Understanding the 410A Refrigerant Strain-Temperature Chart: A Complete Information
Associated Articles: Understanding the 410A Refrigerant Strain-Temperature Chart: A Complete Information
Introduction
With nice pleasure, we’ll discover the intriguing subject associated to Understanding the 410A Refrigerant Strain-Temperature Chart: A Complete Information. Let’s weave attention-grabbing data and provide contemporary views to the readers.
Desk of Content material
Understanding the 410A Refrigerant Strain-Temperature Chart: A Complete Information

Refrigerant R-410A, a hydrofluoroolefin (HFO) mix, is a extensively used refrigerant in fashionable air-con and refrigeration methods. Understanding its pressure-temperature relationship is essential for technicians performing set up, upkeep, and troubleshooting. This text supplies an in depth clarification of the 410A pressure-temperature chart, its functions, and methods to interpret it accurately for environment friendly and secure operation of refrigeration methods.
The Significance of Strain-Temperature Charts
Refrigerants function beneath particular strain and temperature circumstances decided by their thermodynamic properties. Deviating from these parameters can result in inefficient operation, system harm, and even security hazards. The pressure-temperature (P-T) chart serves as a significant instrument for technicians to:
- Decide refrigerant cost: By measuring the system’s strain and evaluating it to the chart’s values at a identified temperature, technicians can estimate the refrigerant cost. An undercharged or overcharged system won’t function optimally.
- Establish potential leaks: A major strain drop, notably when in comparison with the anticipated strain at a given temperature, can point out a refrigerant leak.
- Diagnose system malfunctions: Uncommon strain readings can level in direction of issues like compressor failure, condenser points, or evaporator malfunctions.
- Confirm correct system operation: Confirming that the system’s strain and temperature readings align with the chart’s values ensures the system is functioning accurately.
- Optimize system efficiency: Understanding the pressure-temperature relationship permits technicians to regulate system parameters for optimum effectivity and power financial savings.
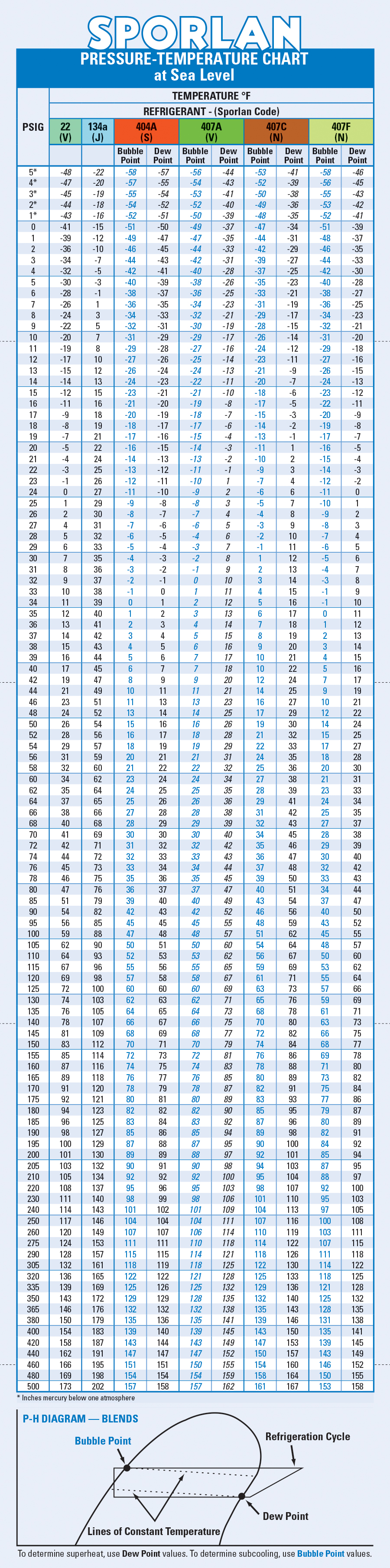
Studying the 410A Strain-Temperature Chart
The 410A P-T chart usually presents information in a graphical format, with strain (often in kilos per sq. inch – PSI or kilopascals – kPa) plotted in opposition to temperature (often in levels Fahrenheit – °F or levels Celsius – °C). The chart typically contains two distinct strains:
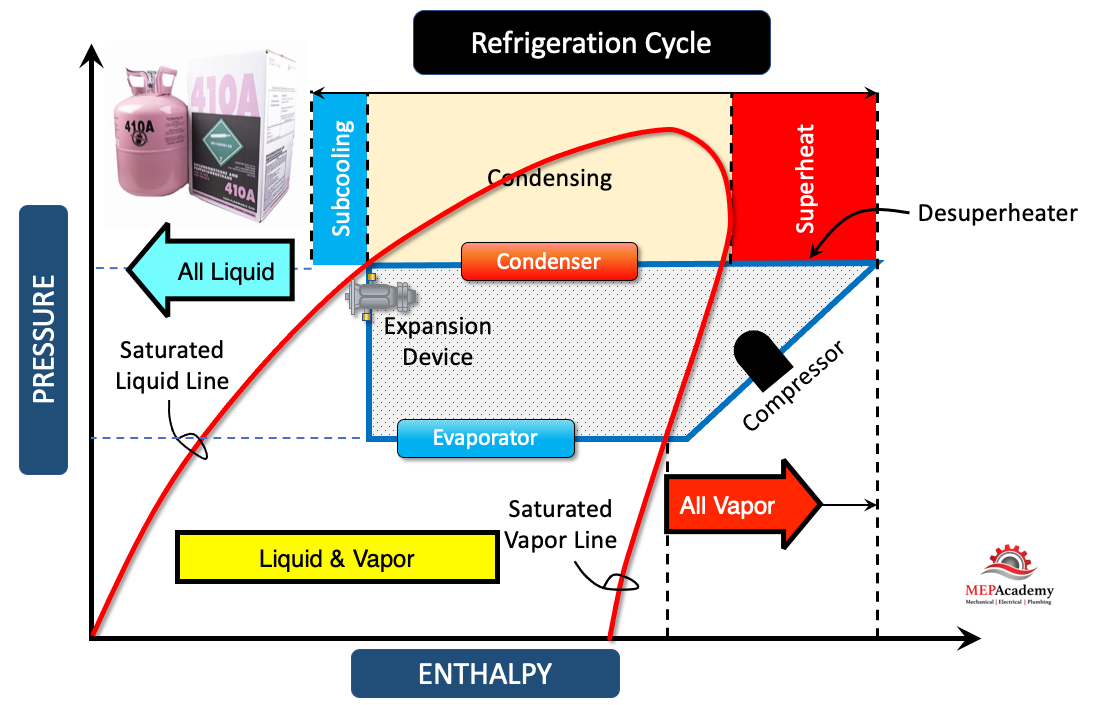
- Saturation Strain Line: This line represents the strain at which the refrigerant adjustments section between liquid and vapor at a given temperature. Factors above this line signify superheated vapor, whereas factors under signify subcooled liquid.
- Superheat and Subcooling Strains: These strains are sometimes included to help in figuring out the superheat and subcooling of the refrigerant. Superheat is the temperature distinction between the precise refrigerant temperature and its saturation temperature at a given strain within the vapor section. Subcooling is the temperature distinction between the precise refrigerant temperature and its saturation temperature at a given strain within the liquid section. Correct superheat and subcooling are essential for environment friendly system operation.
Deciphering the Chart for Completely different System Elements
The 410A P-T chart is used in a different way relying on which a part of the refrigeration cycle is being evaluated.
- Suction Line (Evaporator): The suction line strain and temperature are used to find out the superheat. Low superheat signifies potential restriction, whereas excessive superheat signifies inadequate refrigerant cost. The chart helps decide the anticipated strain primarily based on the measured temperature, permitting for a fast evaluation of superheat.
- Liquid Line (Condenser): The liquid line strain and temperature are used to find out the subcooling. Low subcooling signifies potential restriction or inadequate refrigerant cost, whereas excessive subcooling suggests overcharging. The chart assists in figuring out the anticipated strain primarily based on the measured temperature, permitting for analysis of subcooling.
- Compressor Discharge Line: The discharge line strain is usually increased than the values proven on the chart, indicating superheated vapor leaving the compressor. Whereas the chart does not instantly present discharge strain values, it helps set up the anticipated high-side strain vary primarily based on the condensing temperature.
Elements Affecting 410A Strain-Temperature Readings
A number of components can affect the precise strain and temperature readings in a 410A system, probably inflicting deviations from the chart’s values. These embrace:
- Ambient Temperature: Increased ambient temperatures will result in increased condensing pressures.
- Refrigerant Cost: Undercharging or overcharging will considerably have an effect on strain readings.
- System Restrictions: Blockages within the strains or elements can enhance strain drops and have an effect on readings.
- Compressor Effectivity: A malfunctioning compressor can alter strain and temperature readings.
- Altitude: Increased altitudes end in decrease boiling factors and thus decrease pressures. Specialised charts are sometimes obtainable for increased altitudes.
- Non-condensables: The presence of air or different non-condensables within the system can affect strain readings.
Security Precautions When Utilizing the 410A Strain-Temperature Chart
Utilizing the 410A P-T chart requires warning and adherence to security protocols:
- All the time use acceptable security tools: This contains security glasses, gloves, and correct clothes.
- By no means work on a pressurized system with out correct coaching and expertise: Improper dealing with of refrigerants can result in critical accidents or fatalities.
- Guarantee correct air flow: Refrigerant leaks can displace oxygen and create hazardous environments.
- Comply with producer’s directions: All the time check with the tools and refrigerant producer’s directions for secure operation and upkeep procedures.
- Use calibrated gauges: Inaccurate gauges will result in incorrect readings and probably defective diagnoses.
Conclusion
The 410A pressure-temperature chart is an indispensable instrument for HVAC/R technicians. Understanding methods to interpret this chart accurately is essential for environment friendly troubleshooting, upkeep, and optimum system efficiency. Nonetheless, it is important to do not forget that the chart supplies solely a tenet. Correct coaching, expertise, and adherence to security procedures are paramount when working with refrigerants and refrigeration methods. All the time prioritize security and seek the advice of related trade requirements and producer’s suggestions. Moreover, developments in know-how might result in digital instruments and software program that combine the pressure-temperature charts and supply extra complete diagnostic capabilities, making the technician’s job extra environment friendly and correct. Maintaining-to-date with these developments is significant for continued skilled improvement within the HVAC/R subject.




Closure
Thus, we hope this text has supplied invaluable insights into Understanding the 410A Refrigerant Strain-Temperature Chart: A Complete Information. We thanks for taking the time to learn this text. See you in our subsequent article!
