Understanding and Making use of the R Chart in Statistical Course of Management
Associated Articles: Understanding and Making use of the R Chart in Statistical Course of Management
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate by means of the intriguing matter associated to Understanding and Making use of the R Chart in Statistical Course of Management. Let’s weave attention-grabbing info and provide recent views to the readers.
Desk of Content material
Understanding and Making use of the R Chart in Statistical Course of Management

Statistical Course of Management (SPC) is a strong methodology used to observe and enhance the standard of processes. One of many key instruments inside SPC is the management chart, a graphical illustration of information collected over time that helps establish traits, patterns, and variations in a course of. Among the many numerous management charts, the R chart, particularly designed for monitoring course of variability, performs an important position in sustaining constant high quality. This text delves into the intricacies of the R chart, exploring its software, interpretation, and limitations.
What’s an R Chart?
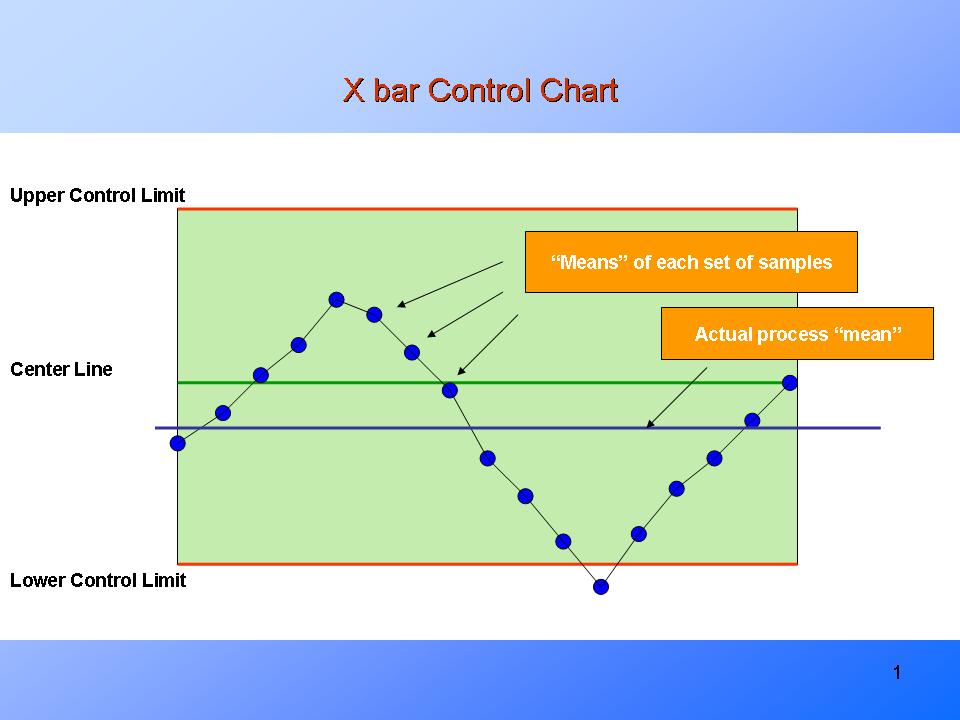
The R chart, quick for Vary chart, is a sort of management chart used to observe the variability inside subgroups of information. In contrast to charts that monitor the typical (X-bar charts), the R chart focuses solely on the vary, which is the distinction between the best and lowest values inside a subgroup. This makes it notably helpful for detecting shifts in course of dispersion, indicating whether or not the method is changing into kind of constant over time.
The R chart’s effectiveness stems from its capacity to shortly sign when the method variability exceeds predetermined limits, suggesting potential issues that may not be instantly obvious by trying on the common alone. A course of with constant averages however rising variability can nonetheless produce unacceptable ranges of defects. The R chart acts as a vigilant guardian in opposition to such eventualities.
The best way to Assemble an R Chart
Setting up an R chart includes a number of key steps:
-
Knowledge Assortment: The primary and most vital step is gathering knowledge. This includes taking samples from the method at common intervals. The dimensions of every pattern (subgroup dimension) must be constant all through the method. A standard subgroup dimension is 4-5 knowledge factors, however the optimum dimension depends upon the particular course of and the character of the information. Bigger subgroup sizes present extra exact estimates of the method variability however require extra knowledge assortment.
-
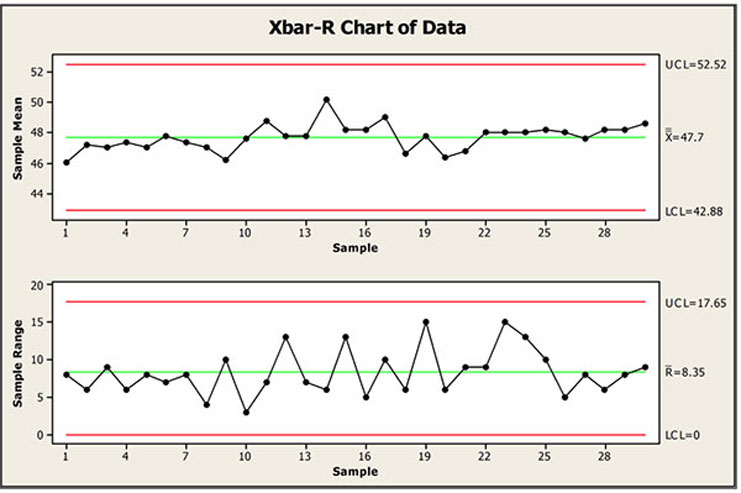
Calculating the Vary: For every subgroup, calculate the vary (R) by subtracting the smallest worth from the biggest worth.
-
Calculating the Common Vary (R-bar): After gathering knowledge for a adequate variety of subgroups (often a minimum of 20-25), calculate the typical vary (R-bar) by summing all the person ranges and dividing by the variety of subgroups. This R-bar represents an estimate of the typical course of variability.
-
Figuring out Management Limits: The management limits are calculated utilizing management chart constants (components) which can be particular to the subgroup dimension. These constants can be found in statistical tables or software program packages. The higher management restrict (UCL) and decrease management restrict (LCL) are calculated as follows:
- *UCL = R-bar UCLR**
- *LCL = R-bar LCLR**
The place UCLR and LCLR are the higher and decrease management limits components respectively, primarily based on the subgroup dimension. For instance, for a subgroup dimension of 5, UCLR is roughly 2.114 and LCLR is roughly 0.
-
Plotting the Chart: Plot the person ranges (R) for every subgroup on the vertical axis in opposition to the subgroup quantity on the horizontal axis. Draw the middle line at R-bar and the UCL and LCL traces.
Deciphering the R Chart
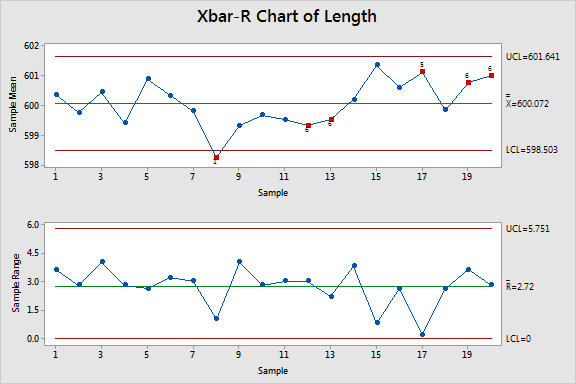
As soon as the R chart is constructed, deciphering it includes in search of alerts that point out a change in course of variability:
-
Factors exterior the management limits: Any level falling above the UCL or beneath the LCL signifies a big improve or lower in course of variability. This alerts a possible downside requiring rapid investigation.
-
Developments: A constant upward or downward development within the plotted factors, even when they continue to be throughout the management limits, suggests a gradual shift in course of variability. This warrants consideration and potential preventative motion.
-
Cycles: Recurring patterns or cycles within the knowledge point out predictable variations within the course of. Understanding the causes of those cycles can result in course of enhancements.
-
Stratification: Clusters of factors constantly above or beneath the middle line, with out crossing the management limits, would possibly point out a hidden supply of variation. Additional investigation is required to establish the underlying trigger.
R Chart in Conjunction with X-bar Chart
The R chart is best when used at the side of an X-bar chart (a chart monitoring the method common). The mix offers a complete image of each the central tendency and the variability of the method. A course of could be thought-about statistically in management provided that each the X-bar and R charts present no alerts of out-of-control conduct. Analyzing each charts collectively permits for a extra thorough understanding of course of efficiency and potential points.
Benefits of Utilizing an R Chart
- Simplicity: The R chart is comparatively simple to grasp and assemble, making it accessible to a variety of customers.
- Early Detection of Variability Modifications: It successfully detects shifts in course of variability, permitting for well timed intervention earlier than vital defects happen.
- Value Financial savings: By figuring out and addressing variability points early, the R chart might help forestall pricey rework, scrap, and buyer dissatisfaction.
- Improved Course of Functionality: By monitoring and controlling variability, the R chart contributes to improved course of functionality and constant product high quality.
Limitations of the R Chart
-
Assumption of Normality: The R chart depends on the idea that the underlying knowledge is often distributed. If the information is considerably non-normal, the R chart may not be dependable. In such instances, various strategies like the usual deviation (sigma) chart is perhaps extra acceptable.
-
Sensitivity to Outliers: Excessive values (outliers) can considerably affect the vary and therefore the management limits. Sturdy strategies which can be much less delicate to outliers is perhaps thought-about if outliers are prevalent.
-
Subgroup Dimension: The selection of subgroup dimension impacts the sensitivity and precision of the R chart. An inappropriate subgroup dimension can result in inaccurate conclusions.
-
Knowledge Assortment Challenges: Correct and constant knowledge assortment is important for the effectiveness of the R chart. Inconsistent sampling or measurement errors can invalidate the outcomes.
Software program for R Chart Development
Varied statistical software program packages, resembling Minitab, JMP, and R, provide instruments for developing and analyzing R charts. These packages automate the calculations and supply superior options resembling automated outlier detection and functionality evaluation. Utilizing software program considerably simplifies the method and reduces the chance of human error.
Conclusion
The R chart is a beneficial instrument within the arsenal of high quality management professionals. Its simplicity, effectiveness in detecting variability adjustments, and comparatively simple implementation make it a extensively used methodology for monitoring course of consistency. Nonetheless, it’s essential to grasp its assumptions and limitations and to make use of it appropriately at the side of different SPC instruments, such because the X-bar chart, for a complete evaluation of course of efficiency. By fastidiously making use of the R chart and deciphering its alerts, organizations can considerably enhance their course of functionality and ship constantly high-quality services or products. The important thing to profitable implementation lies in correct knowledge assortment, correct calculation, and cautious interpretation of the outcomes, resulting in knowledgeable decision-making and steady course of enchancment.





Closure
Thus, we hope this text has offered beneficial insights into Understanding and Making use of the R Chart in Statistical Course of Management. We thanks for taking the time to learn this text. See you in our subsequent article!