The Humble Pie Chart: A Highly effective Device for Knowledge Visualization
Associated Articles: The Humble Pie Chart: A Highly effective Device for Knowledge Visualization
Introduction
With nice pleasure, we’ll discover the intriguing subject associated to The Humble Pie Chart: A Highly effective Device for Knowledge Visualization. Let’s weave attention-grabbing data and provide contemporary views to the readers.
Desk of Content material
The Humble Pie Chart: A Highly effective Device for Knowledge Visualization

The pie chart, or pie diagram, is a ubiquitous device in knowledge visualization. Its easy, round design, segmented into proportional slices representing totally different classes of an entire, makes it immediately recognizable and readily comprehensible, even to these with no robust statistical background. Regardless of its obvious simplicity, the pie chart holds a fancy historical past and possesses each strengths and weaknesses that have to be fastidiously thought of when selecting a visualization methodology. This text will delve into the historical past, building, functions, limitations, and finest practices of utilizing pie charts successfully.
A Transient Historical past:
Whereas pinpointing the precise origin of the pie chart is troublesome, its conceptual roots lie within the early improvement of statistical graphics. Early types of round diagrams representing proportions could be traced again to the seventeenth and 18th centuries, with varied varieties showing in several contexts. Nonetheless, the trendy pie chart as we acknowledge it emerged regularly all through the nineteenth and twentieth centuries, gaining prominence with the rising use of statistical strategies in varied fields. William Playfair, a major determine within the historical past of information visualization, did not straight create the pie chart, however his work in growing different chart varieties laid the groundwork for its eventual widespread adoption. The rise of computing and software program packages additional solidified the pie chart’s place within the visualization toolkit, making its creation considerably simpler and extra accessible.
Development and Interpretation:
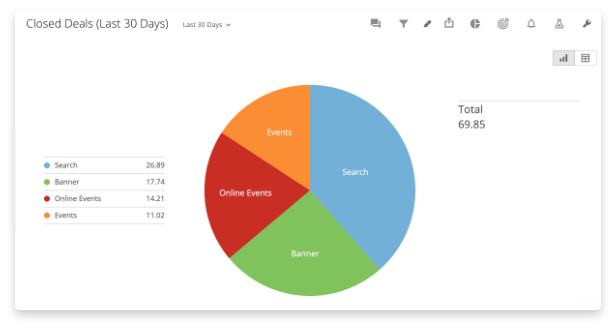
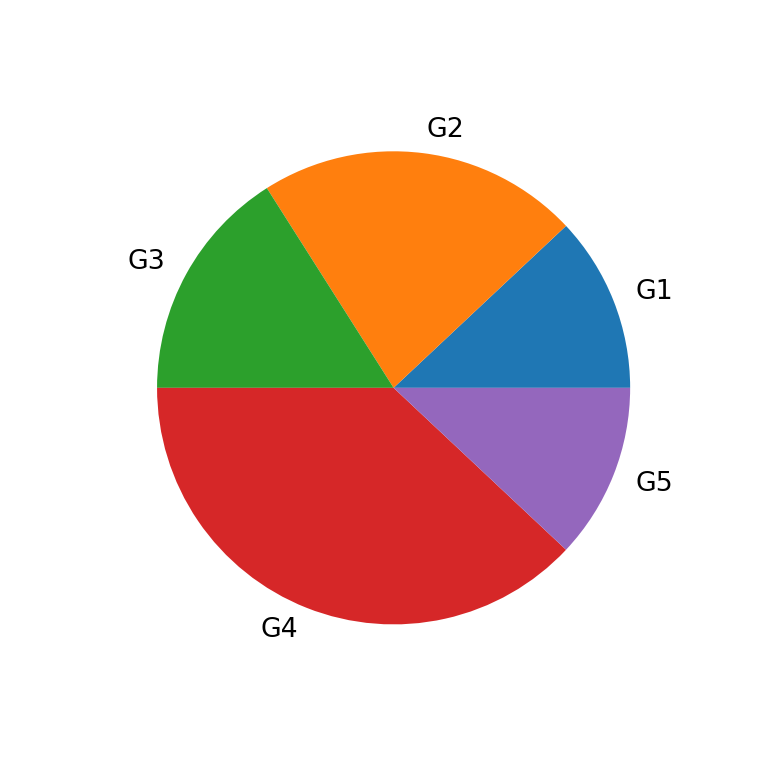
The basic precept behind a pie chart is the illustration of an entire as a circle, with every slice representing a proportion of that entire. The scale of every slice is straight proportional to the magnitude of the info it represents. For instance, if a dataset reveals that 60% of respondents want apples, the apple slice will occupy 60% of the circle’s space. This visible illustration permits for a fast and intuitive grasp of the relative sizes of various classes.
Developing a pie chart includes a number of steps:
-
Knowledge Assortment and Preparation: The method begins with amassing and organizing the related knowledge. This knowledge needs to be categorical, representing totally different classes or teams inside an entire. Numerical values related to every class characterize the magnitude of that class.
-
Calculating Proportions: The following step is to calculate the proportion of every class relative to the overall. That is usually executed by dividing the worth of every class by the sum of all classes and multiplying by 100 to specific the end result as a proportion.
-
Figuring out Angles: Every proportion is then transformed into an angle utilizing the components: Angle = (Share/100) * 360 levels. This angle determines the scale of the slice representing that class within the pie chart.
-
Creating the Chart: Utilizing specialised software program (resembling spreadsheet applications like Excel or devoted visualization instruments) and even by hand with a protractor and compass, the circle is split into slices in line with the calculated angles.
-
Labeling and Annotation: Lastly, every slice is labeled with its corresponding class and its proportion or worth. A title clearly indicating the topic of the chart is important. Including a legend can additional improve readability, particularly when coping with quite a few classes.
Purposes of Pie Charts:
Pie charts discover widespread utility throughout various fields, together with:
-
Enterprise and Finance: Illustrating market share, funds allocation, gross sales efficiency, and buyer demographics.
-
Advertising and Promoting: Presenting survey outcomes, shopper preferences, and marketing campaign effectiveness.
-
Healthcare: Exhibiting the distribution of ailments, affected person demographics, and remedy outcomes.
-
Training: Representing scholar demographics, topic distribution, and efficiency metrics.
-
Science and Analysis: Visualizing experimental outcomes, species distribution, and compositional knowledge.
Limitations and Alternate options:
Regardless of their recognition, pie charts have limitations that have to be thought of:
-
Problem Evaluating Slices: Exact comparability of various slices, particularly when their sizes are related, could be difficult. The human eye just isn’t well-suited for precisely judging small variations in space.
-
Restricted Variety of Classes: Pie charts develop into cluttered and troublesome to interpret when there are too many classes. Greater than 5-7 classes typically make a pie chart much less efficient.
-
Emphasis on Proportions, Not Absolute Values: Pie charts primarily concentrate on relative proportions. Absolute values are sometimes not simply discernible, which could be deceptive if the overall worth just isn’t clearly indicated.
-
Deceptive with Small Percentages: Very small slices could be troublesome to see and interpret, making them much less helpful for representing minor classes.
Alternate options to pie charts embody:
-
Bar charts: Glorious for evaluating classes straight, particularly when coping with a bigger variety of classes.
-
Column charts: Much like bar charts, however with vertical bars.
-
Treemaps: Efficient for representing hierarchical knowledge and displaying proportions inside nested classes.
-
Stacked bar charts: Present the composition of various classes inside a bigger entire.
Finest Practices for Creating Efficient Pie Charts:
To maximise the effectiveness of a pie chart, comply with these finest practices:
-
Restrict the Variety of Classes: Preserve the variety of classes to a manageable stage (ideally 5-7). For bigger datasets, think about various visualization methods.
-
Order Classes Logically: Prepare the slices in a logical order, resembling from largest to smallest or by a particular criterion.
-
Use Clear and Concise Labels: Label every slice clearly with its class and proportion. Keep away from overly lengthy labels.
-
Spotlight Essential Slices: Use shade or different visible cues to emphasise necessary slices.
-
Select Acceptable Colours: Choose colours which can be simple to tell apart and are visually interesting. Keep away from utilizing too many colours.
-
**Present a Clear






Closure
Thus, we hope this text has supplied beneficial insights into The Humble Pie Chart: A Highly effective Device for Knowledge Visualization. We recognize your consideration to our article. See you in our subsequent article!