Understanding and Making use of R Charts: A Complete Information to Vary Management Charts
Associated Articles: Understanding and Making use of R Charts: A Complete Information to Vary Management Charts
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate via the intriguing subject associated to Understanding and Making use of R Charts: A Complete Information to Vary Management Charts. Let’s weave attention-grabbing data and provide contemporary views to the readers.
Desk of Content material
Understanding and Making use of R Charts: A Complete Information to Vary Management Charts
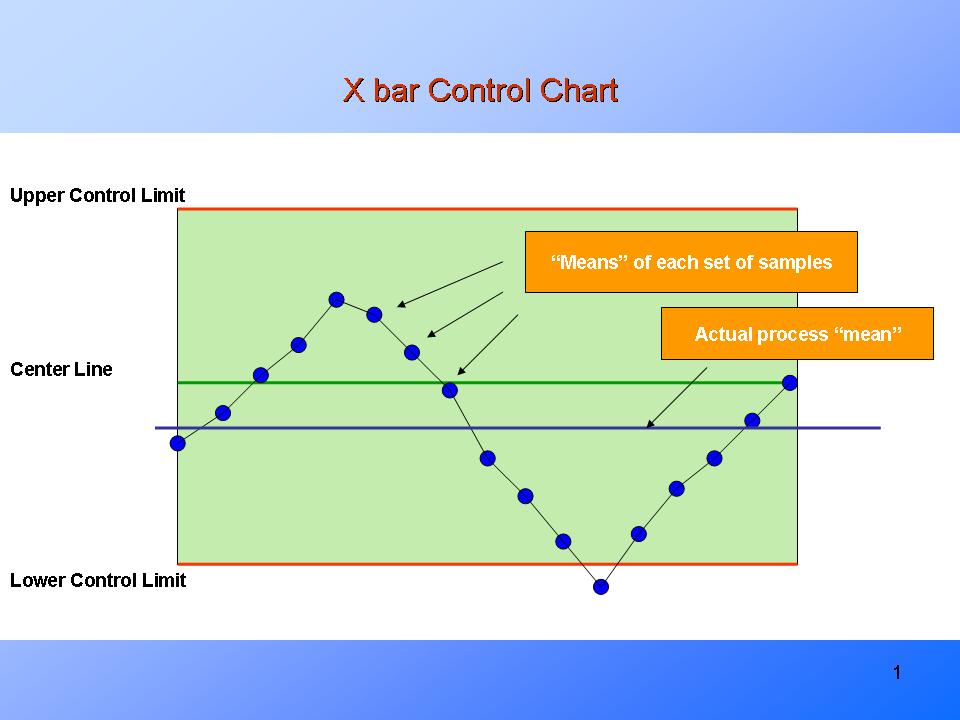
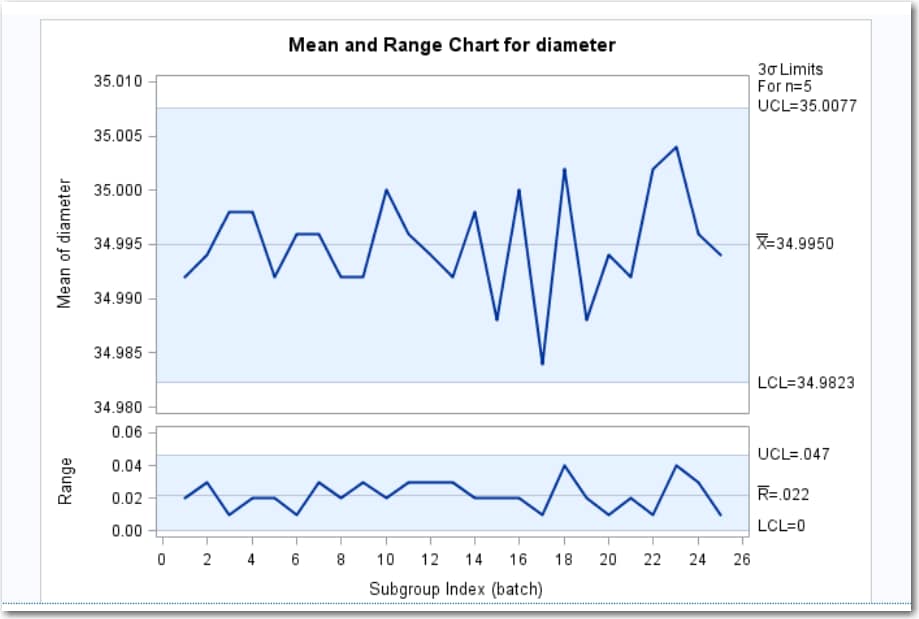
Management charts are indispensable instruments in statistical course of management (SPC), providing a visible illustration of course of stability and figuring out potential sources of variation. Among the many numerous management charts, the R chart, which screens the vary of subgroups, performs an important function in assessing course of variability. Not like the X-bar chart which tracks the common, the R chart focuses particularly on the unfold or dispersion of knowledge inside subgroups. This text delves into the intricacies of R charts, explaining their building, interpretation, and software in various situations.
Understanding the Idea of Vary:
Earlier than diving into the specifics of R chart building, it is important to know the idea of vary. Within the context of SPC, the vary (R) of a subgroup is just the distinction between the biggest and smallest values inside that subgroup. As an example, if a subgroup consists of the measurements 10, 12, 11, and 13, the vary is 13 – 10 = 3. The vary gives a fast and available measure of variability inside a subgroup. Whereas not as statistically environment friendly as the usual deviation, the vary is simpler to calculate and perceive, making it a sensible alternative for a lot of purposes.
Establishing an R Chart:
The development of an R chart includes a number of key steps:
-
Knowledge Assortment: Start by amassing knowledge in subgroups. The dimensions of those subgroups (n) is essential and needs to be chosen rigorously. Subgroup dimension sometimes ranges from 4 to 10, with smaller subgroups providing better sensitivity to small shifts in variability, whereas bigger subgroups present extra steady estimates of the vary. The selection of subgroup dimension usually depends upon the method being monitored and the accessible knowledge.
-
Calculating the Vary for Every Subgroup: For every subgroup, calculate the vary (R) by subtracting the smallest commentary from the biggest commentary.
-
Calculating the Common Vary (R-bar): After calculating the vary for every subgroup, calculate the common vary (R-bar) by summing all the person ranges and dividing by the variety of subgroups (okay). This common vary represents a central estimate of the method variability.
-
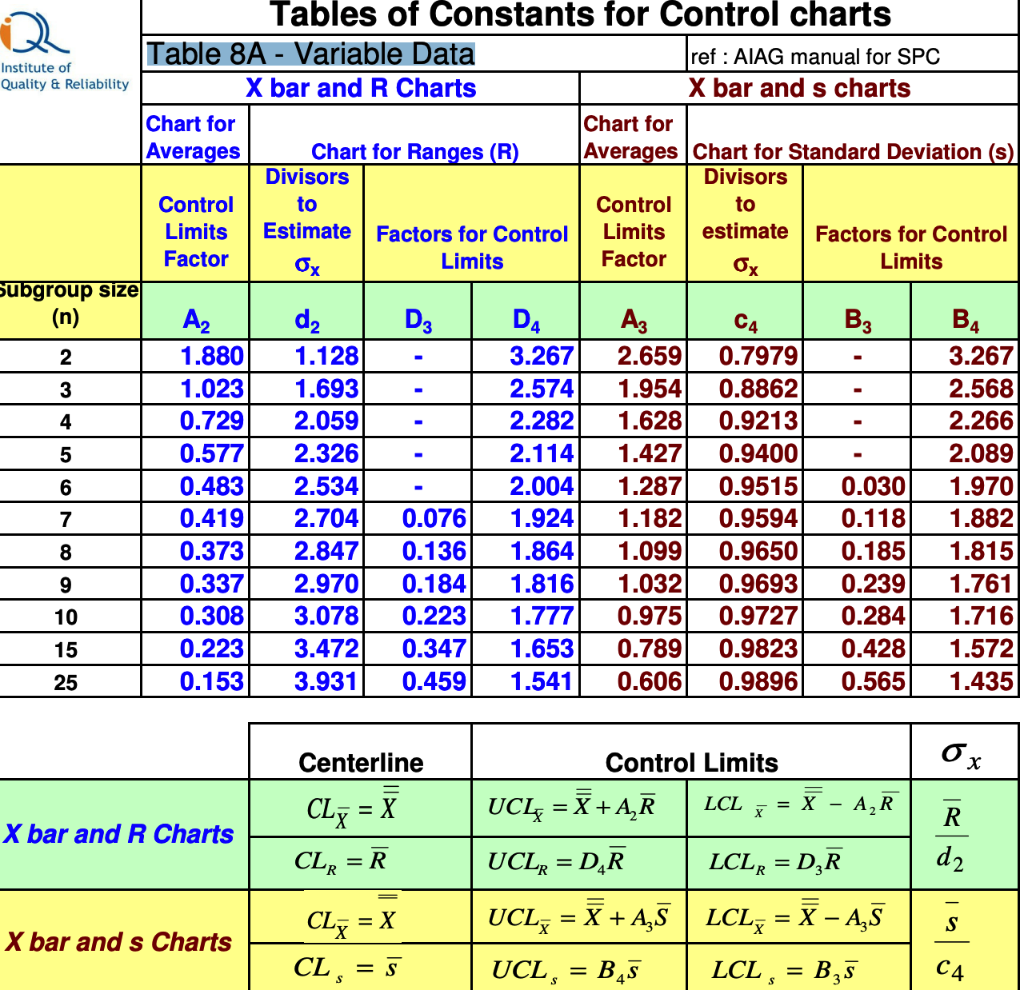
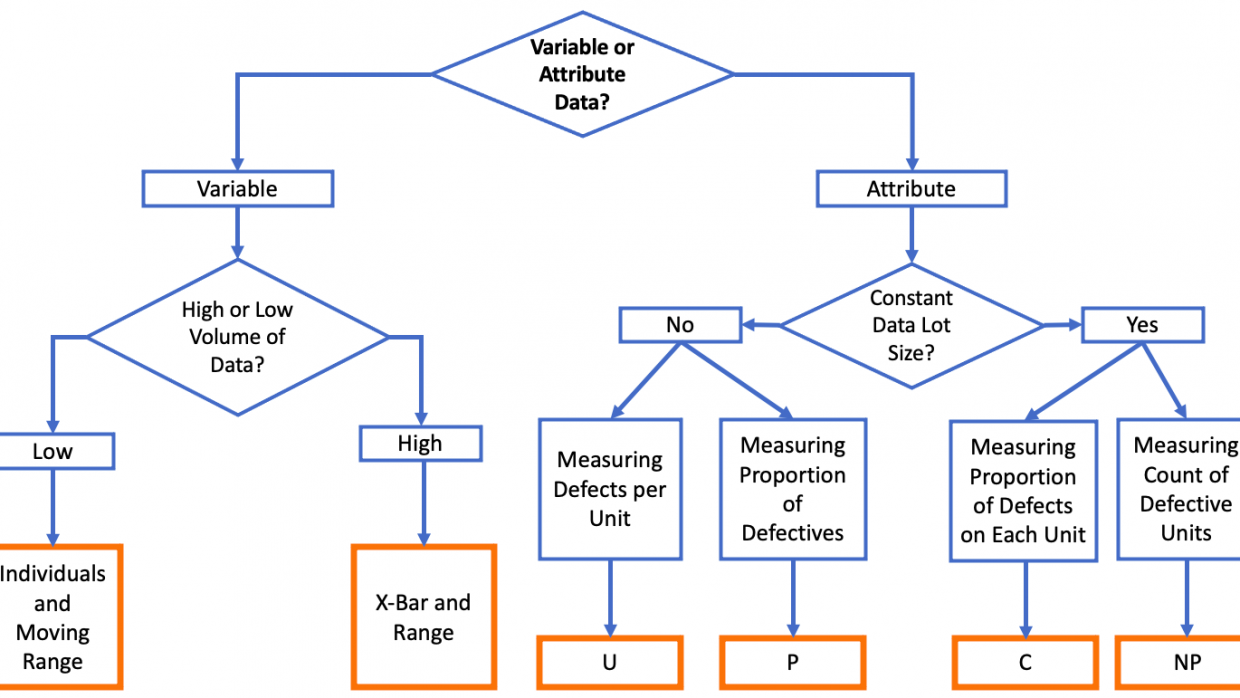
Figuring out Management Limits: The management limits for the R chart are calculated utilizing elements derived from the distribution of the vary. These elements, denoted as D3 and D4, are depending on the subgroup dimension (n) and are available in statistical tables or software program packages. The management limits are calculated as follows:
- *Higher Management Restrict (UCL): D4 R-bar**
- *Decrease Management Restrict (LCL): D3 R-bar**
- Middle Line (CL): R-bar
Word that D3 is zero for subgroup sizes of n ≤ 6. Which means the LCL is usually zero for smaller subgroups, indicating that the vary can’t be damaging.
-
Plotting the Chart: Plot the person ranges for every subgroup on the vertical axis in opposition to the subgroup quantity on the horizontal axis. Draw the middle line (R-bar) and the higher and decrease management limits (UCL and LCL) on the chart.
Deciphering an R Chart:
As soon as the R chart is constructed, deciphering the outcomes is essential for understanding the method variability. The important thing points to think about are:
-
Factors Exterior Management Limits: Any level falling outdoors the higher or decrease management limits signifies that the method variability is considerably completely different from what is predicted. This implies the presence of assignable causes of variation that have to be investigated and addressed.
-
Traits and Patterns: Even when all factors fall throughout the management limits, the presence of developments (e.g., persistently rising or lowering ranges) or patterns (e.g., cyclical variations) suggests potential instability within the course of. These patterns warrant additional investigation to establish potential underlying points.
-
Stratification: The R chart may reveal stratification, the place completely different subgroups exhibit completely different ranges of variability. This may point out the presence of things that have an effect on variability in another way throughout subgroups.
Functions of R Charts:
R charts discover purposes throughout various industries and processes, together with:
-
Manufacturing: Monitoring the variability within the dimensions of manufactured elements, the load of merchandise, or the consistency of chemical compositions.
-
Healthcare: Monitoring the variability in affected person wait instances, the accuracy of medical checks, or the consistency of treatment dosages.
-
Service Industries: Monitoring the variability in service instances, buyer satisfaction scores, or the effectivity of operational processes.
-
High quality Management: Assessing the consistency of services or products throughout completely different batches or manufacturing runs.
R Charts in Conjunction with X-bar Charts:
R charts are sometimes used along with X-bar charts (which monitor the common of subgroups). This mixture gives a complete evaluation of each the central tendency and variability of the method. By analyzing each charts concurrently, one can achieve a deeper understanding of the method efficiency and establish potential sources of variation. For instance, a steady X-bar chart with an unstable R chart signifies that the method common is constant, however the variability is fluctuating, suggesting a necessity to deal with the sources of this variability.
Benefits of Utilizing R Charts:
-
Simplicity: R charts are comparatively easy to assemble and interpret, making them accessible to a variety of customers.
-
Ease of Calculation: The vary is simpler to calculate than the usual deviation, lowering the computational burden.
-
Sensitivity to Modifications in Variability: R charts are delicate to modifications in course of variability, permitting for early detection of potential issues.
-
Value-Effectiveness: The simplicity and ease of use contribute to the cost-effectiveness of implementing R charts in high quality management packages.
Limitations of R Charts:
-
Sensitivity to Outliers: The vary is closely influenced by outliers, which means that excessive values can disproportionately have an effect on the R chart. Strong measures of variability, such because the median absolute deviation, could be most popular within the presence of serious outliers.
-
Much less Statistically Environment friendly than Customary Deviation: The vary is much less statistically environment friendly than the usual deviation, which means that it requires extra knowledge to realize the identical degree of precision.
-
Assumption of Normality: Whereas not strictly required, the effectiveness of R charts is enhanced when the underlying knowledge is roughly usually distributed.
Software program for R Chart Development:
Quite a few statistical software program packages, resembling Minitab, JMP, and R, present instruments for setting up and analyzing R charts. These packages automate the calculations and plotting, simplifying the method and lowering the chance of errors.
Conclusion:
R charts are invaluable instruments for monitoring course of variability in numerous settings. Their simplicity, ease of use, and sensitivity to modifications in variability make them a sensible alternative for a lot of high quality management purposes. Nonetheless, it is important to know their limitations and use them along with different statistical strategies and instruments for a complete evaluation of course of efficiency. By rigorously amassing knowledge, setting up the chart appropriately, and deciphering the outcomes thoughtfully, R charts can considerably contribute to bettering course of stability and lowering variability. Keep in mind that the efficient use of R charts requires a radical understanding of the method being monitored and a dedication to investigating and addressing any recognized sources of variation.



Closure
Thus, we hope this text has supplied invaluable insights into Understanding and Making use of R Charts: A Complete Information to Vary Management Charts. We recognize your consideration to our article. See you in our subsequent article!