between completely different classes. Every class needs to be assigned a singular colour to keep away from confusion and guarantee simple comparability.
- Emphasis and Hierarchy: Shade can be utilized to focus on particular classes or draw consideration to explicit developments. Brighter or extra saturated colours can be utilized to emphasise key information factors.
- Visible Attraction and Branding: A well-chosen palette enhances the general aesthetic enchantment of the chart, making it extra partaking and memorable. Constant use of brand name colours can reinforce model identification.
- Accessibility and Inclusivity: Shade selections should contemplate accessibility for people with colour imaginative and prescient deficiencies, guaranteeing the chart stays comprehensible to everybody.
Selecting the Proper Shade Palette: Key Concerns:
Deciding on an appropriate colour palette includes a cautious consideration of a number of elements:
- Knowledge Sort and Variety of Classes: The variety of classes immediately influences the complexity of the palette. For a couple of classes, a easy, distinct palette is enough. Nevertheless, with many classes, a extra subtle strategy, probably involving sequential or diverging palettes, is required.
- Knowledge Relationships: If the info reveals relationships between classes (e.g., optimistic vs. unfavourable values), a diverging palette, utilizing colours that symbolize opposing ends of a spectrum, can successfully spotlight these relationships.
- Goal Viewers: Take into account the viewers’s background and familiarity with colour conventions. Sure colours may carry cultural or emotional connotations that might affect interpretation.
- Context and Function: The context by which the chart can be used influences colour selections. A presentation for a proper enterprise assembly may require a extra subdued palette than a playful infographic for social media.
- Colorblindness: Roughly 8% of males and 0.5% of ladies expertise some type of colour imaginative and prescient deficiency. Due to this fact, selecting colours with enough distinction and avoiding palettes relying closely on red-green differentiation is essential for inclusivity.
Varieties of Shade Palettes for Bar Charts:
A number of varieties of colour palettes are generally used for bar charts:
- Categorical Palettes: These palettes use distinct, unrelated colours to symbolize completely different classes. The objective is to maximise visible separation and keep away from any implied relationships between classes. Examples embody palettes primarily based on contrasting hues (e.g., blue, inexperienced, yellow, pink) or utilizing a set of analogous colours with enough spacing.
- Sequential Palettes: These palettes use shades of a single colour, starting from gentle to darkish, to symbolize a steady scale or ordered information. They’re notably helpful when the info represents a development or rating.
- Diverging Palettes: These palettes use colours from two opposing ends of a spectrum (e.g., blue-red, green-red) to focus on the distinction between values round a central midpoint. They are perfect for showcasing optimistic and unfavourable deviations from a imply or zero level.
- Qualitative Palettes: These palettes emphasize the visible distinction between classes with out implying any order or relationship. They’re typically vibrant and visually interesting, however cautious consideration is required to make sure enough distinction for accessibility.
Finest Practices for Selecting Colours:
- Restrict the Variety of Colours: Utilizing too many colours can litter the chart and make it troublesome to interpret. Intention for a palette with a manageable variety of colours, sometimes not more than 7-10 for many purposes.
- Use Enough Distinction: Guarantee sufficient distinction between colours, particularly for textual content labels and background. Instruments just like the WebAIM colour distinction checker might help confirm enough distinction for accessibility.
- Take into account Colorblindness: Make use of colorblind-friendly palettes, typically generated utilizing instruments that simulate colour imaginative and prescient deficiencies. Take into account including patterns or different visible cues to additional improve accessibility.
- Preserve Consistency: Use the identical colour for a similar class all through the visualization and throughout associated charts. Consistency ensures readability and avoids confusion.
- Use Shade Strategically: Make use of colour to focus on key findings or draw consideration to particular information factors. Keep away from overusing vivid or saturated colours, as this may overwhelm the viewer.
Instruments and Sources for Selecting Shade Palettes:
A number of instruments and sources can help in choosing efficient colour palettes:
- Shade Brewer: This on-line software gives a spread of colour palettes particularly designed for information visualization, contemplating colorblindness and accessibility.
- Adobe Shade: This software permits customers to create customized colour palettes and discover varied colour harmonies.
- Coolors: A user-friendly on-line software that generates random palettes and permits for personalization and saving.
- Paletton: A complete software that permits exploration of various colour harmonies and gives detailed colour info.
- Tableau and Energy BI: These information visualization platforms supply built-in colour palettes and customization choices.
Past Shade: Enhancing Bar Chart Readability:
Whereas colour is an important aspect, different elements contribute to a bar chart’s readability:
- **Clear Labels and





Closure
Thus, we hope this text has offered useful insights into The Artwork and Science of Bar Chart Shade Palettes: Selecting Colours for Efficient Knowledge Visualization. We thanks for taking the time to learn this text. See you in our subsequent article!