The Snellen Chart and Past: A Deep Dive into the World of Eye Charts
Associated Articles: The Snellen Chart and Past: A Deep Dive into the World of Eye Charts
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate by way of the intriguing matter associated to The Snellen Chart and Past: A Deep Dive into the World of Eye Charts. Let’s weave attention-grabbing info and provide contemporary views to the readers.
Desk of Content material
The Snellen Chart and Past: A Deep Dive into the World of Eye Charts

The standard eye chart, a seemingly easy assortment of letters, numbers, or symbols, holds a major place in ophthalmology and optometry. Greater than only a diagnostic instrument, it represents an enchanting intersection of historical past, science, and design, continuously evolving to satisfy the wants of a various and more and more advanced world. Whereas the identify "Snellen chart" is commonly used generically, it is just one sort amongst many, every with its personal strengths and weaknesses, contributing to a wealthy tapestry of imaginative and prescient testing methodologies. This text will discover the historical past, variations, limitations, and future of those essential devices within the evaluation of visible acuity.
The Genesis of the Snellen Chart: Hermann Snellen and the Beginning of Standardized Imaginative and prescient Testing
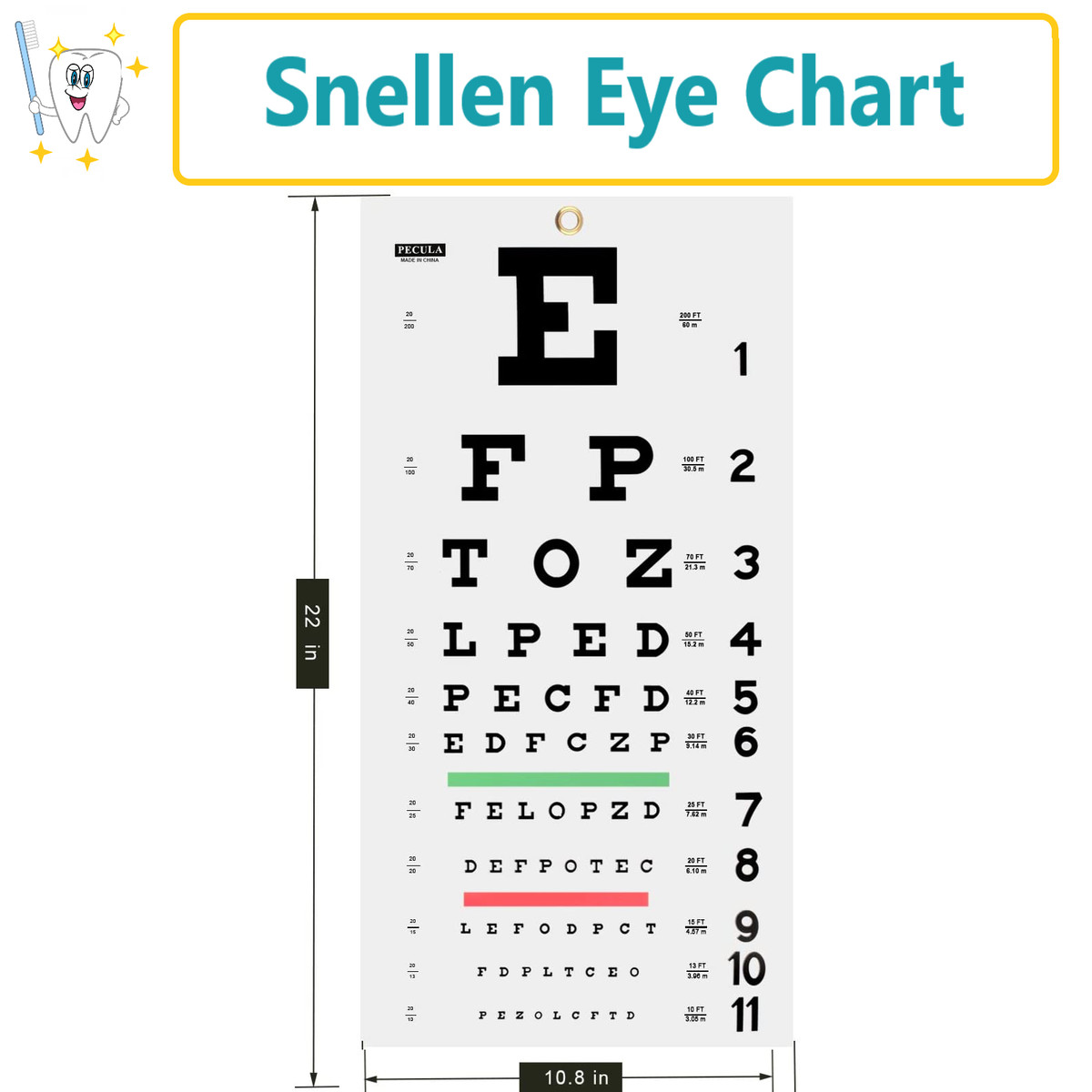
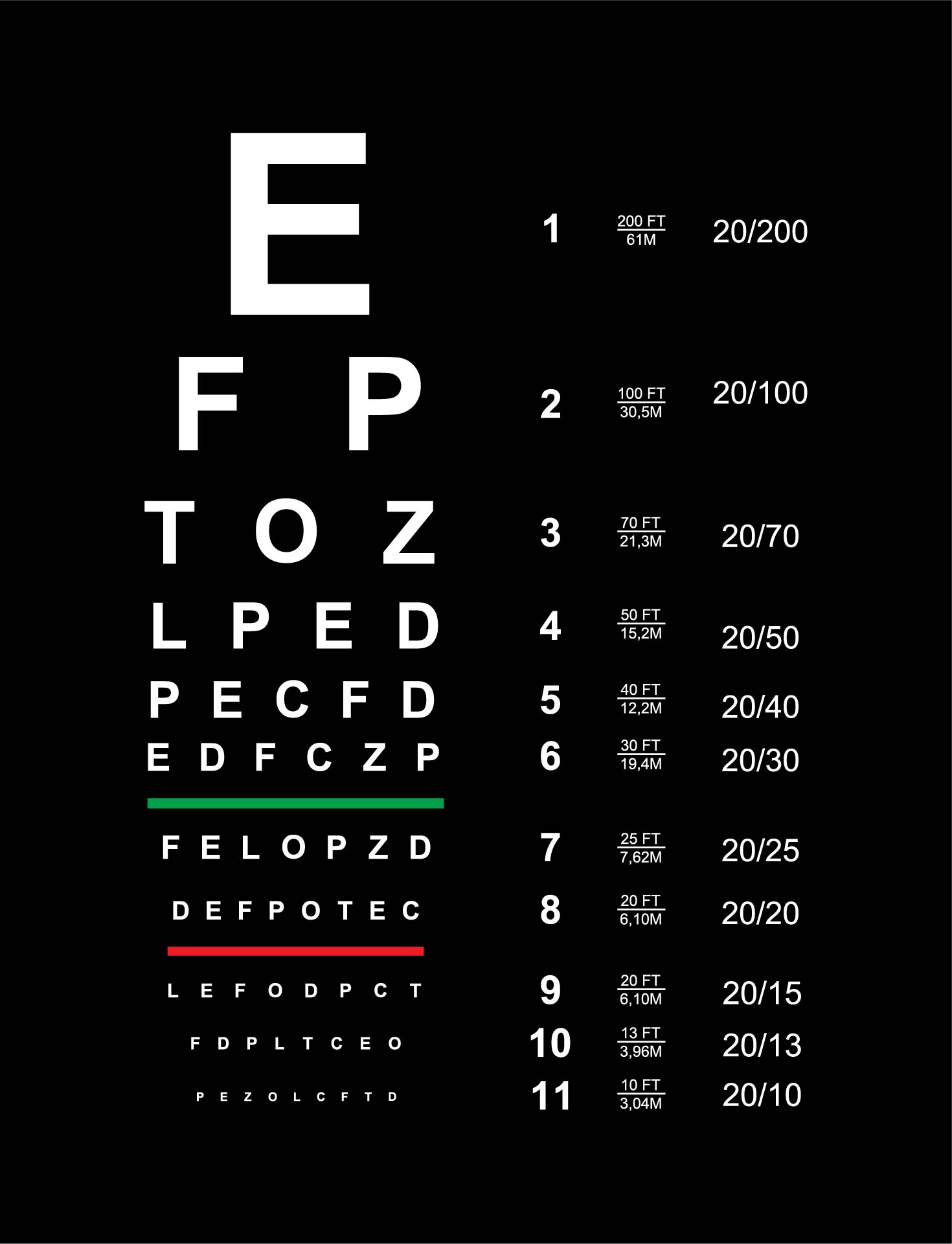
Probably the most well known eye chart is undoubtedly the Snellen chart, named after its inventor, the Dutch ophthalmologist Hermann Snellen. In 1862, Snellen launched his revolutionary chart, aiming to standardize the measurement of visible acuity. Earlier than his innovation, assessing visible means was a subjective and inconsistent course of. Snellen’s genius lay in his creation of a chart with letters of progressively reducing dimension, every designed to be discernible at a selected distance. The now-iconic chart, that includes capital letters of various sizes, relies on the precept that an individual with regular visible acuity (20/20 imaginative and prescient) ought to have the ability to learn the smallest letters from a distance of 20 ft (6 meters).
The Snellen chart’s success stems from its simplicity and reproducibility. The standardized letter sizes, primarily based on the visible angle subtended by every letter, ensured consistency throughout completely different charts and testing environments. This standardization revolutionized ophthalmology, offering a dependable and quantifiable measure of visible acuity, essential for analysis, remedy planning, and monitoring the progress of eye circumstances. Using capital letters, particularly designed with equal stroke width and spacing, minimized the affect of particular person letter recognition on the general consequence.
Past the Snellen: A Spectrum of Eye Chart Variations
Whereas the Snellen chart stays a cornerstone of imaginative and prescient testing, quite a few variations and various charts have emerged over time, every tailor-made to particular wants and populations. These variations tackle limitations of the unique Snellen chart and cater to people with various visible wants and cognitive skills.
-
LogMAR Charts: The LogMAR (Logarithm of the Minimal Angle of Decision) chart represents a major development. In contrast to the Snellen chart, which has erratically spaced letter sizes, the LogMAR chart options letters of equally spaced sizes, akin to equal steps in visible acuity. This logarithmic scale gives a extra exact and statistically strong measurement of visible acuity, significantly helpful in analysis and medical trials.
-
Bailey-Lovie Charts: Much like LogMAR charts, Bailey-Lovie charts additionally use equally spaced letter sizes, however with a special letter association designed to reduce the results of letter familiarity and recognition. That is significantly essential in assessing true visible acuity, impartial of the affected person’s prior data of the letters.
-
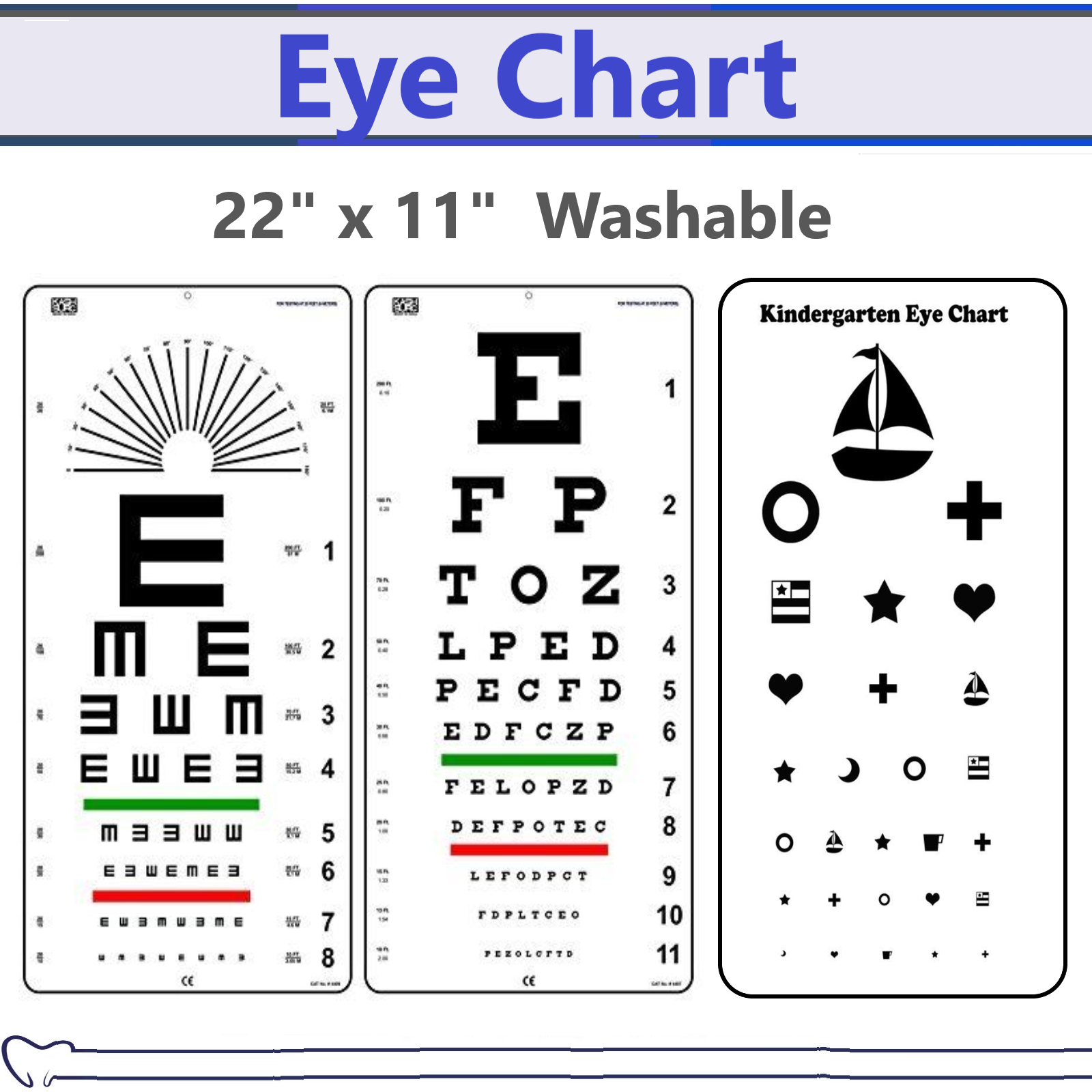
LEA Charts: These charts make the most of symbols as an alternative of letters, making them ideally suited for assessing the visible acuity of pre-literate youngsters or people with language obstacles. The symbols are designed to be equally recognizable throughout completely different cultures and languages.
-
Landolt C Charts: These charts use a "C" formed image with a break in numerous orientations. The affected person is requested to point the route of the break, eliminating the affect of letter recognition and making it appropriate for testing people who should not but literate.
-
Tumbling E Charts: These charts use the letter "E" in numerous orientations, requiring the affected person to point the route the "E" is pointing. That is one other non-verbal methodology significantly helpful for youngsters and people with communication difficulties.
-
Image Charts: These charts make the most of recognizable photos as an alternative of letters or symbols, particularly designed for younger youngsters or people with cognitive impairments. The images are chosen for his or her simplicity and familiarity.
Limitations and Issues of Eye Chart Utilization
Regardless of their widespread use and vital contribution to ophthalmology, eye charts should not with out limitations. A number of components can affect the accuracy and reliability of visible acuity measurements obtained utilizing eye charts:
-
Refractive Error: Uncorrected refractive errors (myopia, hyperopia, astigmatism) considerably have an effect on the outcomes obtained from eye charts. Correct refraction is important earlier than performing visible acuity testing.
-
Illumination: Inadequate or uneven illumination can compromise the accuracy of the check. Standardized lighting circumstances are essential for dependable outcomes.
-
Distance and Chart Dimension: The gap between the affected person and the chart, in addition to the scale of the chart itself, have to be exactly measured and maintained.
-
Affected person Cooperation: The affected person’s consideration, understanding of the directions, and willingness to cooperate are important for acquiring correct outcomes. That is significantly essential when testing younger youngsters or people with cognitive impairments.
-
Cultural and Linguistic Components: The selection of symbols or letters on the chart needs to be applicable for the affected person’s cultural and linguistic background. Utilizing unfamiliar symbols or letters can result in inaccurate outcomes.
-
Testing Setting: Distractions and environmental components can affect the check outcomes. A quiet and managed testing surroundings is essential for accuracy.
The Way forward for Eye Chart Know-how
The sphere of eye chart expertise is continually evolving. Latest advances have led to the event of computerized and automatic visible acuity testing programs. These programs provide a number of benefits over conventional paper-based charts, together with:
-
Improved Accuracy: Computerized programs can present extra exact and goal measurements of visible acuity.
-
Elevated Effectivity: Automated programs can considerably scale back the time required for testing.
-
Enhanced Information Administration: Computerized programs can retailer and handle check outcomes extra effectively.
-
Adaptive Testing: Some computerized programs make the most of adaptive testing algorithms, which alter the issue of the check primarily based on the affected person’s efficiency. This enables for extra environment friendly and exact measurement of visible acuity.
Moreover, analysis is ongoing into creating new and modern strategies for assessing visible acuity, together with the usage of digital actuality and augmented actuality applied sciences. These applied sciences have the potential to offer much more correct, environment friendly, and fascinating strategies for evaluating visible perform.
Conclusion:
The evolution of eye charts displays the continual pursuit of precision and accessibility in ophthalmology. From Snellen’s groundbreaking invention to the delicate computerized programs of at this time, these devices have performed a pivotal function in diagnosing, managing, and monitoring visible impairments. Whereas the essential precept of assessing visible acuity at a standardized distance stays unchanged, the variations in chart design and technological developments proceed to enhance the accuracy, effectivity, and inclusivity of imaginative and prescient testing, guaranteeing that everybody, no matter age, literacy, or cultural background, can obtain a dependable evaluation of their visible capabilities. The way forward for eye charts guarantees even higher precision and personalised testing methodologies, finally contributing to improved eye care and a greater understanding of visible perform.




Closure
Thus, we hope this text has offered helpful insights into The Snellen Chart and Past: A Deep Dive into the World of Eye Charts. We thanks for taking the time to learn this text. See you in our subsequent article!