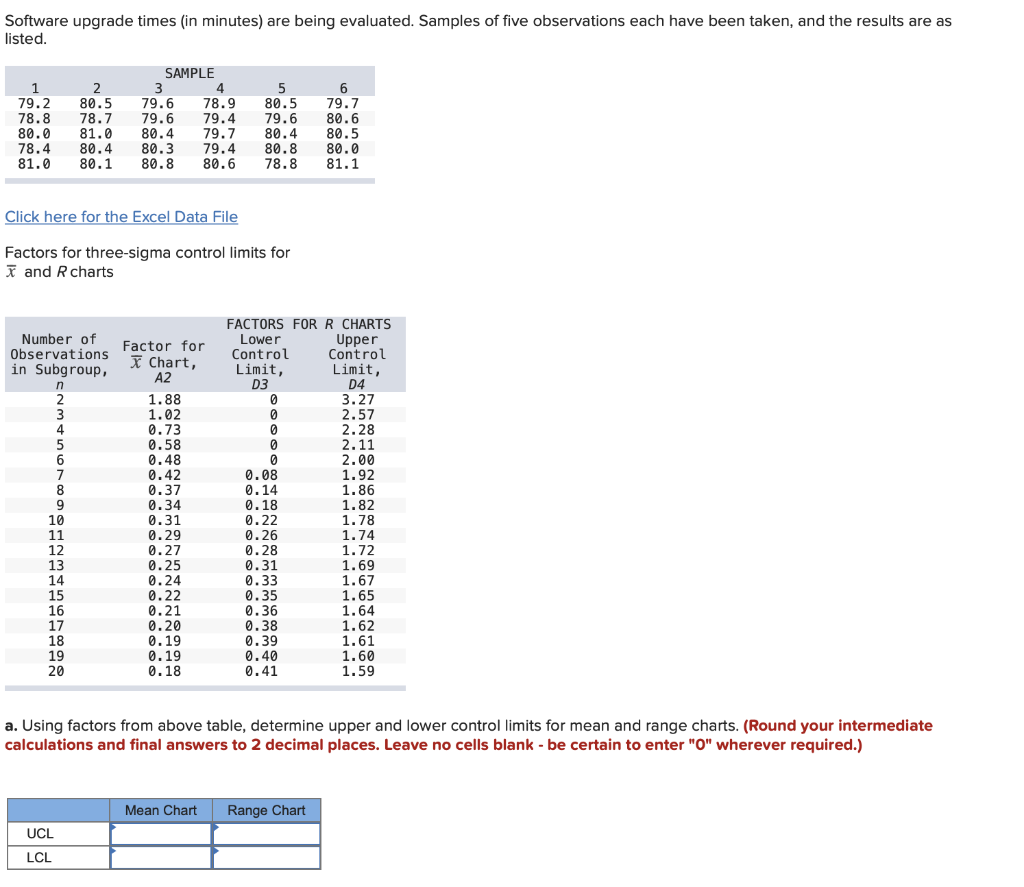
Understanding and Implementing R Charts with Management Limits: A Complete Information
Associated Articles: Understanding and Implementing R Charts with Management Limits: A Complete Information
Introduction
With nice pleasure, we’ll discover the intriguing subject associated to Understanding and Implementing R Charts with Management Limits: A Complete Information. Let’s weave attention-grabbing data and supply contemporary views to the readers.
Desk of Content material
Understanding and Implementing R Charts with Management Limits: A Complete Information
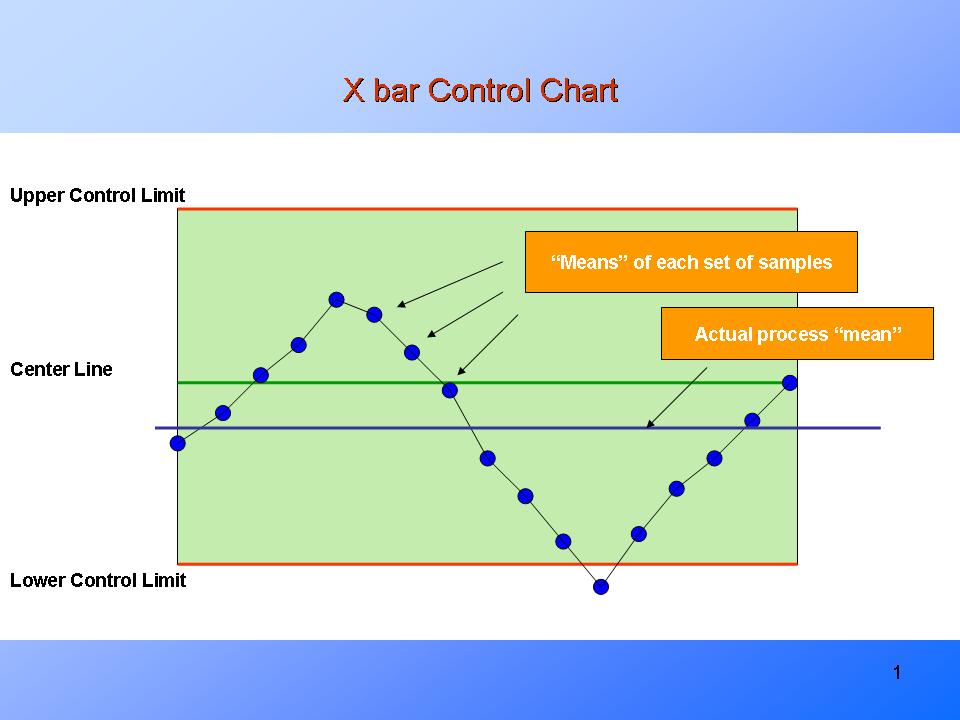
Management charts are important instruments in statistical course of management (SPC) used to watch and enhance the standard of processes. Among the many numerous sorts of management charts, the R chart performs a vital position in monitoring the variability inside subgroups of information. This text delves into the intricacies of R charts, explaining their building, interpretation, and software, with a deal with understanding and using management limits successfully.
What’s an R Chart?
An R chart, often known as a variety chart, is a management chart that tracks the vary (the distinction between the most important and smallest values) inside subgroups of information collected from a course of. Not like X-bar charts which monitor the common of subgroups, R charts particularly deal with the variation inside these subgroups. Constant variability is a key indicator of course of stability, and deviations from this stability are sometimes the primary signal of impending issues. By monitoring the vary, the R chart helps establish shifts in course of variability which may not be instantly obvious by trying on the common alone.
Why Use an R Chart?
The first objective of an R chart is to detect particular trigger variation – unpredictable, assignable causes of variation that deviate from the inherent, frequent trigger variation of the method. These particular causes might be something from machine malfunction to modifications in uncooked supplies or operator error. By promptly figuring out these particular causes, corrective actions might be taken to forestall defects and enhance course of consistency. R charts are notably helpful when:
- Course of variability is a major concern: If the primary goal is to attenuate variation, the R chart is a vital software.
- Subgroup information is available: R charts require information collected in subgroups, sometimes taken at common intervals or from a single manufacturing run.
- Easy and simply understood illustration of variation: The visible illustration of the vary makes it comparatively easy to interpret and perceive.
Establishing an R Chart: A Step-by-Step Information
Creating an R chart includes a number of steps:
-
Knowledge Assortment: Gather information in subgroups of a constant measurement (n). The subgroup measurement must be fastidiously chosen primarily based on the method and the information assortment methodology. Smaller subgroups (e.g., n=4, n=5) are extra delicate to small shifts in variation, whereas bigger subgroups are much less delicate however present extra exact estimates of the common vary.
-
Calculate the Vary for Every Subgroup: For every subgroup, calculate the vary (R) by subtracting the smallest worth from the most important worth.
-
Calculate the Common Vary (R-bar): Sum the ranges for all subgroups and divide by the variety of subgroups (okay). This provides the common vary (R-bar), which represents the common variation inside the subgroups.
R-bar = ΣRi / okaythe place:- ΣRi = sum of ranges for all subgroups
- okay = variety of subgroups
-
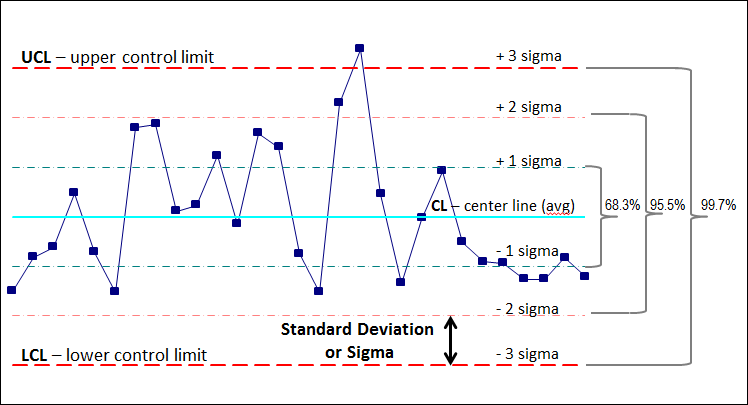
Decide Management Limits: The management limits for the R chart are calculated utilizing management chart constants (d2, D3, D4) that are depending on the subgroup measurement (n). These constants are available in statistical tables or software program packages. The management limits are:
- Higher Management Restrict (UCL): UCL = D4 * R-bar
- Decrease Management Restrict (LCL): LCL = D3 * R-bar
Word that D3 is 0 for small subgroup sizes (n ≤ 6), which means the LCL is 0 in these instances. This means {that a} vary of 0 is feasible and never essentially indicative of an issue.
-
Plot the Knowledge: Plot the vary (R) for every subgroup on the chart, together with the middle line (R-bar) and the UCL and LCL.
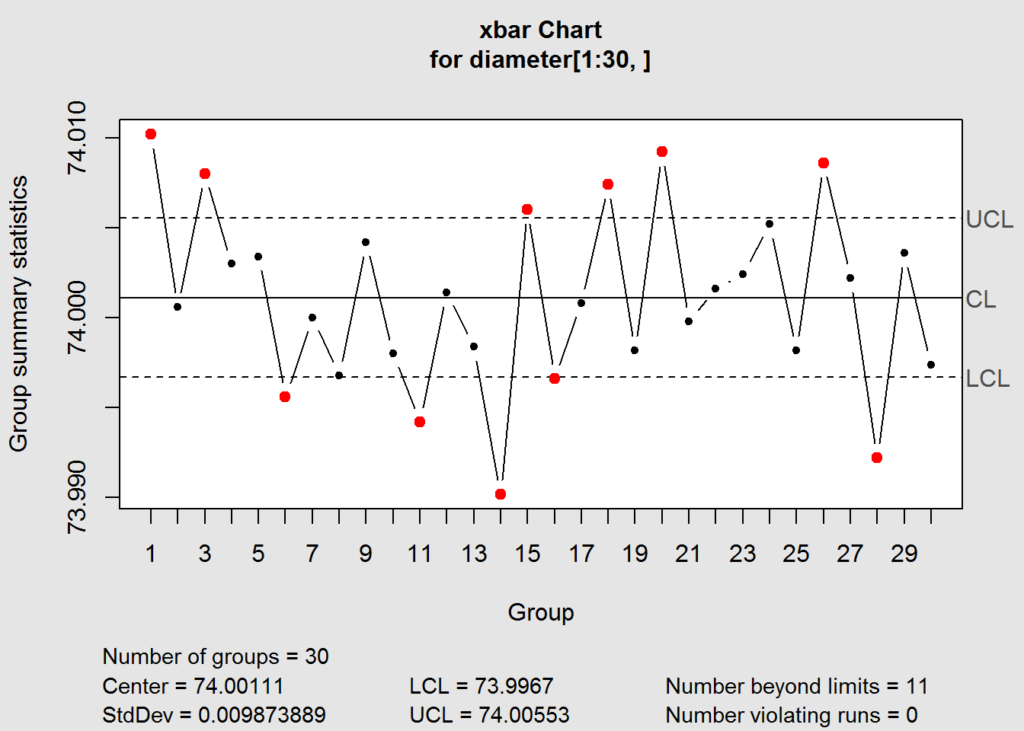
Deciphering the R Chart:
As soon as the R chart is constructed, decoding the outcomes is essential. Factors exterior the management limits point out particular trigger variation, requiring investigation and corrective motion. The next situations warrant consideration:
-
Factors past the UCL or LCL: These factors counsel vital modifications in course of variability, probably indicating an issue. Investigation ought to deal with figuring out the basis explanation for this elevated variation.
-
Tendencies: A constant upward or downward pattern within the ranges, even when all factors stay inside the management limits, signifies a possible downside. This pattern means that the method variability is altering over time.
-
Stratification: Clustering of factors above or under the middle line, even when inside the management limits, may counsel hidden stratification within the information. This would possibly point out that various factors are influencing the method at completely different occasions.
-
Cycles: Recurring patterns or cycles within the ranges may point out periodic influences on the method, corresponding to each day or weekly variations.
Selecting the Proper Subgroup Dimension:
The selection of subgroup measurement (n) considerably impacts the sensitivity and effectiveness of the R chart. Bigger subgroups present extra steady estimates of the common vary however are much less delicate to small shifts in variability. Smaller subgroups are extra delicate however might be extra noisy and fewer exact. The optimum subgroup measurement is a steadiness between sensitivity and stability, usually decided by experimentation and course of information. Frequent subgroup sizes vary from 4 to 10.
Software program for R Chart Creation:
Varied statistical software program packages simplify the method of making and decoding R charts. Fashionable choices embody:
- Minitab: A extensively used statistical software program bundle with intensive SPC capabilities.
- JMP: One other highly effective statistical software program bundle providing strong management charting options.
- R: A free and open-source statistical programming language with quite a few packages for management charting.
- Excel: Whereas not as subtle as devoted statistical software program, Excel can be utilized to create primary R charts utilizing built-in features or add-ins.
Limitations of R Charts:
Whereas R charts are highly effective instruments, they’ve limitations:
- Assumption of normality: R charts assume that the underlying information is roughly usually distributed. Important deviations from normality can have an effect on the accuracy of the management limits.
- Sensitivity to outliers: Outliers can considerably affect the vary and warp the management limits. Cautious information checking and outlier evaluation are important.
- Restricted data on particular causes: R charts establish the presence of particular trigger variation however do not essentially pinpoint the particular trigger. Additional investigation is commonly required.
Conclusion:
The R chart is a useful software for monitoring course of variability and figuring out particular trigger variation. By understanding the ideas of its building, interpretation, and limitations, practitioners can successfully use R charts to enhance course of consistency and scale back defects. Combining R charts with X-bar charts supplies a complete method to monitoring each the central tendency and variability of a course of, resulting in extra strong course of management and steady enchancment. Do not forget that efficient implementation requires cautious information assortment, acceptable subgroup measurement choice, and an intensive understanding of the method being monitored. Using statistical software program can considerably simplify the method and improve the accuracy of the evaluation. By diligently monitoring and decoding R charts, organizations can obtain vital positive aspects in high quality and effectivity.




Closure
Thus, we hope this text has offered useful insights into Understanding and Implementing R Charts with Management Limits: A Complete Information. We recognize your consideration to our article. See you in our subsequent article!