us nationwide debt vs gdp chart
Associated Articles: us nationwide debt vs gdp chart
Introduction
With nice pleasure, we’ll discover the intriguing subject associated to us nationwide debt vs gdp chart. Let’s weave fascinating data and provide recent views to the readers.
Desk of Content material
The US Nationwide Debt vs. GDP: A Chart That Tells a Story of Development, Disaster, and Uncertainty

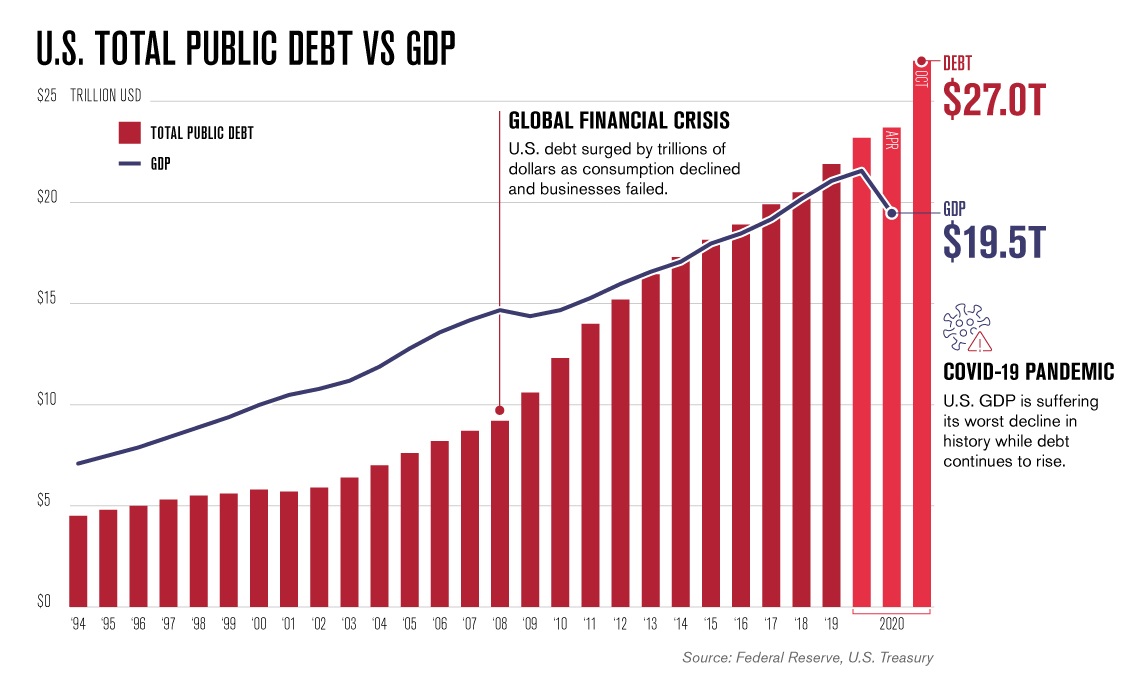
The connection between a nation’s nationwide debt and its Gross Home Product (GDP) is a vital indicator of its long-term fiscal well being. For america, this relationship, typically visualized by way of a chart plotting debt-to-GDP ratio over time, offers a compelling narrative of financial booms, busts, and the enduring problem of managing public funds. This text delves deep into the importance of the US nationwide debt vs. GDP chart, exploring its historic developments, the elements influencing its fluctuations, and the implications for the way forward for the American financial system.
Understanding the Debt-to-GDP Ratio:
The debt-to-GDP ratio is an easy but highly effective metric. It expresses the entire nationwide debt (the accrued sum of presidency borrowing) as a proportion of the nation’s GDP (the entire worth of products and providers produced inside a yr). A decrease ratio typically suggests a stronger fiscal place, indicating that the federal government can extra simply service its debt with out straining the financial system. Conversely, a excessive ratio can sign potential dangers, together with increased curiosity funds, diminished authorities spending capability in different areas, and elevated vulnerability to financial shocks.
Analyzing the US nationwide debt vs. GDP chart reveals a posh story. Whereas the ratio has fluctuated significantly all through historical past, a number of distinct intervals stand out:
1. The Pre-World Struggle II Period (Earlier than 1940): Previous to the Second World Struggle, the US debt-to-GDP ratio remained comparatively low. Authorities spending was typically modest, and the financial system skilled intervals of each development and recession, however the debt burden was manageable. This era highlights the comparatively secure fiscal place of the US earlier than the onset of large-scale international conflicts and the enlargement of the welfare state.
2. The World Struggle II Increase and Bust (1940-Nineteen Fifties): The Second World Struggle dramatically altered the fiscal panorama. Huge authorities spending on navy tools, personnel, and wartime manufacturing led to a pointy improve within the nationwide debt. The debt-to-GDP ratio soared to unprecedented ranges, reflecting the extraordinary monetary dedication required for the conflict effort. The post-war interval noticed a gradual decline within the ratio, aided by robust financial development and a interval of relative peace. This era demonstrates the affect of main exterior shocks on nationwide debt ranges.
3. The Nice Society and Vietnam Struggle (Nineteen Sixties-Nineteen Seventies): The Nineteen Sixties and Nineteen Seventies witnessed one other vital rise within the debt-to-GDP ratio. Elevated authorities spending on social packages (the "Nice Society" initiatives) and the Vietnam Struggle contributed to this improve. Concurrently, financial challenges, together with inflation and stagflation, hampered the federal government’s capability to cut back the debt burden by way of financial development. This era emphasizes the interaction between formidable social coverage and the potential for fiscal pressure.
4. The Reagan Period and Past (Eighties-2000s): The Reagan administration’s tax cuts, coupled with elevated navy spending, led to a considerable improve within the nationwide debt. This era highlights the talk surrounding supply-side economics and its affect on authorities funds. The next many years noticed a combined image, with intervals of debt discount adopted by additional will increase, influenced by financial recessions, tax cuts, and ongoing authorities spending commitments.
5. The Submit-2008 Monetary Disaster and Past (2008-Current): The 2008 monetary disaster triggered a dramatic surge within the nationwide debt. Authorities intervention to stabilize the monetary system and stimulate the financial system led to large will increase in authorities borrowing. The next financial restoration was sluggish, additional limiting the federal government’s capability to cut back the debt. This era underscores the vulnerability of even massive economies to monetary crises and the substantial fiscal prices of responding to such occasions. The COVID-19 pandemic additional exacerbated this development, with unprecedented ranges of presidency spending on stimulus packages and healthcare initiatives.
Elements Influencing the Debt-to-GDP Ratio:
A number of key elements affect the motion of the US nationwide debt vs. GDP ratio:
- Authorities Spending: Will increase in authorities spending on numerous packages, together with protection, social safety, Medicare, and Medicaid, straight contribute to a rising nationwide debt.
- Tax Income: The quantity of tax income collected by the federal government considerably impacts the debt-to-GDP ratio. Decrease tax charges or financial downturns cut back tax income, resulting in increased borrowing.
- Financial Development: Robust financial development will increase GDP, thus lowering the debt-to-GDP ratio even when the nationwide debt itself is rising. Conversely, financial recessions cut back GDP, rising the ratio.
- Curiosity Charges: Increased rates of interest improve the price of servicing the nationwide debt, probably resulting in the next debt-to-GDP ratio.
- Fiscal Coverage: Authorities choices relating to taxation and spending straight affect the nationwide debt and, consequently, the debt-to-GDP ratio.
- Financial Coverage: The Federal Reserve’s financial coverage choices can have an effect on rates of interest and financial development, not directly impacting the debt-to-GDP ratio.
Implications for the Future:
The persistently excessive and rising US nationwide debt-to-GDP ratio raises a number of necessary considerations:
- Elevated Curiosity Funds: A bigger debt requires increased curiosity funds, probably crowding out different authorities spending priorities.
- Diminished Authorities Flexibility: A excessive debt-to-GDP ratio can restrict the federal government’s capability to reply successfully to future financial crises or unexpected occasions.
- Elevated Danger of Inflation: Extreme authorities borrowing can probably result in inflation if not managed rigorously.
- Impression on International Confidence: A persistently excessive debt-to-GDP ratio can erode confidence within the US financial system and its capability to handle its funds.
Conclusion:
The US nationwide debt vs. GDP chart isn’t just a set of information factors; it is a highly effective visible illustration of the nation’s fiscal historical past and its ongoing challenges. Understanding the historic developments, the contributing elements, and the potential implications is essential for knowledgeable policymaking and public discourse. Whereas the present excessive debt-to-GDP ratio presents vital challenges, efficient fiscal administration, sustainable financial development, and considerate coverage choices are important to make sure the long-term fiscal well being and stability of america. The chart serves as a relentless reminder of the necessity for accountable fiscal stewardship and a dedication to addressing the nation’s long-term debt burden. Additional analysis and evaluation are wanted to discover potential options and mitigate the dangers related to a excessive debt-to-GDP ratio, guaranteeing a sustainable future for the American financial system. The continued debate surrounding fiscal coverage, tax reform, and authorities spending will proceed to form the trajectory of this important indicator, and its cautious monitoring stays important for understanding the financial well being of the nation.







Closure
Thus, we hope this text has offered precious insights into us nationwide debt vs gdp chart. We respect your consideration to our article. See you in our subsequent article!