Unveiling the Pareto Chart: A Deep Dive into Prioritization and Downside Fixing
Associated Articles: Unveiling the Pareto Chart: A Deep Dive into Prioritization and Downside Fixing
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate by means of the intriguing subject associated to Unveiling the Pareto Chart: A Deep Dive into Prioritization and Downside Fixing. Let’s weave fascinating info and provide contemporary views to the readers.
Desk of Content material
Unveiling the Pareto Chart: A Deep Dive into Prioritization and Downside Fixing
The Pareto chart, a deceptively easy but powerfully insightful software, is a cornerstone of high quality administration and course of enchancment methodologies. Named after the Italian economist Vilfredo Pareto, who noticed that 80% of Italy’s land was owned by 20% of the inhabitants (the notorious "80/20 rule"), the Pareto chart visually represents the relative significance of various components contributing to a selected drawback or consequence. It is a hybrid chart, combining the options of a bar chart and a line graph, offering a compelling narrative about information distribution and providing a transparent path in the direction of focused problem-solving. This in-depth exploration will delve into the definition, building, functions, limitations, and interpretations of Pareto charts, illustrating their versatility throughout various fields.
Defining the Pareto Chart: A Visible Illustration of Prioritization
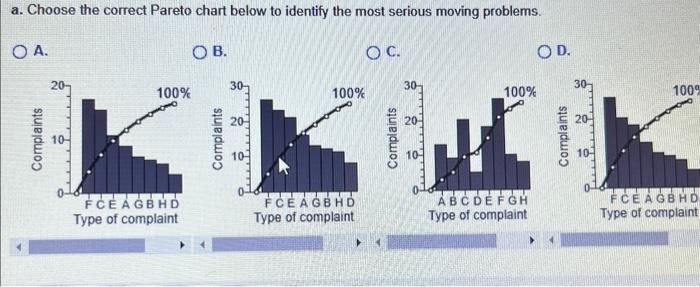
At its core, a Pareto chart is a bar graph that ranks classes in descending order of frequency or affect. The peak of every bar represents the frequency or magnitude of a particular class, clearly showcasing the relative contribution of every issue to the general drawback. Crucially, a cumulative frequency line graph is superimposed on the bar chart. This line depicts the operating whole of frequencies, visually demonstrating the cumulative proportion of the full drawback attributable to the ranked classes. The intersection of this cumulative frequency line with the 80% mark on the vertical axis usually highlights the "important few" – the small variety of classes answerable for the lion’s share of the issue.
The elemental goal of the Pareto chart is to establish and prioritize essentially the most important components contributing to a particular subject. By visually representing the information on this means, it facilitates a data-driven method to problem-solving, permitting for targeted efforts on addressing essentially the most impactful points first. This focused method maximizes effectivity and assets, stopping the dissipation of effort on much less important components.
Developing a Pareto Chart: A Step-by-Step Information
Making a Pareto chart entails a number of key steps:
-
Outline the Downside: Clearly articulate the issue you are attempting to research. This ensures that information assortment and interpretation are targeted and related. For instance, if the issue is "excessive buyer grievance charges," the chart will give attention to the classes of buyer complaints.
-
Accumulate Knowledge: Collect related information associated to the outlined drawback. This information must be categorized into distinct teams or components contributing to the issue. For the client grievance instance, classes would possibly embrace product defects, late deliveries, poor customer support, billing points, and so on.
-
Tally the Frequencies: Rely the occurrences or frequency of every class. For example, report the variety of complaints associated to every class.
-
Rank the Classes: Prepare the classes in descending order of frequency, beginning with essentially the most frequent class.
-
Calculate Percentages: Decide the share of the full that every class represents. That is accomplished by dividing the frequency of every class by the full variety of occurrences and multiplying by 100.
-
Calculate Cumulative Percentages: Calculate the cumulative proportion for every class by including the share of the present class to the cumulative proportion of the previous classes.
-
Create the Chart: Assemble the bar chart, with the classes on the horizontal axis and their frequencies (or percentages) on the vertical axis. Superimpose the cumulative frequency line graph on the bar chart, plotting the cumulative percentages in opposition to the classes.
-
**Label and






Closure
Thus, we hope this text has offered helpful insights into Unveiling the Pareto Chart: A Deep Dive into Prioritization and Downside Fixing. We thanks for taking the time to learn this text. See you in our subsequent article!