Unveiling the Energy of the Pareto Chart: A Complete Information to Prioritization and Drawback Fixing
Associated Articles: Unveiling the Energy of the Pareto Chart: A Complete Information to Prioritization and Drawback Fixing
Introduction
With nice pleasure, we are going to discover the intriguing matter associated to Unveiling the Energy of the Pareto Chart: A Complete Information to Prioritization and Drawback Fixing. Let’s weave fascinating info and supply contemporary views to the readers.
Desk of Content material
Unveiling the Energy of the Pareto Chart: A Complete Information to Prioritization and Drawback Fixing
The Pareto chart, named after the Italian economist Vilfredo Pareto, is a strong visible instrument used for figuring out and prioritizing essentially the most important components contributing to a specific drawback or consequence. Primarily based on the Pareto precept, also called the 80/20 rule, which means that roughly 80% of results come from 20% of causes, the chart successfully highlights the "very important few" from the "trivial many." This enables for targeted effort and useful resource allocation, resulting in extra environment friendly and efficient problem-solving and course of enchancment.
This text delves into the intricacies of Pareto charts, exploring their building, functions throughout numerous fields, benefits, limitations, and greatest practices for efficient utilization.
Understanding the Mechanics of a Pareto Chart:
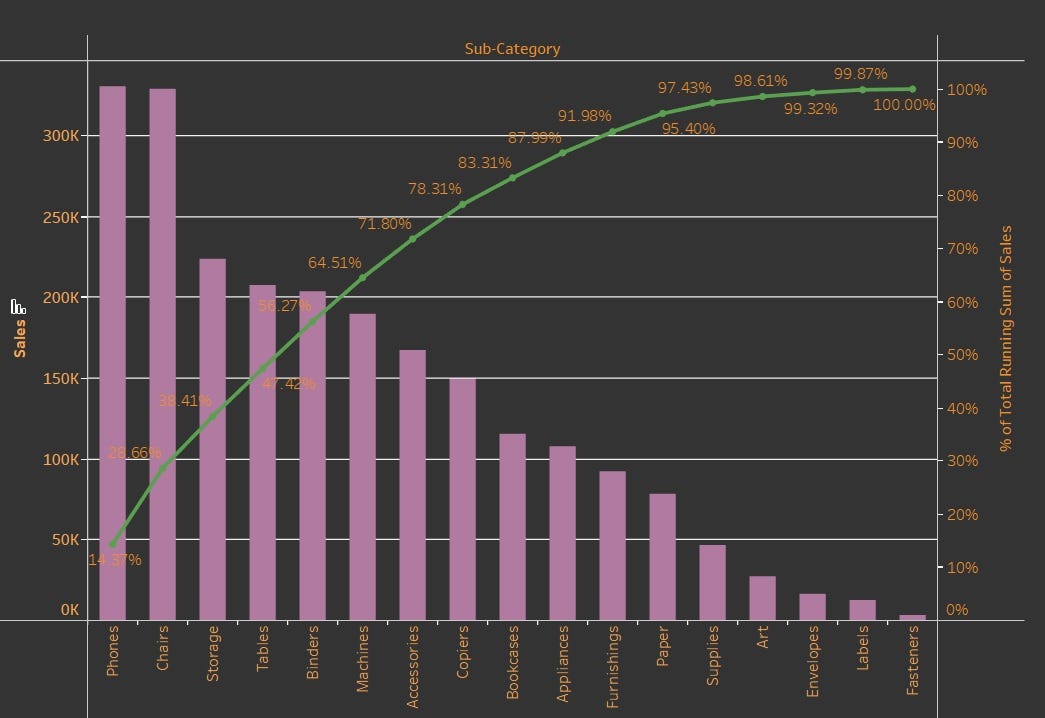
A Pareto chart is a hybrid of a bar chart and a line graph. The bars characterize the frequency or magnitude of various classes of an issue, organized in descending order from left to proper. The tallest bar represents essentially the most important issue, adopted by the subsequent most vital, and so forth. The road graph, superimposed on the bar chart, represents the cumulative share of the full impact. This cumulative share line visually demonstrates the cumulative affect of the components, highlighting the purpose the place the "very important few" attain the 80% threshold.
Key Parts of a Pareto Chart:
- Horizontal Axis (X-axis): This axis lists the classes of the issue, usually organized in descending order of frequency or affect. These classes may very well be defects, causes of errors, buyer complaints, or another related issue.
-
Vertical Axis (Y-axis): This axis shows two scales:
- Frequency/Magnitude: The peak of every bar represents the frequency or magnitude of every class.
- Cumulative Share: The road graph exhibits the cumulative share of the full impact as you progress from left to proper throughout the classes.
- Bars: Every bar represents a selected class and its frequency or magnitude. The bars are often coloured for higher visible attraction and readability.
- Line Graph: This line represents the cumulative share of the full impact. It helps determine the purpose the place a small variety of classes account for a big share of the issue.
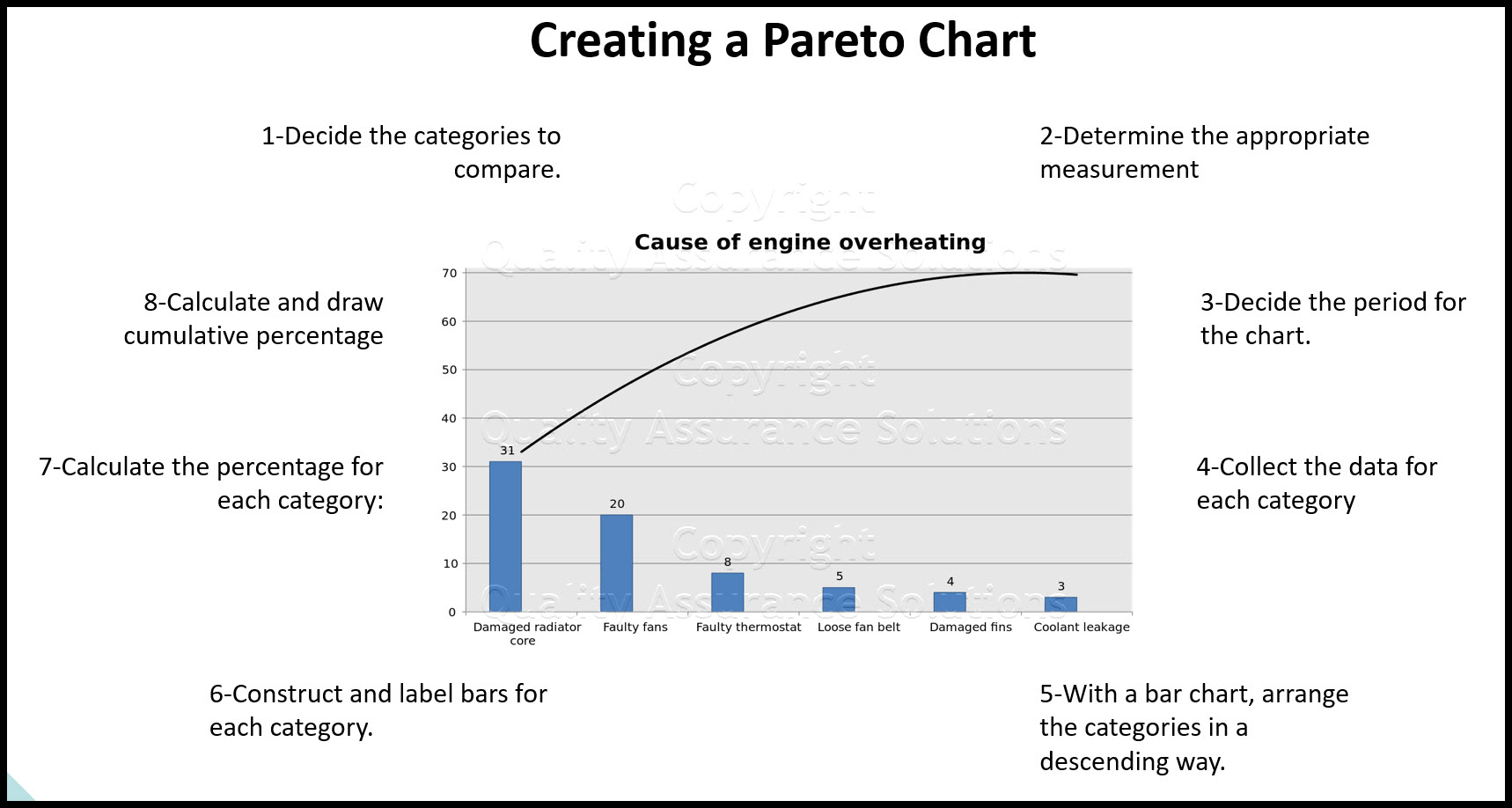
Setting up a Pareto Chart: A Step-by-Step Information:
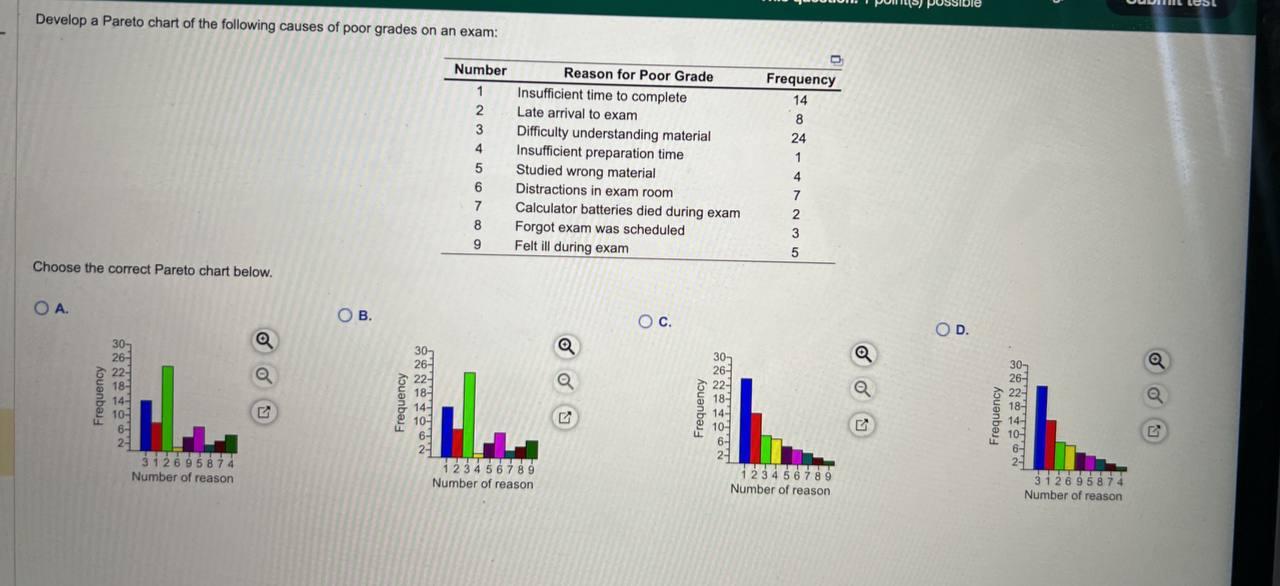
- Outline the Drawback: Clearly outline the issue you are making an attempt to resolve. This ensures you gather the correct knowledge and focus your efforts successfully.
- Gather Information: Collect knowledge associated to the issue. This knowledge ought to be categorized appropriately. For instance, if you happen to’re analyzing buyer complaints, you may categorize them by product, kind of criticism, or buyer section.
- Categorize Information: Arrange the collected knowledge into related classes. Be certain that classes are mutually unique and collectively exhaustive.
- Tally the Frequency/Magnitude: Rely the variety of occurrences or measure the magnitude of every class.
- Calculate Percentages: Calculate the proportion of every class relative to the full.
- Calculate Cumulative Percentages: Add the chances cumulatively from left to proper.
- Create the Chart: Draw the bar chart with classes on the X-axis and frequency/magnitude on the Y-axis. Superimpose the road graph representing the cumulative percentages.
- Label the Chart: Clearly label the axes, bars, and the cumulative share line. Add a title to the chart that clearly describes the issue being analyzed.
Functions of Pareto Charts Throughout Industries:
The flexibility of Pareto charts extends throughout quite a few industries and functions:
- Manufacturing: Figuring out essentially the most frequent varieties of defects in a manufacturing course of, enabling targeted enchancment efforts.
- High quality Management: Pinpointing the foremost causes of high quality points, resulting in simpler high quality management methods.
- Healthcare: Analyzing the most typical causes of hospital readmissions or affected person complaints, facilitating focused interventions.
- Buyer Service: Figuring out essentially the most frequent buyer complaints, permitting for the event of improved customer support methods.
- Challenge Administration: Figuring out the essential duties or points impacting mission timelines and budgets, enabling efficient useful resource allocation.
- Gross sales and Advertising and marketing: Analyzing gross sales knowledge to determine the top-performing merchandise or buyer segments, informing advertising and gross sales methods.
- Security Administration: Figuring out the main causes of office accidents, resulting in the implementation of focused security enhancements.
- Provide Chain Administration: Figuring out essentially the most frequent causes of provide chain disruptions, enabling proactive danger mitigation methods.
Benefits of Utilizing Pareto Charts:
- Prioritization: Clearly identifies essentially the most important components contributing to an issue, permitting for targeted efforts on the "very important few."
- Visualization: Supplies a transparent and concise visible illustration of the information, making it simpler to know and talk.
- Improved Determination-Making: Facilitates data-driven decision-making by highlighting the areas the place enhancements could have the best affect.
- Useful resource Allocation: Allows environment friendly allocation of assets by focusing efforts on essentially the most impactful components.
- Drawback Fixing: Streamlines the problem-solving course of by offering a structured method to figuring out and addressing root causes.
- Communication: Successfully communicates advanced knowledge to stakeholders with various ranges of technical experience.
Limitations of Pareto Charts:
- Subjectivity in Categorization: The effectiveness of a Pareto chart is dependent upon the correct and significant categorization of knowledge. Poor categorization can result in deceptive conclusions.
- Oversimplification: Might oversimplify advanced issues by focusing solely on the "very important few," doubtlessly neglecting essential components represented within the "trivial many."
- Information Dependency: The accuracy of the chart depends closely on the standard and completeness of the information collected. Inaccurate or incomplete knowledge can result in incorrect conclusions.
- Ignoring Interactions: The chart does not explicitly present the interactions between completely different classes, which is perhaps essential in understanding the basis causes of the issue.
- Temporal Issues: The chart represents a snapshot in time. Elements contributing to an issue might change over time, requiring periodic updates of the chart.
Greatest Practices for Efficient Utilization of Pareto Charts:
- Clear Drawback Definition: Start with a transparent and concise definition of the issue you are attempting to resolve.
- Correct Information Assortment: Be certain that knowledge is collected precisely and constantly.
- Significant Categorization: Develop a logical and significant categorization scheme that precisely displays the underlying components contributing to the issue.
- Common Updates: Commonly replace the chart to mirror adjustments within the knowledge over time.
- Mix with Different Instruments: Use Pareto charts along with different problem-solving instruments, akin to root trigger evaluation, to realize a extra complete understanding of the issue.
- Contextual Interpretation: Interpret the outcomes throughout the context of the precise scenario. Do not assume that the 80/20 rule will at all times apply exactly.
Conclusion:
The Pareto chart is a useful instrument for prioritizing issues, figuring out key components, and driving efficient options. By visually representing the relative significance of various components contributing to an issue, it permits targeted efforts and useful resource allocation, resulting in improved effectivity and effectiveness throughout varied fields. Whereas limitations exist, understanding these limitations and following greatest practices ensures the correct and efficient utilization of this highly effective analytical instrument. By combining the Pareto chart with different problem-solving strategies, organizations can leverage its energy to attain important enhancements in processes, merchandise, and total efficiency.





Closure
Thus, we hope this text has supplied precious insights into Unveiling the Energy of the Pareto Chart: A Complete Information to Prioritization and Drawback Fixing. We respect your consideration to our article. See you in our subsequent article!