The Energy of Tables and Charts: A Complete Information to Information Visualization
Associated Articles: The Energy of Tables and Charts: A Complete Information to Information Visualization
Introduction
With nice pleasure, we are going to discover the intriguing matter associated to The Energy of Tables and Charts: A Complete Information to Information Visualization. Let’s weave attention-grabbing info and supply recent views to the readers.
Desk of Content material
The Energy of Tables and Charts: A Complete Information to Information Visualization

Information, in its uncooked type, is usually overwhelming and tough to interpret. Numbers, figures, and statistics will be meaningless and not using a clear methodology of presentation. That is the place tables and charts step in, reworking complicated information into simply digestible and insightful visuals. They’re elementary instruments for information visualization, permitting us to establish developments, patterns, and anomalies shortly and successfully. This text explores the world of tables and charts, analyzing their differing kinds, purposes, and the essential issues for efficient information illustration.
Understanding the Fundamentals: Tables vs. Charts
Whereas each tables and charts serve the aim of presenting information, they differ considerably of their strategy and suitability for varied eventualities.
Tables: Tables are structured grids that current information in rows and columns. They excel at presenting exact numerical information, permitting for simple comparability of particular values. Every row sometimes represents a single commentary or information level, whereas columns characterize completely different variables or attributes. Tables are perfect for:
- Detailed information presentation: When exact values are essential and should be readily accessible.
- Information comparability: Facilitating the comparability of a number of variables throughout completely different classes.
- Information evaluation groundwork: Serving as the inspiration for extra complicated evaluation and the creation of charts.
- Presenting massive datasets with many variables: Whereas probably overwhelming visually, tables can deal with considerably extra information factors than charts.
Limitations of Tables:
- Poor visualization of developments and patterns: Figuring out developments or relationships between variables requires cautious handbook inspection.
- Overwhelming for big datasets: Massive tables will be tough to navigate and interpret, resulting in cognitive overload.
- Ineffective for speaking complicated relationships: Tables battle to successfully present correlations or causal relationships between variables.
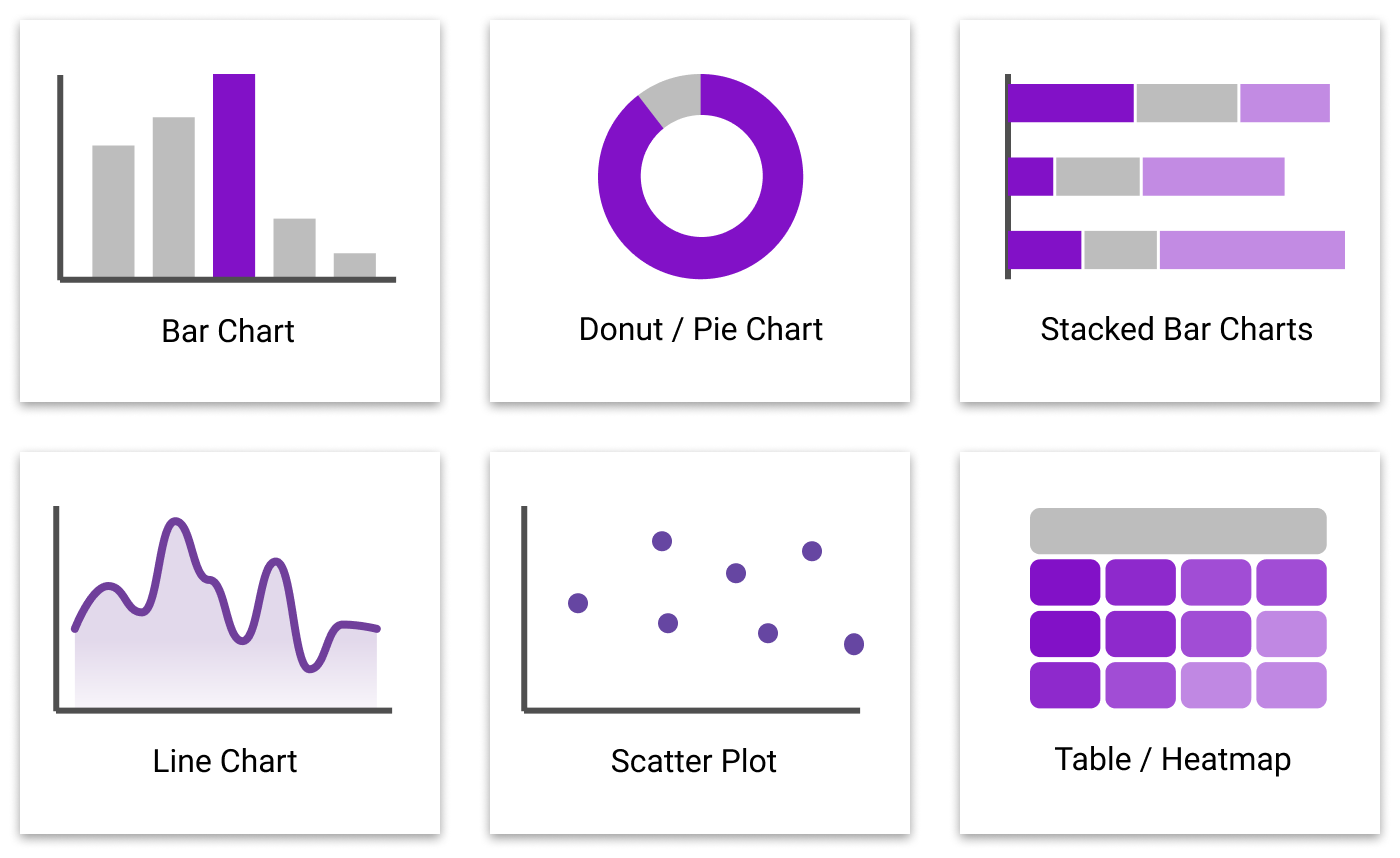
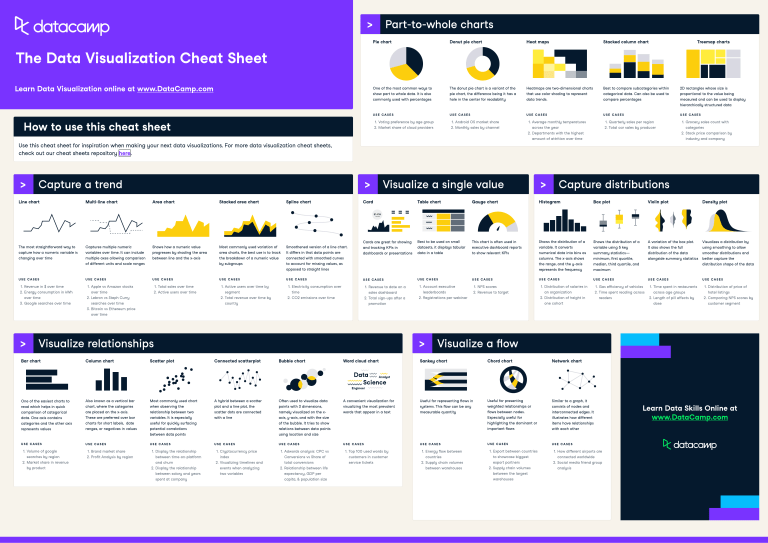
Charts: Charts are graphical representations of information, utilizing visible parts like bars, traces, or factors for instance relationships and developments. They’re superior to tables in conveying patterns and insights shortly and effectively. Totally different chart sorts are suited to completely different information sorts and analytical targets. Some frequent chart sorts embrace:
- Bar Charts: Ideally suited for evaluating categorical information throughout completely different teams. Vertical bar charts (column charts) are generally used, whereas horizontal bar charts are higher suited to longer labels.
- Line Charts: Wonderful for displaying developments and modifications over time or steady variables. A number of traces can be utilized to match completely different classes.
- Pie Charts: Helpful for displaying the proportion of various classes inside a complete. Nevertheless, they turn out to be much less efficient with many classes.
- Scatter Plots: Illustrate the connection between two steady variables, revealing correlations and potential outliers.
- Space Charts: Just like line charts, however the space below the road is crammed, emphasizing the magnitude of change over time.
- Histograms: Present the distribution of a single steady variable, illustrating frequency counts inside specified ranges.
- Field Plots: Show the distribution of information, together with median, quartiles, and outliers, making it straightforward to match distributions throughout teams.
- Heatmaps: Signify information as colours, displaying the depth or magnitude of a variable throughout a matrix.
- Geographic Maps: Visualize information geographically, displaying spatial patterns and distributions.
Selecting the Proper Chart Kind:
Deciding on the suitable chart sort is essential for efficient information visualization. Contemplate the next components:
- Kind of information: Categorical, numerical, steady, or time-series information dictate the acceptable chart sort.
- Goal of visualization: Do you wish to examine values, present developments, illustrate proportions, or reveal correlations?
- Viewers: The extent of technical experience of your viewers ought to affect the complexity of the chart.
- Information quantity: The quantity of information will have an effect on the readability and effectiveness of various chart sorts.
Greatest Practices for Creating Efficient Tables and Charts:
- Clear and concise titles: The title ought to precisely replicate the info introduced.
- Labeled axes and legends: Guarantee all axes and legends are clearly labeled and straightforward to know.
- Applicable scaling: Select scales that precisely characterize the info with out distortion.
- Constant formatting: Keep consistency in fonts, colours, and types for improved readability.
- Minimalist design: Keep away from pointless muddle and give attention to the important thing info.
- Information accuracy and integrity: Guarantee the info is correct and dependable.
- Accessibility: Contemplate accessibility for customers with disabilities, utilizing acceptable colour distinction and different textual content descriptions.
- Contextual info: Present enough context to assist the viewers perceive the info’s that means and implications.
Instruments for Creating Tables and Charts:
Quite a few software program instruments and platforms can be found for creating tables and charts, starting from easy spreadsheet packages like Microsoft Excel and Google Sheets to highly effective information visualization instruments like Tableau, Energy BI, and R with ggplot2. The selection of instrument depends upon the complexity of the info, the specified stage of customization, and the consumer’s technical expertise.
Conclusion:
Tables and charts are indispensable instruments for information evaluation and communication. By understanding their strengths and limitations, and following greatest practices for design and creation, we are able to successfully remodel uncooked information into significant insights, facilitating higher decision-making and fostering a deeper understanding of the world round us. The cautious collection of the suitable desk or chart sort, coupled with a transparent and concise presentation, ensures that the info speaks for itself, revealing hidden patterns and facilitating knowledgeable conclusions. Mastering the artwork of information visualization is essential for anybody working with information, no matter their discipline or experience. The flexibility to speak information successfully is a precious talent that empowers people and organizations to make higher selections primarily based on proof and perception.
![]()


Closure
Thus, we hope this text has offered precious insights into The Energy of Tables and Charts: A Complete Information to Information Visualization. We hope you discover this text informative and useful. See you in our subsequent article!