Understanding and Using X-bar and R Charts for Course of Management
Associated Articles: Understanding and Using X-bar and R Charts for Course of Management
Introduction
On this auspicious event, we’re delighted to delve into the intriguing matter associated to Understanding and Using X-bar and R Charts for Course of Management. Let’s weave attention-grabbing info and provide contemporary views to the readers.
Desk of Content material
Understanding and Using X-bar and R Charts for Course of Management
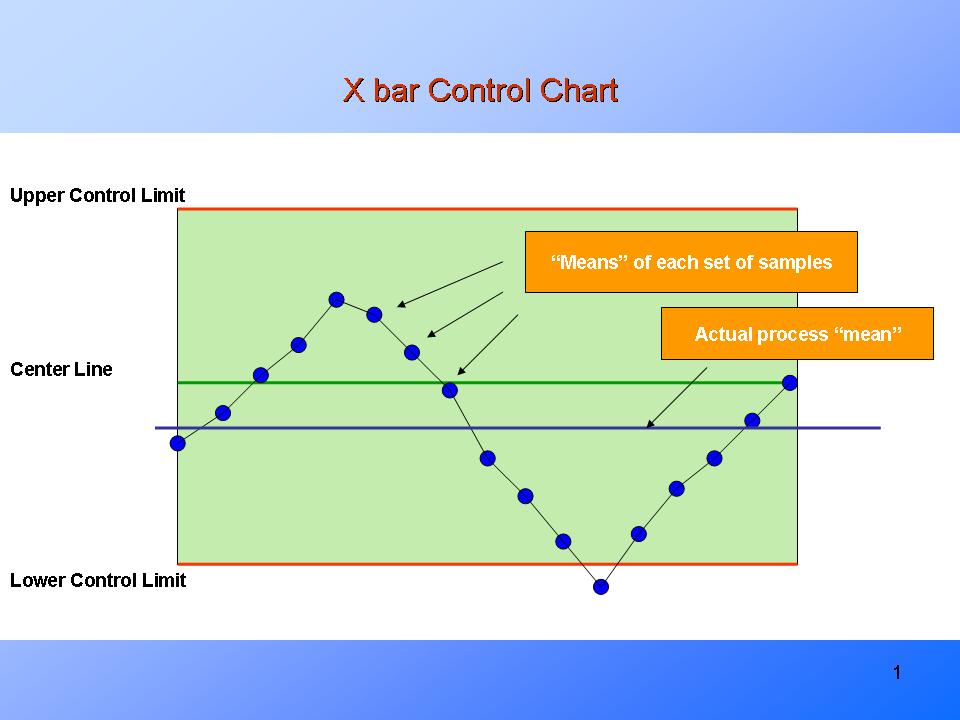
Statistical Course of Management (SPC) is a robust methodology used to observe and enhance manufacturing and different processes. A cornerstone of SPC is the usage of management charts, graphical instruments that show information over time, permitting for the identification of tendencies, patterns, and anomalies indicative of course of instability. Among the many most generally used management charts are the X-bar and R charts, a robust duo usually employed collectively to observe the central tendency and variability of a course of. This text will delve into the intricacies of X-bar and R charts, exploring their development, interpretation, and sensible functions.
The Basis: Understanding Course of Variability
Earlier than diving into the specifics of X-bar and R charts, it is essential to know the idea of course of variability. No course of is completely constant; inherent variations exist on account of quite a few elements, together with uncooked supplies, gear put on, operator talent, and environmental circumstances. These variations may be categorized into two principal sorts:
-
Widespread Trigger Variation: This represents the inherent, random variation inside a course of that is at all times current. It is a pure a part of the method and usually comparatively small. Widespread trigger variation is predictable and steady in the long term.
-
Particular Trigger Variation: This refers to variation attributable to assignable causes, occasions exterior the traditional working circumstances. These might embrace machine malfunctions, operator errors, modifications in uncooked supplies, or environmental shifts. Particular trigger variation is unpredictable and signifies a course of that is uncontrolled.
The first aim of X-bar and R charts is to tell apart between widespread trigger and particular trigger variation, enabling proactive intervention to handle points earlier than they result in important issues.
Introducing the X-bar and R Chart Duo
The X-bar chart screens the central tendency (common) of a course of, whereas the R chart tracks the vary (the distinction between the most important and smallest values) inside subgroups of information. They’re used collectively as a result of monitoring solely the common does not present an entire image of course of stability. A course of can have a steady common however nonetheless exhibit extreme variability, rendering it unreliable. Conversely, a course of with a extremely variable common will seemingly have a excessive vary. By analyzing each the common and vary concurrently, we get a complete understanding of the method’s efficiency.
Developing the X-bar and R Chart
The development of X-bar and R charts includes a number of key steps:
-
Subgroup Sampling: Knowledge is collected in subgroups, usually consisting of 4 to five observations. The scale of the subgroup must be chosen fastidiously, balancing the necessity for adequate information to precisely estimate the method parameters with the sensible constraints of information assortment. Subgroups must be collected sequentially, representing a snapshot of the method at a specific time.
-
Calculating Subgroup Statistics: For every subgroup, calculate the next:
- X-bar (x̄): The typical of the observations inside the subgroup.
- R: The vary of the observations inside the subgroup (largest worth minus smallest worth).
-
Calculating Total Statistics: After amassing a adequate variety of subgroups (usually 20-25), calculate the next total statistics:
- X-double bar (x̄̄): The typical of all of the subgroup averages (x̄). This represents the general course of common.
- R-bar (R̄): The typical of all of the subgroup ranges (R). This represents the common vary of the method.
-
Figuring out Management Limits: Management limits are calculated utilizing management chart constants (elements derived from statistical tables) that rely on the subgroup dimension. The formulation for the management limits are:
-
X-bar Chart:
- Higher Management Restrict (UCL): x̄̄ + A₂R̄
- Heart Line (CL): x̄̄
- Decrease Management Restrict (LCL): x̄̄ – A₂R̄
-
R Chart:
- Higher Management Restrict (UCL): D₄R̄
- Heart Line (CL): R̄
- Decrease Management Restrict (LCL): D₃R̄
The values of A₂, D₃, and D₄ are constants present in management chart constants tables, available in statistical textbooks and software program packages. These constants account for the variability inherent in estimating the method parameters from the pattern information. For instance, for a subgroup dimension of 5, A₂ = 0.577, D₃ = 0, and D₄ = 2.115.
-
-
Plotting the Charts: The subgroup averages (x̄) are plotted on the X-bar chart, and the subgroup ranges (R) are plotted on the R chart. The management limits and heart strains are drawn on each charts.
Deciphering the Charts
The interpretation of X-bar and R charts hinges on figuring out factors that fall exterior the management limits or exhibit non-random patterns inside the limits.
-
Factors Outdoors Management Limits: Any level falling above the UCL or beneath the LCL on both chart signifies a possible particular trigger variation. This requires investigation to determine and rectify the foundation trigger.
-
Non-Random Patterns Inside Management Limits: Even when all factors fall inside the management limits, non-random patterns can point out course of instability. These patterns embrace:
- Developments: A constant upward or downward motion of factors.
- Cycles: Recurring patterns of excessive and low values.
- Stratification: Knowledge persistently clustering round sure values.
- Mixtures: Knowledge exhibiting two distinct distributions.
These patterns counsel that whereas the method could seem steady primarily based on the management limits, underlying points may be current that warrant additional investigation.
Sensible Functions and Benefits
X-bar and R charts discover widespread software throughout varied industries, together with:
- Manufacturing: Monitoring dimensions, weights, and different vital course of parameters.
- Healthcare: Monitoring affected person wait occasions, medicine errors, and an infection charges.
- Service Industries: Monitoring buyer satisfaction scores, name dealing with occasions, and order success occasions.
The benefits of utilizing X-bar and R charts embrace:
- Early Detection of Issues: Permits for proactive identification and correction of course of points earlier than they result in important defects or losses.
- Course of Enchancment: Supplies helpful insights into course of variability, enabling the event of methods for enchancment.
- Lowered Waste: By minimizing defects and variability, X-bar and R charts contribute to lowered waste and improved effectivity.
- Goal Evaluation: Supplies an goal and data-driven strategy to course of monitoring, minimizing subjective interpretations.
Limitations and Issues
Whereas X-bar and R charts are highly effective instruments, it is essential to acknowledge their limitations:
- Assumption of Normality: The calculation of management limits assumes that the information is generally distributed. If the information is considerably non-normal, various management charts may be extra applicable.
- Subgroup Choice: The selection of subgroup dimension and sampling methodology is essential for correct interpretation. Incorrect subgrouping can result in deceptive outcomes.
- Knowledge Integrity: The accuracy of the charts relies on the accuracy and reliability of the collected information. Inaccurate information will result in inaccurate conclusions.
Conclusion
X-bar and R charts are important instruments for anybody looking for to implement efficient Statistical Course of Management. By monitoring each the central tendency and variability of a course of, these charts present a robust technique of figuring out and addressing points, resulting in improved course of stability, lowered waste, and enhanced total efficiency. Nonetheless, their profitable implementation requires a radical understanding of their development, interpretation, and limitations. Cautious planning, applicable information assortment, and a dedication to steady enchancment are key to maximizing the advantages of X-bar and R charts. The mix of those charts provides a complete view of course of efficiency, enabling data-driven decision-making and a pathway to steady enchancment. Understanding and successfully using these charts is an important step in direction of reaching operational excellence.

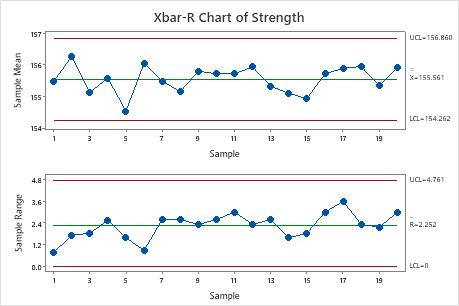

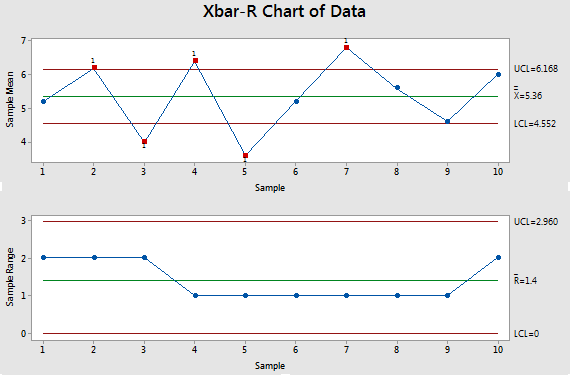


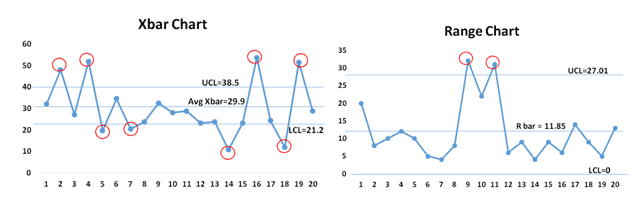

Closure
Thus, we hope this text has offered helpful insights into Understanding and Using X-bar and R Charts for Course of Management. We thanks for taking the time to learn this text. See you in our subsequent article!