X-bar and R Chart Instance Issues: A Complete Information
Associated Articles: X-bar and R Chart Instance Issues: A Complete Information
Introduction
With nice pleasure, we are going to discover the intriguing subject associated to X-bar and R Chart Instance Issues: A Complete Information. Let’s weave fascinating data and provide recent views to the readers.
Desk of Content material
X-bar and R Chart Instance Issues: A Complete Information
Management charts, particularly X-bar and R charts, are basic instruments in Statistical Course of Management (SPC). They visually signify course of stability and assist establish sources of variation. Whereas conceptually easy, mastering their utility requires understanding numerous situations and potential pitfalls. This text delves into a number of instance issues, demonstrating how you can assemble and interpret X-bar and R charts, highlighting widespread challenges, and providing options for efficient course of management.
Understanding X-bar and R Charts
Earlier than diving into examples, let’s briefly evaluate the core rules. X-bar charts observe the common (imply) of a course of attribute over time, whereas R charts monitor the vary (distinction between the biggest and smallest values) inside subgroups. These charts are used collectively to evaluate each the central tendency and the variability of a course of. Subgroups, usually consisting of 4-5 knowledge factors collected at common intervals, are important for efficient evaluation. The logic is that variation inside a subgroup is attributed to widespread trigger variation, whereas variation between subgroups alerts potential particular trigger variation requiring investigation.
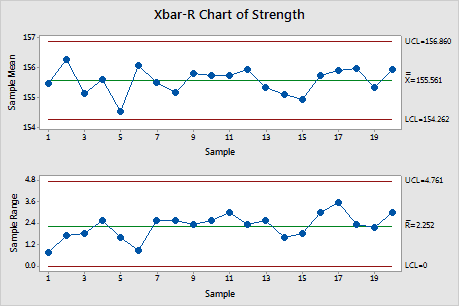
Instance Drawback 1: Secure Course of with Small Variation
Let’s contemplate a producing course of producing metallic shafts. The diameter is a crucial high quality attribute. We gather 25 subgroups of measurement 5, measuring the diameter of every shaft in millimeters. The information is offered beneath (simplified for demonstration):
| Subgroup | Measurement 1 | Measurement 2 | Measurement 3 | Measurement 4 | Measurement 5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 10.01 | 10.00 | 10.02 | 9.99 | 10.00 |
| 2 | 9.98 | 10.01 | 10.00 | 9.99 | 10.02 |
| … | … | … | … | … | … |
| 25 | 10.00 | 10.01 | 9.99 | 10.00 | 10.02 |
Resolution:
-
Calculate the subgroup means (X-bar) and ranges (R) for every subgroup. This includes calculating the common and the distinction between the biggest and smallest measurements for every subgroup.
-
Calculate the general common of the subgroup means (X-double bar) and the common vary (R-bar). These are used to determine the central line and management limits for the charts.
-
Decide the management limits for the X-bar chart. This usually makes use of components from management chart constants tables (e.g., A2, D3, D4 for subgroups of measurement 5). The formulation are:
- Higher Management Restrict (UCL) = X-double bar + A2 * R-bar
- Decrease Management Restrict (LCL) = X-double bar – A2 * R-bar
-
Decide the management limits for the R chart. The formulation are:
- UCL = D4 * R-bar
- LCL = D3 * R-bar (Be aware: D3 is usually 0 for small subgroup sizes)
-
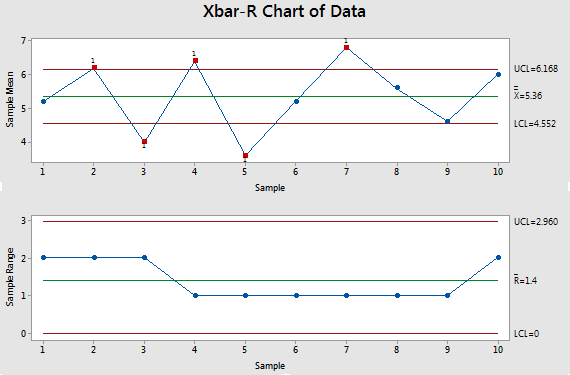
Plot the X-bar and R values on their respective charts. If all factors fall throughout the management limits, the method is taken into account statistically steady.
Instance Drawback 2: Course of with Out-of-Management Factors
Now, let’s assume an identical situation, however with some launched variation. Suppose a machine malfunctioned in the course of the manufacturing course of, resulting in a number of out-of-control factors.
Resolution:
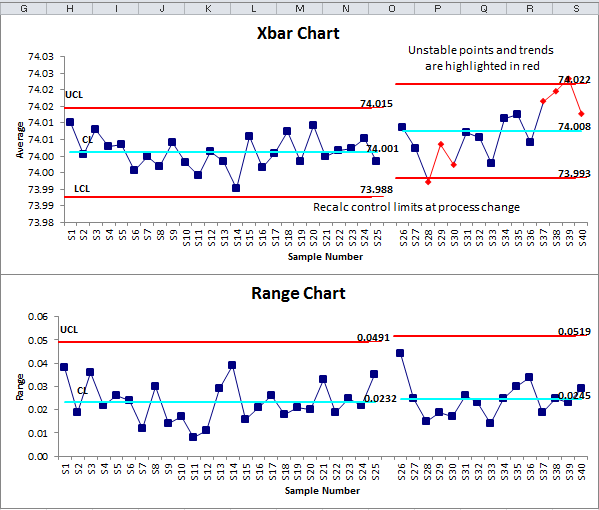
Following the identical steps as Instance 1, we’d assemble the X-bar and R charts. Nevertheless, on this case, we’d observe factors falling outdoors the management limits on both the X-bar or R chart (or each). This means particular trigger variation.
Investigating Out-of-Management Factors:
Figuring out out-of-control factors is simply step one. The subsequent essential step is to research the trigger of the variation. This may contain:
- Reviewing manufacturing data: Checking for machine malfunctions, operator errors, or modifications in uncooked supplies.
- Inspecting the affected merchandise: Analyzing the bodily traits of the merchandise related to the out-of-control factors.
- Analyzing environmental components: Contemplating temperature, humidity, or different environmental circumstances that may have influenced the method.
As soon as the foundation trigger is recognized, corrective actions needs to be applied to get rid of the particular trigger variation and stop recurrence. After corrective motion, new knowledge needs to be collected to confirm the effectiveness of the applied modifications and make sure the course of returns to a state of statistical management.
Instance Drawback 3: Stratification and its Influence
Lets say a scenario the place two totally different operators are operating the identical machine. We’d observe totally different common diameters and ranges for every operator. That is an instance of stratification, the place hidden components affect the method.
Resolution:
As an alternative of mixing knowledge from each operators, we should always create separate X-bar and R charts for every operator. This permits us to establish potential variations of their efficiency and tackle any underlying points. If the variability between operators is important, coaching or course of changes is perhaps essential to standardize the method.
Instance Drawback 4: Coping with Non-Regular Information
X-bar and R charts assume that the info is roughly usually distributed. Nevertheless, real-world knowledge might not at all times meet this assumption. What if our knowledge is skewed or comprises outliers?
Resolution:
A number of approaches can be utilized:
- Information Transformation: Reworking the info (e.g., utilizing logarithmic or sq. root transformations) can generally normalize the distribution.
- Sturdy Management Charts: These charts are much less delicate to outliers and non-normality. Examples embody median charts and modified management charts.
- Bigger Subgroup Sizes: Utilizing bigger subgroup sizes can enhance the normality approximation.
Instance Drawback 5: Selecting the Proper Subgroup Measurement
The selection of subgroup measurement is essential. Too small a subgroup may masks variation, whereas too giant a subgroup may obscure necessary shifts within the course of.
Resolution:
The optimum subgroup measurement depends upon a number of components, together with:
- The frequency of information assortment: Subgroups needs to be collected regularly sufficient to detect shifts within the course of.
- The price of knowledge assortment: Bigger subgroups improve the price of knowledge assortment.
- The method itself: The character of the method and the kind of variation current will affect the optimum subgroup measurement.
Conclusion
Understanding and making use of X-bar and R charts successfully requires cautious consideration of a number of components. This text has offered numerous instance issues, demonstrating the significance of correct knowledge assortment, chart building, interpretation, and the investigation of out-of-control factors. By mastering these ideas, practitioners can leverage X-bar and R charts to enhance course of stability, cut back variability, and improve product high quality. Do not forget that the profitable utility of SPC includes not simply statistical evaluation but in addition a deep understanding of the method itself and a dedication to steady enchancment. Additional exploration into extra superior management charts and statistical strategies can improve the effectiveness of your course of management methods.




Closure
Thus, we hope this text has supplied helpful insights into X-bar and R Chart Instance Issues: A Complete Information. We recognize your consideration to our article. See you in our subsequent article!