Understanding and Using X-Axis and Y-Axis Charts: A Complete Information
Associated Articles: Understanding and Using X-Axis and Y-Axis Charts: A Complete Information
Introduction
On this auspicious event, we’re delighted to delve into the intriguing matter associated to Understanding and Using X-Axis and Y-Axis Charts: A Complete Information. Let’s weave fascinating data and supply contemporary views to the readers.
Desk of Content material
Understanding and Using X-Axis and Y-Axis Charts: A Complete Information
X-axis and Y-axis charts, also called Cartesian charts or coordinate graphs, are elementary instruments for visualizing knowledge and relationships between variables. Their simplicity belies their energy and flexibility, making them indispensable throughout quite a few fields, from scientific analysis and monetary evaluation to social research and on a regular basis knowledge illustration. This text will present a complete overview of x-axis and y-axis charts, exploring their development, interpretation, differing types, and purposes, together with issues for efficient knowledge visualization.
The Basis: Cartesian Coordinates
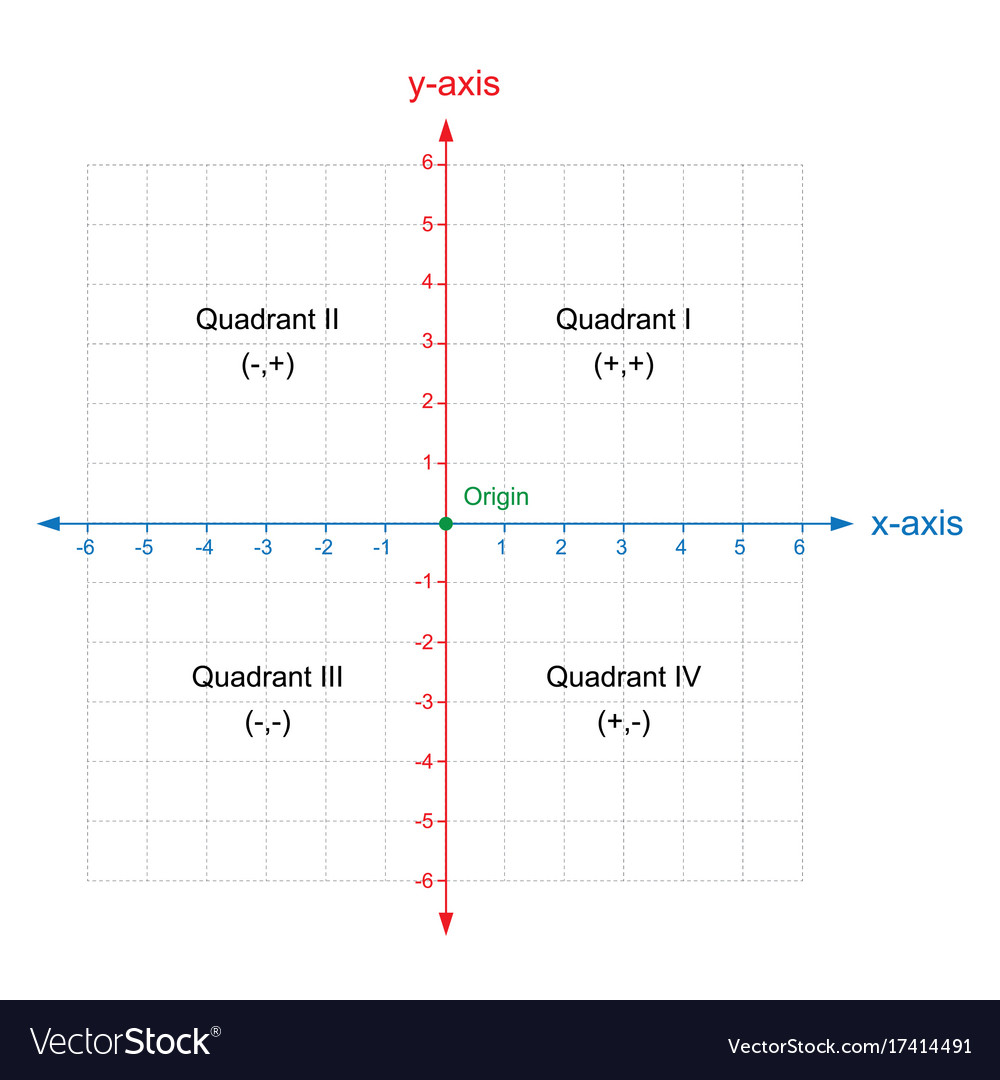
The cornerstone of any x-axis and y-axis chart is the Cartesian coordinate system, named after the famend mathematician René Descartes. This technique defines a two-dimensional airplane utilizing two perpendicular strains:
-
X-axis (Horizontal Axis): This axis sometimes represents the impartial variable. The impartial variable is the one that’s manipulated or managed in an experiment or statement. It is the variable that’s believed to trigger a change within the different variable.
-
Y-axis (Vertical Axis): This axis sometimes represents the dependent variable. The dependent variable is the one that’s measured or noticed in response to adjustments within the impartial variable. It is the variable that’s believed to be affected by the impartial variable.
The intersection of the x-axis and y-axis is known as the origin, represented by the coordinates (0,0). Each level on the airplane could be uniquely recognized by its x-coordinate (horizontal place) and its y-coordinate (vertical place), written as an ordered pair (x, y).
Sorts of X-Axis and Y-Axis Charts:
Whereas the fundamental precept stays the identical, varied chart sorts make the most of the x-axis and y-axis framework to signify knowledge in numerous methods, every with its strengths and weaknesses:
-
Line Graphs: These charts are perfect for displaying developments and adjustments over time or throughout a steady vary of values. Information factors are related by strains, revealing patterns of enhance, lower, or stability. Line graphs are notably helpful for visualizing knowledge with a temporal part, akin to inventory costs over time or inhabitants progress over many years.
-
Scatter Plots: Scatter plots show the connection between two variables with out implying a direct causal hyperlink. Every knowledge level is represented as a dot on the graph, and the general sample of the factors can reveal correlations (optimistic, unfavourable, or none). Scatter plots are continuously utilized in statistical evaluation to determine correlations and potential relationships between variables.
-
Bar Charts: Bar charts are wonderful for evaluating totally different classes or teams. Rectangular bars signify the values of every class, with the size of the bar equivalent to the magnitude of the worth. Bar charts could be vertical or horizontal, and they’re efficient for visualizing discrete knowledge, akin to gross sales figures for various merchandise or the variety of college students in numerous grades.
-
Histograms: Histograms are much like bar charts however are particularly used to signify the frequency distribution of a steady variable. The x-axis represents the vary of values, divided into intervals (bins), and the y-axis represents the frequency or rely of information factors falling inside every interval. Histograms are sometimes used to visualise knowledge distributions and determine patterns like skewness or modality.
-
Space Charts: Space charts are much like line graphs, however the space beneath the road is stuffed with colour. This emphasizes the cumulative impact of the information over time or throughout classes. Space charts are notably efficient for visualizing proportions or cumulative totals.
Decoding X-Axis and Y-Axis Charts:
Successfully decoding x-axis and y-axis charts requires cautious consideration to a number of key parts:
-
Axes Labels: Clear and concise labels are essential for understanding what every axis represents. Items of measurement must be explicitly said (e.g., "Temperature (°C)," "Time (years)," "Gross sales ($)."
-
Scale: The size of every axis determines the visible illustration of the information. An inappropriately chosen scale can distort the notion of the information’s patterns. Think about using a constant scale and avoiding pointless breaks within the axes.
-
Information Factors: The place of every knowledge level supplies details about the values of the corresponding x and y variables. Search for developments, patterns, outliers, and clusters of information factors.
-
**




Closure
Thus, we hope this text has offered precious insights into Understanding and Using X-Axis and Y-Axis Charts: A Complete Information. We admire your consideration to our article. See you in our subsequent article!