Understanding the pH Chart of Water: A Complete Information
Associated Articles: Understanding the pH Chart of Water: A Complete Information
Introduction
On this auspicious event, we’re delighted to delve into the intriguing subject associated to Understanding the pH Chart of Water: A Complete Information. Let’s weave attention-grabbing data and supply recent views to the readers.
Desk of Content material
Understanding the pH Chart of Water: A Complete Information
Water, the elixir of life, is much extra advanced than its seemingly easy chemical formulation (H₂O) suggests. Its properties, and consequently its affect on the environment and well being, are considerably influenced by its pH degree. This text delves into the intricacies of the water pH chart, explaining its significance, the way it’s measured, the components influencing pH, and the implications of various pH ranges for varied functions.
What’s pH?
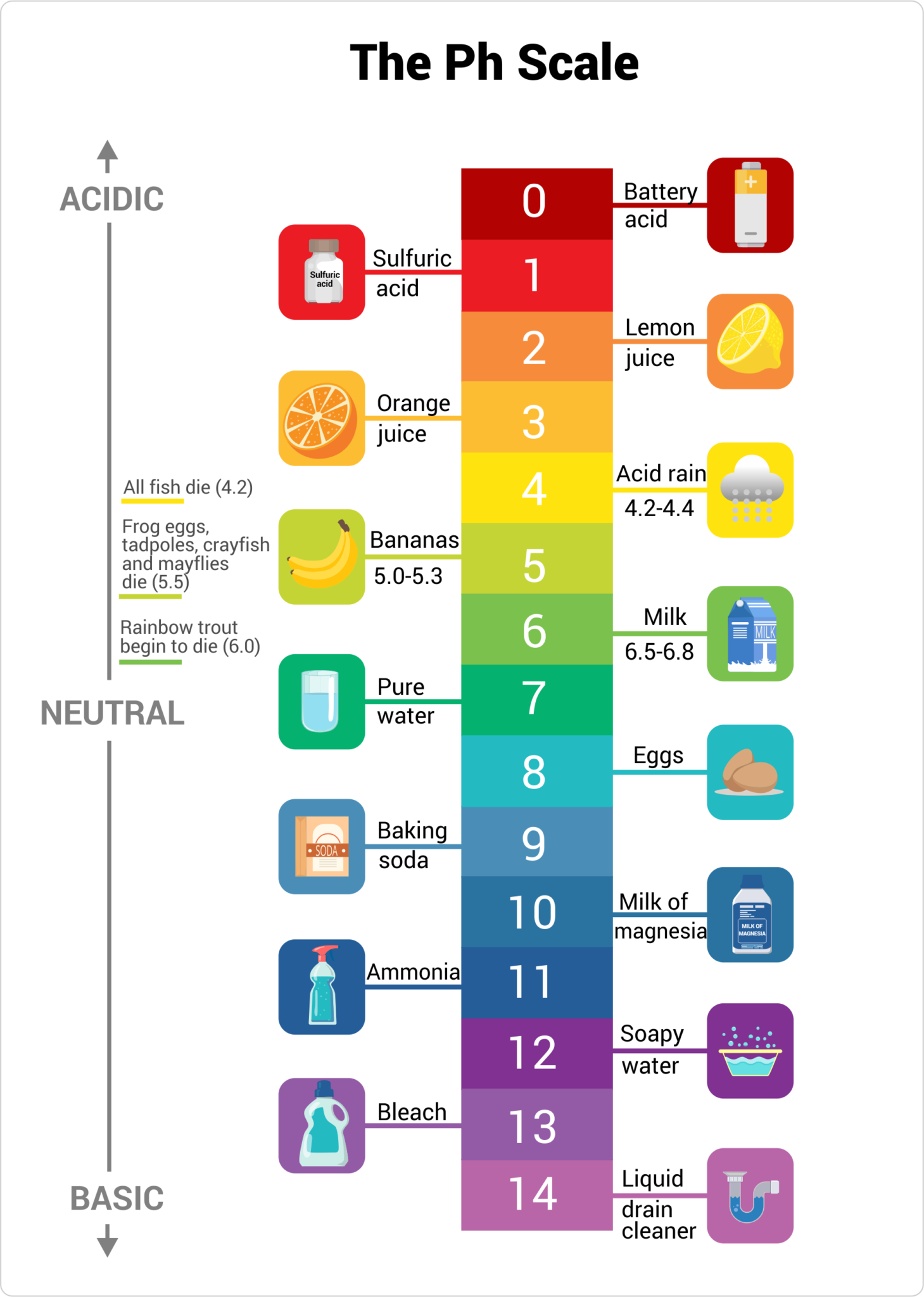
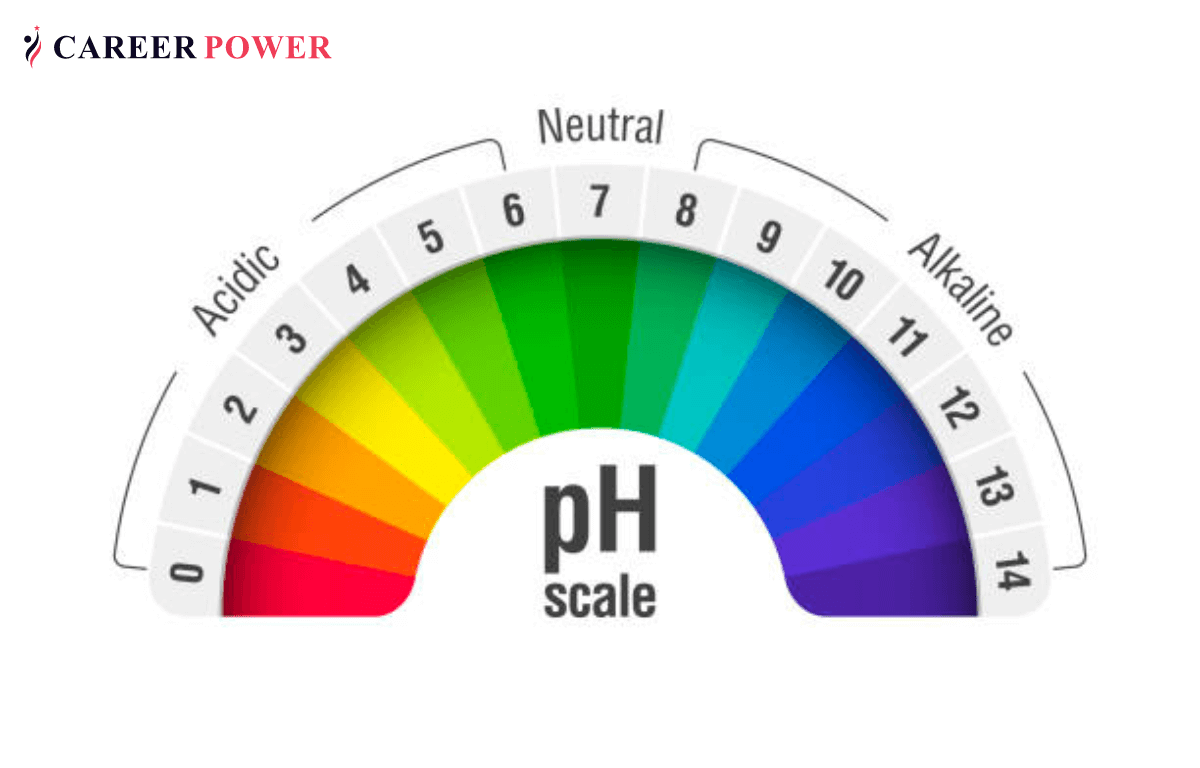
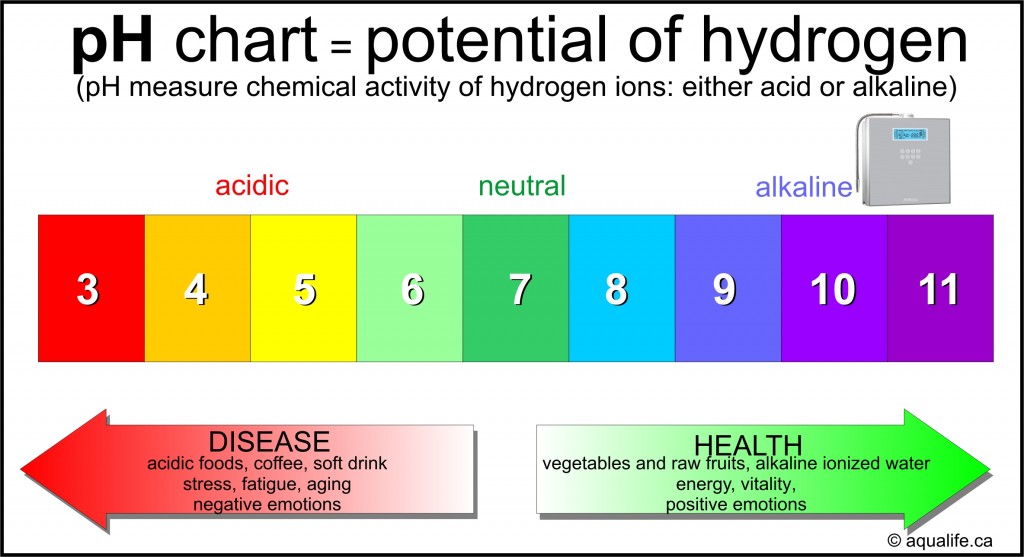
pH stands for "potential of hydrogen," a measure of the acidity or alkalinity of an answer. It is a logarithmic scale starting from 0 to 14, with 7 representing impartial. A pH worth under 7 signifies acidity, whereas a worth above 7 signifies alkalinity (or basicity). Every entire quantity change on the dimensions represents a tenfold change in hydrogen ion (H⁺) focus. For example, an answer with a pH of 6 is ten instances extra acidic than an answer with a pH of seven, and 100 instances extra acidic than an answer with a pH of 8.
The Water pH Chart: A Visible Illustration
Whereas not a chart within the conventional graphical sense, the pH scale itself acts as a chart for understanding the acidity and alkalinity of water. It is essential to know that this scale is just not linear however logarithmic, as defined above. A typical illustration would present the numbers 0 to 14, with 7 clearly marked as impartial. Usually, color-coding is used to visually symbolize the completely different ranges:
-
0-3: Extremely Acidic: This vary is extraordinarily corrosive and infrequently present in pure water sources until considerably polluted. Industrial wastewater would possibly fall into this vary.
-
3-6: Acidic: Barely acidic water will be present in some pure sources, typically because of the presence of dissolved minerals or atmospheric pollution like acid rain.
-
6-7: Barely Acidic: This can be a frequent vary for a lot of pure water sources.
-
7: Impartial: Pure water at 25°C (77°F) has a pH of seven.
-
7-8: Barely Alkaline: Many pure mineral waters fall inside this barely alkaline vary.
-
8-11: Alkaline: This vary is extra frequent in water sources wealthy in minerals like calcium and magnesium.
-
11-14: Extremely Alkaline: Extremely alkaline water is much less frequent naturally however will be present in some particular geological areas or on account of industrial processes. This degree of alkalinity will be corrosive as nicely.
Measuring Water pH:
A number of strategies exist for measuring the pH of water, starting from easy residence testing kits to stylish laboratory devices:
-
pH Check Strips (Litmus Paper): These are cheap and available, offering a fast, albeit much less exact, indication of pH. They modify colour relying on the pH of the water.
-
pH Meters (Electrodes): These digital gadgets present a extra correct and exact measurement of pH. They encompass a sensor (electrode) that’s immersed within the water pattern. The meter then shows the pH studying. Calibration with customary buffer options is essential for correct readings.
-
pH Indicators: Chemical options that change colour at particular pH ranges. These are sometimes utilized in titrations to find out the pH of an answer.
Elements Affecting Water pH:
Quite a few components affect the pH of water, each naturally and anthropogenically:
-
Dissolved Minerals: The presence of minerals like calcium carbonate (limestone), magnesium, and bicarbonates considerably influences water pH. These minerals can buffer the water, resisting adjustments in pH.
-
Carbon Dioxide (CO₂): Atmospheric CO₂ dissolves in water, forming carbonic acid (H₂CO₃), which lowers the pH. This can be a important contributor to acid rain.
-
Acid Rain: Air pollution from industrial emissions and car exhaust releases sulfur dioxide (SO₂) and nitrogen oxides (NOx) into the environment. These gases react with water vapor to kind sulfuric acid and nitric acid, resulting in acid rain, which lowers the pH of water our bodies.
-
Natural Matter: Decomposition of natural matter in water can launch acids, reducing the pH.
-
Soil Composition: The composition of the soil by way of which water percolates influences its pH. Acidic soils can lead to acidic water.
-
Temperature: Temperature can have an effect on the solubility of gases like CO₂, influencing pH.
-
Human Actions: Industrial discharge, agricultural runoff (containing fertilizers and pesticides), and sewage disposal can considerably alter the pH of water our bodies.
Implications of Totally different pH Ranges:
The pH of water has important implications for varied features of life and trade:
-
Aquatic Life: Most aquatic organisms thrive inside a selected pH vary. Excessive acidity or alkalinity will be deadly to many species, disrupting aquatic ecosystems. Fish, for example, are delicate to pH adjustments, and their survival is compromised exterior their optimum pH vary.
-
Human Well being: Whereas consuming water with barely acidic or alkaline pH is usually secure, excessive values can pose well being dangers. Extremely acidic water can corrode pipes, leaching heavy metals into the water. Extremely alkaline water may also have hostile well being results.
-
Agriculture: Soil pH considerably impacts plant development. Optimum pH ranges fluctuate relying on the plant species. Inappropriate pH ranges can hinder nutrient uptake and negatively affect crop yields.
-
Industrial Processes: Many industrial processes require water with a selected pH vary. Deviation from the optimum pH can have an effect on product high quality, gear corrosion, and total effectivity.
-
Corrosion: Extremely acidic or alkaline water will be corrosive to pipes and different infrastructure, resulting in pricey repairs and potential contamination.
Sustaining Optimum Water pH:
Sustaining optimum water pH is essential for varied functions. A number of strategies will be employed:
-
Buffering: Including buffering brokers, akin to calcium carbonate, may help stabilize the pH of water, resisting adjustments.
-
Neutralization: Including acids or bases to neutralize the pH to the specified degree. This requires cautious management and monitoring.
-
Water Remedy: Water remedy vegetation make the most of varied strategies to regulate the pH of water, making certain it is secure for human consumption and different functions. This typically includes filtration, coagulation, and disinfection processes.
Conclusion:
The pH chart, or extra precisely, the pH scale, is a basic software for understanding the acidity and alkalinity of water. Its significance extends far past a easy numerical worth, impacting aquatic life, human well being, agriculture, trade, and infrastructure. Understanding the components that affect water pH and the implications of various pH ranges is important for sustaining wholesome ecosystems and making certain secure and environment friendly utilization of this valuable useful resource. Common monitoring and applicable administration methods are essential for preserving water high quality and mitigating the unfavourable penalties of pH imbalances. Additional analysis and developments in water remedy applied sciences are important in addressing the challenges posed by variations in water pH and making certain the sustainable administration of this important useful resource for future generations.






Closure
Thus, we hope this text has offered priceless insights into Understanding the pH Chart of Water: A Complete Information. We thanks for taking the time to learn this text. See you in our subsequent article!